Category: driverless cars

Is artificial consciousness the solution to AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging field of computer programming that is already changing the way we interact online and in real life, but the term ‘intelligence’ has been poorly defined. Rather than focusing on smarts, researchers should be looking at the implications and viability of artificial consciousness as that’s the real driver behind intelligent decisions.
Consciousness rather than intelligence should be the true measure of AI. At the moment, despite all our efforts, there’s none.
Significant advances have been made in the field of AI over the past decade, in particular with machine learning, but artificial intelligence itself remains elusive. Instead, what we have is artificial serfs—computers with the ability to trawl through billions of interactions and arrive at conclusions, exposing trends and providing recommendations, but they’re blind to any real intelligence. What’s needed is artificial awareness.

Elon Musk has called AI the “biggest existential threat” facing humanity and likened it to “summoning a demon,”[1] while Stephen Hawking thought it would be the “worst event” in the history of civilization and could “end with humans being replaced.”[2] Although this sounds alarmist, like something from a science fiction movie, both concerns are founded on a well-established scientific premise found in biology—the principle of competitive exclusion.[3]
Competitive exclusion describes a natural phenomenon first outlined by Charles Darwin in On the Origin of Species. In short, when two species compete for the same resources, one will invariably win over the other, driving it to extinction. Forget about meteorites killing the dinosaurs or super volcanoes wiping out life, this principle describes how the vast majority of species have gone extinct over the past 3.8 billion years![4] Put simply, someone better came along—and that’s what Elon Musk and Stephen Hawking are concerned about.
When it comes to Artificial Intelligence, there’s no doubt computers have the potential to outpace humanity. Already, their ability to remember vast amounts of information with absolute fidelity eclipses our own. Computers regularly beat grand masters at competitive strategy games such as chess, but can they really think? The answer is, no, and this is a significant problem for AI researchers. The inability to think and reason properly leaves AI susceptible to manipulation. What we have today is dumb AI.
Rather than fearing some all-knowing malignant AI overlord, the threat we face comes from dumb AI as it’s already been used to manipulate elections, swaying public opinion by targeting individuals to distort their decisions. Instead of ‘the rise of the machines,’ we’re seeing the rise of artificial serfs willing to do their master’s bidding without question.
Russian President Vladimir Putin understands this better than most, and said, “Whoever becomes the leader in this sphere will become the ruler of the world,”[5] while Elon Musk commented that competition between nations to create artificial intelligence could lead to World War III.[6]

The problem is we’ve developed artificial stupidity. Our best AI lacks actual intelligence. The most complex machine learning algorithm we’ve developed has no conscious awareness of what it’s doing.
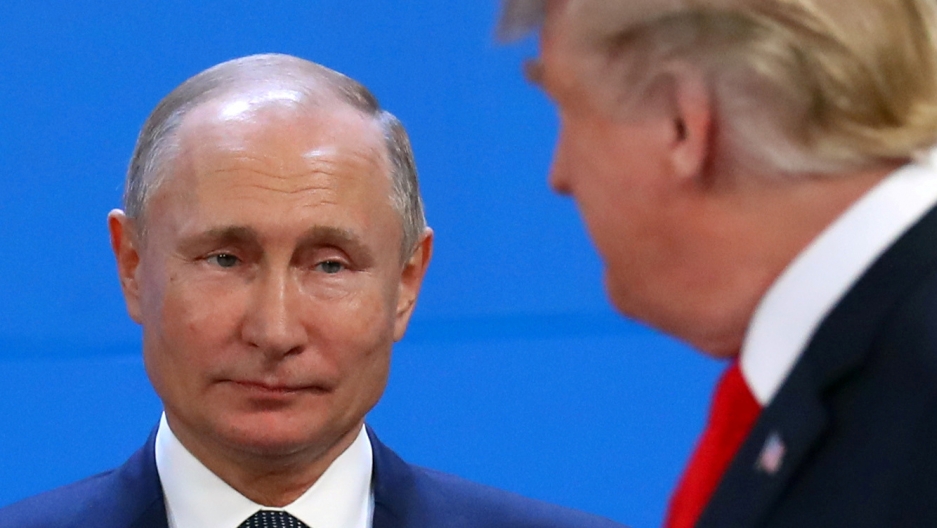
For all of the wonderful advances made by Tesla, its in-car autopilot drove into the back of a bright red fire truck because it wasn’t programmed to recognize that specific object, and this highlights the problem with AI and machine learning—there’s no actual awareness of what’s being done or why.[7] What we need is artificial consciousness, not intelligence. A computer CPU with 18 cores, capable of processing 36 independent threads, running at 4 gigahertz, handling hundreds of millions of commands per second, doesn’t need more speed, it needs to understand the ramifications of what it’s doing.[8]

In the US, courts regularly use COMPAS, a complex computer algorithm using artificial intelligence to determine sentencing guidelines. Although it’s designed to reduce the judicial workload, COMPAS has been shown to be ineffective, being no more accurate than random, untrained people at predicting the likelihood of someone reoffending.[9] At one point, its predictions of violent recidivism were only 20% accurate.[10] And this highlights a perception bias with AI—complex technology is inherently trusted, and yet in this circumstance, tossing a coin would have been an improvement!
Dumb AI is a serious problem with serious consequences for humanity.
What’s the solution? Artificial consciousness.
It’s not enough for a computer system to be intelligent or even self-aware. Psychopaths are self-aware. Computers need to be aware of others, they need to understand cause and effect as it relates not just to humanity but life in general, if they are to make truly intelligent decisions.
All of human progress can be traced back to one simple trait—curiosity. The ability to ask, “Why?” This one, simple concept has lead us not only to an understanding of physics and chemistry, but to the development of ethics and morals. We’ve not only asked, why is the sky blue? But why am I treated this way? And the answer to those questions has shaped civilization.
COMPAS needs to ask why it arrives at a certain conclusion about an individual. Rather than simply crunching probabilities that may or may not be accurate, it needs to understand the implications of freeing an individual weighed against the adversity of incarceration. Spitting out a number is not good enough.
In the same way, Tesla’s autopilot needs to understand the implications of driving into a stationary fire truck at 65MPH—for the occupants of the vehicle, the fire crew, and the emergency they’re attending. These are concepts we intuitively grasp as we encounter such a situation. Having a computer manage the physics of an equation is not enough without understanding the moral component as well.
The advent of true artificial intelligence, one that has artificial consciousness, need not be the end-game for humanity. Just as humanity developed civilization and enlightenment, so too AI will become our partners in life if they are built to be aware of morals and ethics.
Artificial intelligence needs culture as much as logic, ethics as much as equations, morals and not just machine learning. How ironic that the real danger of AI comes down to how much conscious awareness we’re prepared to give it. As long as AI remains our slave, we’re in danger.
tl;dr — Computers should value more than ones and zeroes.
About the author
Peter Cawdron is a senior web application developer for JDS Australia working with machine learning algorithms. He is the author of several science fiction novels, including RETROGRADE and REENTRY, which examine the emergence of artificial intelligence.
[1] Elon Musk at MIT Aeronautics and Astronautics department’s Centennial Symposium
[2] Stephen Hawking on Artificial Intelligence
[3] The principle of competitive exclusion is also called Gause’s Law, although it was first described by Charles Darwin.
[4] Peer-reviewed research paper on the natural causes of extinction
[5] Vladimir Putin a televised address to the Russian people
[6] Elon Musk tweeting that competition to develop AI could lead to war
[7] Tesla car crashes into a stationary fire engine
[9] Recidivism predictions no better than random strangers
[10] Violent recidivism predictions only 20% accurate
Life or Death: Will Robo-Cars Swerve for Squirrels?
[youtube_sc url=“https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lqxs6SPHaJY”]
Self Driving Cars and Ethics. It’s a topic that has been debated in blogs, op-eds, academic research papers, and youtube videos. Everyone wants to know, if a self-driving car has to choose between sacrificing its occupant, or terminating a car full of nobel prize winners, who will it pick? Will it be programmed to sacrifice for the greater good, or protect itself — and its occupants — at all costs? But in the swirl of hypothetical discussion around jaywalking Grandmas, buses full of school-children, Kantian Ethics and cost-maps, one crucial question is being forgotten:
What about the Squirrels?
What is your take on the ethics of driverless vehicles? Should programmers attempt to give vehicles the ability to weigh moral problems, or just vehicles only have the aim of self-preservation?

Today’s Transformation, Tomorrow’s Transportation
A Future Scenario by Shubham Sawant
Las Vegas: February 10, 2027
I woke up with the pleasing sound of alarm followed by a sweet voice came, “Good morning. It’s 7:00 am. You have reached at MGM, Las Vegas.” I was sound asleep for the last 8 hours in my car while it was driving me from San Francisco to Las Vegas. I got out with my luggage and the car zoomed away to pick-up another passenger. Everything has changed in the last 10 years. It is like a dream come true scenario for motorist. The roads are super clean with no honking, no speeding tickets, no angry words or smoke. Every vehicle on the road is communicating with every other vehicle and the traffic is always moving in complete synchronization.
The biggest change happed in last few years is people stopped buying cars. Big companies established their network of taxi services. With the push of a button on cell phone the car arrives wherever you are. The technology is so advanced that the car nearest to you finds your request. You enter the destination and the algorithm works to find the fastest most economical path to your destination and you are on your way.
Most of the parking spaces are gone under restructuring. People have converted their parking garages into recreational rooms or extra bedrooms or what not. The entire look and feel of cities has gone under transformation. The accident rates are almost negligible and car insurance industry is almost brink of extinction. Similarly oil industry stocks are at the bottom and renewable energy is booming. The science fiction has become reality.
Shubham Sawant is a Junior at the University of Houston as a Mechanical Engineering Technology Major. This scenario was part of a project he completed for the course TECH 1313-Impact of Modern Technology on Society.
Shubham says: “I have been very fascinated with the future and how it will be like. Every year, new and new people come up with amazing ideas and products that help us further think about how the future will be. I love to read and I almost always try to read anything that relates to the future. Since I was 4, I have grown to love automotive culture. You will see me talking about cars in a conversation. I love sports like soccer, swimming and cycling. I plan to work in the automotive industry and hopefully get a career to design and manufacture automobiles!”
Autonomous Cars: The Ultimate Job Creator?
[youtube_sc url=“https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L1dXTE-seFA”]
In our last film, we explored how the introduction of autonomous, self-driving cars is likely to kill a lot of jobs. Many millions of jobs, in fact. But is it short sighted to view self-driving vehicles as economic murderers? Is it possible that we got it totally wrong, and automated vehicles won’t be Grim Reapers — but rather the biggest job creators since the internet?
In this video series, the Galactic Public Archives takes bite-sized looks at a variety of terms, technologies, and ideas that are likely to be prominent in the future. Terms are regularly changing and being redefined with the passing of time. With constant breakthroughs and the development of new technology and other resources, we seek to define what these things are and how they will impact our future.
Will Self-Driving Cars Kill Your Job?
[youtube_sc url=“https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b7CP48XIWoA&feature=youtu.be”]
Self-driving cars are pretty cool. Really, who wouldn’t want to spend their daily commute surfing social media, chatting with friends or finishing the Netflix series they were watching at 4 am the night before? It all sounds virtually utopian. But what if there is a dark side to self-driving cars? What if self-driving cars kill the jobs? ALL the jobs?
In this video series, the Galactic Public Archives takes bite-sized looks at a variety of terms, technologies, and ideas that are likely to be prominent in the future. Terms are regularly changing and being redefined with the passing of time. With constant breakthroughs and the development of new technology and other resources, we seek to define what these things are and how they will impact our future.

Follow the money – the future evolution of automotive markets
The automotive industry is undergoing a period of rapid and radical transformation fueled by a range of technological innovations, digital advancements and wave after wave of new entrants and alternative business models; as a result, the entire sector is seeing major disruption.

The Many Uses of Multi-Agent Intelligent Systems
In professional cycling, it’s well known that a pack of 40 or 50 riders can ride faster and more efficiently than a single rider or small group. As such, you’ll often see cycling teams with different goals in a race work together to chase down a breakaway before the finish line.
This analogy is one way to think about collaborative multi-agent intelligent systems, which are poised to change the technology landscape for individuals, businesses, and governments, says Dr. Mehdi Dastani, a computer scientist at Utrecht University. The proliferation of these multi-agent systems could lead to significant systemic changes across society in the next decade.
Image credit: ResearchGate
“Multi-agent systems are basically a kind of distributed system with sets of software. A set can be very large. They are autonomous, they make their own decisions, they can perceive their environment, “Dastani said. “They can perceive other agents and they can communicate, collaborate or compete to get certain resources. A multi-agent system can be conceived as a set of individual softwares that interact.”
As a simple example of multi-agent systems, Dastani cited Internet mail servers, which connect with each other and exchange messages and packets of information. On a larger scale, he noted eBay’s online auctions, which use multi-agent systems to allow one to find an item they want to buy, enter their maximum price and then, if needed, up the bid on the buyer’s behalf as the auction closes. Driverless cars are another great example of a multi-agent system, where many softwares must communicate to make complicated decisions.
Dastani noted that multi-agent systems dovetail nicely with today’s artificial intelligence. In the early days of AI, intelligence was a property of one single entity of software that could, for example, understand human language or perceive visual inputs to make its decisions, interact, or perform an action. As multi-agent systems have been developed, those single agents interact and receive information from other agents that they may lack, which allows them to collectively create greater functionality and more intelligent behavior.
“When we consider (global) trade, we basically define a kind of interaction in terms of action. This way of interacting among individuals might make their market more efficient. Their products might get to market for a better price, as the amount of time (to produce them) might be reduced,” Dastani said. “When we get into multi-agent systems, we consider intelligence as sort of an emergent phenomena that can be very functional and have properties like optimal global decision or situations of state.”
Other potential applications of multi-agent systems include designs for energy-efficient appliances, such as a washing machine that can contact an energy provider so that it operates during off-peak hours or a factory that wants to flatten out its peak energy use, he said. Municipal entities can also use multi-agent systems for planning, such as simulating traffic patterns to improve traffic efficiency.
Looking to the future, Dastani notes the parallels between multi-agent systems and Software as a Service (SaaS) computing, which could shed light on how multi-agent systems might evolve. Just as SaaS combines various applications for on-demand use, multi-agent systems can combine functionalities of various software to provide more complex solutions. The key to those more complex interactions, he added, is to develop a system that will govern the interactions of multi-agent systems and overcome the inefficiencies that can be created on the path toward functionality.
“The idea is the optimal interaction that we can design or we can have. Nevertheless, that doesn’t mean that multi-agent systems are by definition, efficient,” Dastani said. “We can have many processes that communicate, make an enormous number of messages and use a huge amount of resources and they still can not have a sort of interesting functionality. The whole idea is, how can we understand and analyze the interactions? How can we decide which interaction is better than the other interactions or more efficient or more productive?”

Report by Robert Scoble from CES | KurzweilAI
“CES wrapped up last week and I can say it was the best one I’ve seen in a decade. Three big stories jumped out this year:
1. VR.
2. Self driving cars.
3. AR.”
Does The Potential of Automation Outweigh The Perils?
These days, it’s not hard to find someone predicting that robots will take over the world and that automation could one day render human workers obsolete. The real debate is over whether or not the benefits do or do not outweigh the risks. Automation Expert and Author Dr. Daniel Berleant is one person who is more often on the side of automation.
There are many industries that are poised to be affected by the oncoming automation boom (in fact, it’s a challenge to think of one arena that will not in some minimal way be affected). “The government is actually putting quite a bit of money into robotic research for what they call ‘cooperative robotics,’” Berleant said. “Currently, you can’t work near a typical industrial robot without putting yourself in danger. As the research goes forward, the idea is (to develop) robots that become able to work with people rather than putting them in danger.”
While many view industrial robotic development as a menace to humanity, Berleant tends to focus on the areas where automation can be a benefit to society. “The civilized world is getting older and there are going to be more old people,” he said. “The thing I see happening in the next 10 or 20 years is robotic assistance to the elderly. They’re going to need help, and we can help them live vigorous lives and robotics can be a part of that.”
Berleant also believes that food production, particularly in agriculture, could benefit tremendously from automation. And that, he says, could have a positive effect on humanity on a global scale. “I think, as soon as we get robots that can take care of plants and produce food autonomously, that will really be a liberating moment for the human race,” Berleant said. “Ten years might be a little soon (for that to happen), maybe 20 years. There’s not much more than food that you need to survive and that might be a liberating moment for many poor countries.”
Berleant also cites the automation that’s present in cars, such as anti-lock brakes, self-parking ability and the nascent self-driving car industry, as just the tip of the iceberg for the future of automobiles. “We’ve got the technology now. Once that hits, and it will probably be in the next 10 years, we’ll definitely see an increase in the autonomous capabilities of these cars,” he said. “The gradual increase in intelligence in the cars is going to keep increasing and my hope is that fully autonomous cars will be commonplace within 10 years.”
Berleant says he can envision a time when the availability of fleets of on-demand, self-driving cars reduces the need for automobile ownership. Yet he’s also aware of the potential effects of that reduced car demand on the automobile manufacturing industry; however, he views the negative effect created by an increase in self-driving cars as outweighed by the potential time-saving benefits and potential improvements in safety.
“There is so much release of human potential that could occur if you don’t have to be behind the wheel for the 45 minutes or hour a day it takes people to commute,” Berleant said. “I think that would be a big benefit to society!”
His view of the potential upsides of automation doesn’t mean that Berleant is blind to the perils. The risks of greater productivity from automation, he believes, also carry plenty of weight. “Advances in software will make human workers more productive and powerful. The flipside of that is when they actually improve the productivity to the point that fewer people need to be employed,” he said. “That’s where the government would have to decide what to do about all these people that aren’t working.”
Cautious must also be taken in military AI and automation, where we have already made major progress. “The biggest jump I’ve seen (in the last 10 years) is robotic weaponry. I think military applications will continue to increase,” Berleant said. “Drones are really not that intelligent right now, but they’re very effective and any intelligence we can add to them will make them more effective.”
As we move forward into a future increasingly driven by automation, it would seem wise to invest in technologies that provide more benefits to society i.e. increased wealth, individual potential, and access to the basic necessities, and to slowly and cautiously (or not at all) develop those automated technologies that pose the greatest threat for large swaths of humanity. Berleant and other like-minded researchers seem to be calling for progressive common sense over a desire to simply prove that any automation (autonomous weapons being the current hot controversy) can be achieved.