A UCLA-led research team has identified a chemical cocktail that enables the production of large numbers of muscle stem cells, which can self-renew and give rise to all types of skeletal muscle cells.


High-precision delivery of microrobots at the whole-body scale is of considerable importance for efforts toward targeted therapeutic intervention. However, vision-based control of microrobots, to deep and narrow spaces inside the body, remains a challenge. Here, we report a soft and resilient magnetic cell microrobot with high biocompatibility that can interface with the human body and adapt to the complex surroundings while navigating inside the body. We achieve time-efficient delivery of soft microrobots using an integrated platform called endoscopy-assisted magnetic actuation with dual imaging system (EMADIS).

Wiesendanger points out that unlike SARS and MERS, no intermediate host between bats and humans has been found more than a year since the start of the pandemic. Thus far, there is no evidence for the zoonotic theory to explain the outbreak.
Indeed, during the joint China-WHO report issued on Feb. 9, Liang Wannian, head of the Chinese National Health Commission’s Expert Panel of COVID-19 Response, stated that 50000 samples of wild animals from 300 different species (including bats) as well as 11000 farm animals in 31 Chinese provinces — taken between November 2019 and March 2020 — had all tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the virus which causes COVID-19.
The researcher claimed that the SARS-CoV-2 virus is “astonishingly effective” at binding to human receptor cells (hACE2). He said this is due to its special hACE2 binding domains paired with the furin cleavage sites of the virus’ telltale spike protein.
He stated that this is the first time a coronavirus has exhibited both characteristics and that it points to a “non-natural origin.” Within the betacoronaviruses of sarbecovirus lineage B, the polybasic furin cleavage site is unique to SARS-CoV-2, according to News Medical Life Sciences.
Wiesendanger noted that there were no bats sold at the infamous Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, where the first known superspreader event began. Liang has stated that no animals or “animal products” had tested positive for the virus there and that individuals who contracted COVID early on had not visited the market.”
Year-long study of pandemic’s origin concludes it started with ‘laboratory accident’ in Wuhan.
Summary: A new technique which involves fusing human and chimpanzee skin cells that have been modified to act like stem cells, allowed researchers to identify two novel genetic differences between humans and chimps.
Source: Stanford University.
One of the best ways to study human evolution is by comparing us with nonhuman species that, evolutionarily speaking, are closely related to us. That closeness can help scientists narrow down precisely what makes us human, but that scope is so narrow it can also be extremely hard to define. To address this complication, researchers from Stanford University have developed a new technique for comparing genetic differences.

Tyson’s latest book “Cosmic Queries” covers the gamut from early Earth’s pond scum to potential multiverses to out-of-the-box ideas about the potential that we live in a false vacuum cosmos.
After the past year’s pandemic pall, it’s nice to be reminded that we remain inextricably connected to the cosmos beyond Earth’s atmosphere. In the new book “Cosmic Queries: StarTalk’s Guide to Who We Are, How We Got Here, and Where We’re Going,” astrophysicist and StarTalk podcast host Neil DeGrasse Tyson, along with George Mason University physics professor James Trefil, clearly remind us of our cosmic legacy.
Tyson, Director of New York City’s Hayden Planetarium at the American Museum of Natural History, is well known for his ability to provoke the public into thinking harder about our place in the cosmos. And “Cosmic Queries” does just that. Tyson and Trefil succinctly lead the reader through almost every aspect of cosmic history while addressing age-old questions with new verve.
Designed with a wealth of graphic and color images with pithy captions, the book is also peppered with amusing tweets from Tyson’s own Twitter account over the last decade. The book and his tweets touch on some of StarTalk’s recurring themes, such as Why is the universe the way it is? Are we alone? And how it all began and how it might all end?

“The research is part of an explosion of new techniques and ideas for studying early development. Today, in the same issue of Nature, two other research groups are reporting a leap forward in creating ”artificial” human embryos.
Those teams managed to coax ordinary skin cells and stem cells to self-assemble into look-alike early human embryos they call ”blastoids,” which they grew for about 10 days in the lab. Several kinds of artificial models of embryos have been described before, but those described today are among the most complete, because they possess the cells needed to form a placenta. That means they are a step closer to being viable human embryos that could develop further, even until birth.
Scientists say that they would never try to establish a pregnancy with artificial embryos—an act that would be forbidden today in most countries.
Researchers are growing embryos outside the body longer than has ever been possible.

Dr James Desmond, DVM, Co-Founder, Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection (LCRP), discussing his work at LCRP, as well as his zoonotic disease surveillance work with EcoHealth.
Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection (LCRP — https://www.liberiachimpanzeerescue.org/) is the first and only chimpanzee sanctuary and conservation center in Liberia rescuing chimpanzees who are victims of the illegal bush meat and pet trades. The organization has over 40 orphaned chimpanzees, nearly all under the age of five, currently under their care.
Dr. James Desmond is the co-founder Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection. He is a wildlife veterinarian and a consultant specializing in emerging disease and the illegal wildlife trade. He graduated from Tufts Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine, earning a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine degree and a Masters in Comparative Biomedical Sciences. Alongside his work with Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection, Dr. Desmond leads research on infectious disease, including identifying novel wildlife reservoirs for the Ebola virus.
Jenny Desmond is a co-founder of Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection and she leads the team who cares for chimpanzees serving as “mom” to the 40+ orphans, nurturing them and helping them form bonds with the other chimpanzees in the organization’s care to ensure they have fulfilling lives in their sanctuary family, providing love, enrichment, and refuge.
James and Jenny were recently the focus of a TV series, Baby Chimp Rescue, which aired on BBC and AMC.
IMPORTANT NOTE: **Chimpanzees are not and should not be pets or forced to live with humans.** The chimpanzee orphans at LCRP’s sanctuary in West Africa are victims of the bushmeat and illegal pet trade. Their mothers were tragically killed by poachers and require around the clock care. Thanks to the dedicated caregivers and staff, the orphans are being rehabilitated so that they will be able to thrive with others in a natural and safe environment when they’re older. Please support LCRP’s efforts to rescue chimpanzees in need and keep wild chimps wild.
Following in my recent series on subjects that are all the rage in anti-aging and longevity circles, to help you get a good grasp of the essentials so you can know what all the talk is about, and can make informed judgements rather than just following the herd blindly. This time it is on Metformin. This is a drug widely known as a diabetes drug and it has been in use for a very long time, indeed it is one of the most prescribed drugs there is. Recently it has also been a buzz word in the anti aging/longevity communities following the review of data and with it s mechanism of action, being touted and recommended by a variety of voices in the public domain. But how does it work, and how could it improve longevity? Is it safe? Well, if you want to go into a bit more depth and know all the details, I have put together a video which helps you understand what all the fuss is about. And whatever you are doing, have a great day.
Metformin is very popular in the anti aging paradigm currently so let’s have a look at what it is, what it offers, and what the trade offs are… because, well, it is always wise to have all the data.
In this video I will look at the history of metformin and describe its mechanism of action before delving into the current thoughts on its use as an anti aging supplement and longevity benefits due to its overall health benefits.
If you would like to know more about longevity in general as well as the hallmarks of aging then why not check out this video next.
If you would like to look at the articles and studies mentioned they can be found at these links.
Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC209533/
Metformin Is a Direct SIRT1-Activating Compound: Computational Modeling and Experimental Validation.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6232372/

A unique — details are a bit sketch 
Requirements:
Human; all nationalities accepted.
Be willing to relocate to Mars.
Previous SMS experience working around black holes.
Hands-on experience repairing or replacing broken parts on machinary and/or colleagues.
A Can Do Attitude.
The ability to work alone and part of an android team with minimal supervision and zero compliance to logic.
Available for travel to different planets on a regular basis.
Dangerous Goods or Hazardous Materials Recognition Training preferred but not necessary. OTJ will be provided. Please ensure your tetanus vaccine is up-to-date!
A unique Russian Aerospace-Robotics Farm is hiring — details are a bit sketch 
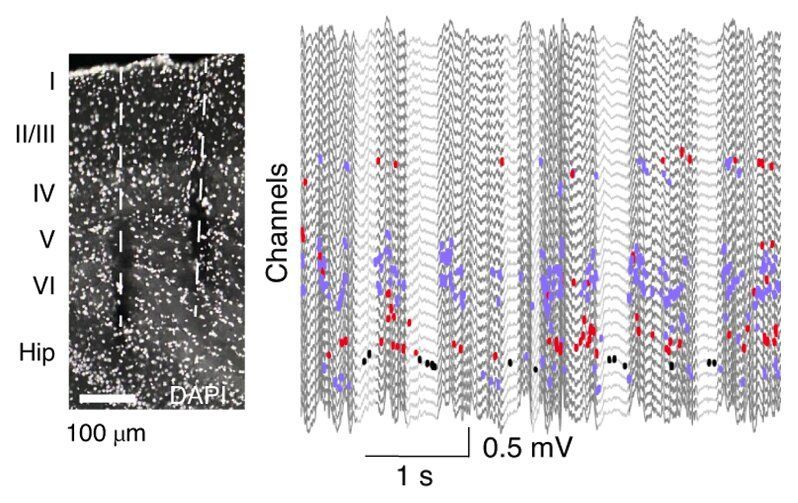
Typically, pyramidal cells and GABAergic interneurons in the brain are activated simultaneously. A team of neuroscientists at New York University, however, recently identified a unique class of neurons that do not fire at the same time as all principal neurons, cells and interneurons. Interestingly, the team found that these specific neurons are most active during the DOWN state of non-REM (NREM) sleep, when all other neuron types are silent.
“As is often the case in science, our discovery was a true serendipity,” György Buzsáki, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told MedicalXpress. “By collecting sleep recordings in deep layers of the cortex, we observed that spikes of some rare neurons occasionally occurred during the so-called ‘DOWN state’ epochs of sleep. No neuron was supposed to do such thing, as DOWN state is known (and identified by) by its complete neuronal silence (lack of spikes).”
The neocortex, a set of layers in a region of the brain called cerebral cortex, is rebooted thousands of times every night from the transient (50−300 ms long) DOWN state. In their study, Buzsáki and his colleagues identified a class of neurons that appear to be most active when all other neurons (i.e., excitatory pyramidal and inhibitory neurons) are silent, in the DOWN state, during NREM stages of sleep. In their follow up experiments, they showed that these neurons are neuroglia-form cells found in the deeper layers of the neocortex, which specifically express genes known as ID2 and Nkx2.1.