4D printing works the same as 3D printing, the only difference is that the printing material allows the object to change shape based on environmental factors.
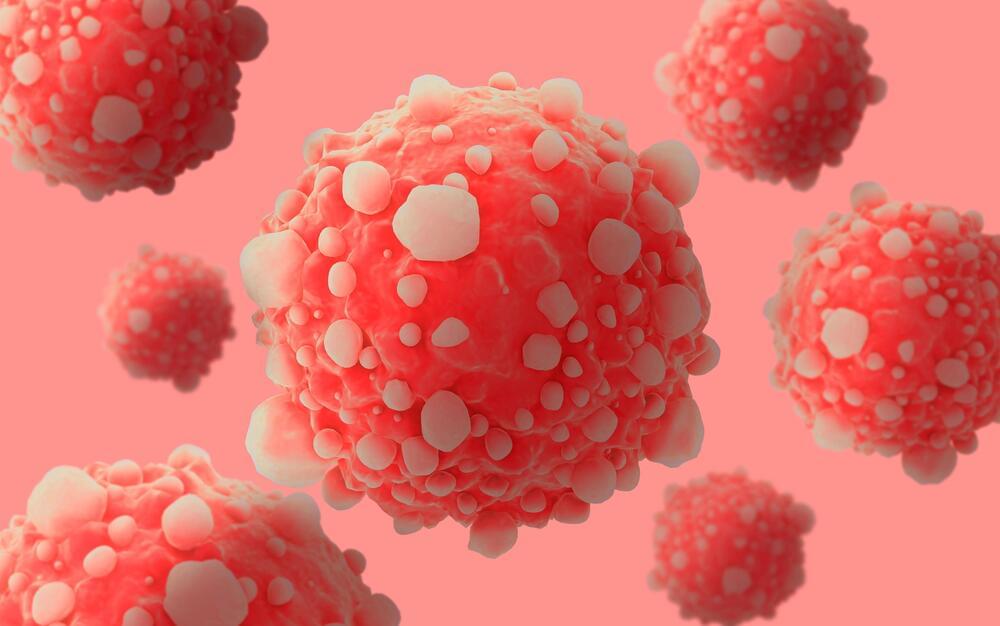
In this case, the bots’ hydrogel material allows them to morph into different shapes when they encounter a change in pH levels — and cancer cells, as it happens, are usually more acidic than normal cells.
The microrobots were then placed in an iron oxide solution, to give them a magnetic charge.
This combination of shape-shifting and magnetism means the bots could become assassins for cancer — destroying tumors without the usual collateral damage on the rest of the body.
Full Story:
A school of fish-y microbots could one day swim through your veins and deliver medicine to precise locations in your body — and cancer patients may be the first people to benefit from this revolution in nanotechnology.
How it works: Scientists recently printed teeny tiny microbots in the shape of different animals, like fish, crabs, and even butterflies. But the coolest thing with these bots is that they don’t stay in one shape — they can morph into different shapes because they are 4D-printed.






 As they highlighted the world of high-tech in ‘Netherlands in 2050,’ the hosts truly did bring the dress to life as rather than just explaining what happens, they showed us, with host Rachel Rosier enjoying the process firsthand at the Shapeways’ facility in Eindhoven. Keep in mind, again, that these dresses are in demand for the permanent collections of museums.
As they highlighted the world of high-tech in ‘Netherlands in 2050,’ the hosts truly did bring the dress to life as rather than just explaining what happens, they showed us, with host Rachel Rosier enjoying the process firsthand at the Shapeways’ facility in Eindhoven. Keep in mind, again, that these dresses are in demand for the permanent collections of museums.