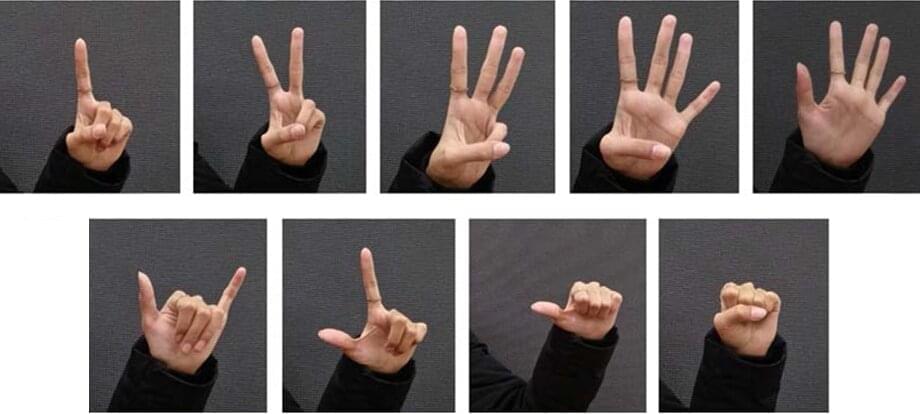
In the 2002 science fiction blockbuster film “Minority Report,” Tom Cruise’s character John Anderton uses his hands, sheathed in special gloves, to interface with his wall-sized transparent computer screen. The computer recognizes his gestures to enlarge, zoom in, and swipe away. Although this futuristic vision for computer-human interaction is now 20 years old, today’s humans still interface with computers by using a mouse, keyboard, remote control, or small touch screen. However, much effort has been devoted by researchers to unlock more natural forms of communication without requiring contact between the user and the device. Voice commands are a prominent example that have found their way into modern smartphones and virtual assistants, letting us interact and control devices through speech.
Hand gestures constitute another important mode of human communication that could be adopted for human-computer interactions. Recent progress in camera systems, image analysis and machine learning have made optical-based gesture recognition a more attractive option in most contexts than approaches relying on wearable sensors or data gloves, as used by Anderton in “Minority Report.” However, current methods are hindered by a variety of limitations, including high computational complexity, low speed, poor accuracy, or a low number of recognizable gestures. To tackle these issues, a team led by Zhiyi Yu of Sun Yat-sen University, China, recently developed a new hand gesture recognition algorithm that strikes a good balance between complexity, accuracy, and applicability.