This article is an excerpt from a report by Partners in Foresight, The Home of the 2020s: Scenarios for How We Might Live in the Post-Pandemic Future.
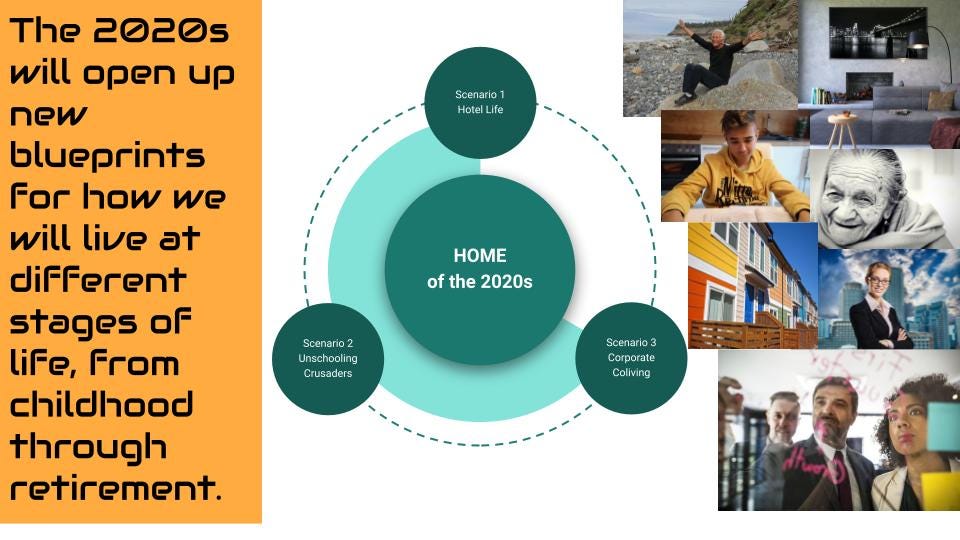
Scenario Vignette 1: Hotel Life
Hotels and abandoned malls become pandemic-proof senior citizen communities
Travel and retail sectors were never the same after the 2020 disruptions. It was not that they never recovered, but they were never the same.
By 2030, a glut of abandoned real estate (hotel, entertainment, and retail that had succumbed to economic pressures of the pandemic) had become gradually renovated to accommodate a growing North American retirement population. They borrowed pandemic-proofing ideas from communities in China built in response to COVID-19 and retrofitted blueprints of housing designed for Mars colonization. Futuristic concepts were thrown at a single social problem: how to build safe, sustainable, and economical retirement communities and nursing homes.
The living arrangement could provide adventure, allowing for a surprising variety of movement and mobility. Hotels became more like timeshares where residents would move (in clusters, aka “pods”) from place to place, seasonally sometimes. The once-thriving international tourism economy still sputtered in 2030, but groups of older Americans revitalized the classic recreational hotspots of the 20th century (Yellowstone, the Grand Canyon, the Great Smoky Mountains). Older people who had survived had become precious members of society after the pandemic and they were seen as honored guests at all national landmarks.
For less mobile seniors, outdated malls were transformed to indoor cities with clinics, exercise trails, and community kitchens all within hundreds of steps of where seniors slept in dormitory-like rooms. Green renovations to the buildings themselves allowed for indoor gardening/farms and many of the cooperatives had a net-zero impact thanks to effective sustainable design elements. Senior citizens were well-looked after by respectful physicians, social workers, and health care professionals in these settings. Young people often volunteered to help out. There was recreation and education for all ages and abilities, and it was given freely to anyone over age 65. The operations were fully funded by taxes (US $0.01) on e-commerce retail transactions.
Scenario Vignette 2: Unschooling Crusaders
A generation embraces homeschooling in lockdown
Edgar is a 15-year-old American boy who, for as long as he could remember, has been homeschooled by his parents who were working from home.
They never dropped him off in a school carpool line or packed him a lunch to eat away from home. Instead, the entire family found a different rhythm in the wake of the 2020 Covid-19 pandemic. Edgar was only five years old in 2020, so he lacks memory of a time before his parents worked at home and helped him take online classes.
In his early teenage years, Edgar’s interests began to surpass any existing online school curriculum. His parents transitioned him to an unschooling approach, letting Edgar pursue his passions rather than a pre-established curriculum. With his parents’ support, Edgar is now planning to enter college early and has started a nonprofit organization to support ecological and social justice.
A lot of kids in Edgar’s generation discovered unschooling because of the pandemic. It wasn’t just the healthcare systems that were overwhelmed in 2020 America; public school systems were, too. Edgar and some of his peers were lucky to have parents that worked from home during the lockdowns. Their classmates that didn’t have such privilege lost everything when schools closed. Some fell behind academically, some got sick, and some disappeared completely. Many of their parents worked in retail, restaurants, travel, and various “essential” jobs.
Unschoolers like Edgar were actually drawn to unschooling when they noticed the vastly different experiences they and their friends had in their early years even though they were in the same public school systems at the time. Unschooling, an unlikely school reform movement, was on its way by 2030…with young people in charge of their own learning.
Scenario Vignette 3: Corporate Coliving
Class of 2030 MBA grad moves into a communal home sponsored by her employer
After the pandemic, the US higher education system was a disaster. Student loans had been forgiven and eliminated by 2025 and a lot of new options to finance college had appeared.
A student called Haley opted for the sponsorship route — the Big4 consulting group had prescreened students from her high school and Haley had been selected to be sponsored at a university and housed after graduation. All she had to do was accept a 10-year assignment with Big4 after college at a subsistence salary (45% less than a non-coliving salary), and all her living expenses would be covered. Even in college and throughout grad school all of Haley’s meal, housing, and transportation expenses were subsidized by the corporation which she’d later call work and home. Part of the way the company paid the tuition of their future employees was by eliminating office space altogether.
They’d once occupied vast and palatial offices in urban centers around the globe. Instead, Big4 had put their money into coliving/coworking spaces starting in 2020. Having early access to the talent pipeline ensured a smooth transition and, as a plus, kept training costs down. Housing and feeding employees had shown to be a much better business proposition than generous salaries, according to the Big4 shareholders.
Haley daydreamed on her way to meet a date at the café. Although she’d been out of the bubble a few times, she mostly stayed within a group of coworkers with similar jobs, upbringings, and educational backgrounds. It dawned on her now that coliving, which sprung from the economic and psychological aftermath of COVID-19, could seem highly social but was actually incredibly isolating. She remembered a popular meme she had seen often as a teen during the 2020 lockdown that showed a flustered figure standing in a messy room, asking: “Am I working at home or living at work?” Even in 2030, no one knew the answer.
View the full report The Home of the 2020s: Scenarios for How We Might Live in the Post-Pandemic Future: https://bit.ly/2TbCYf2