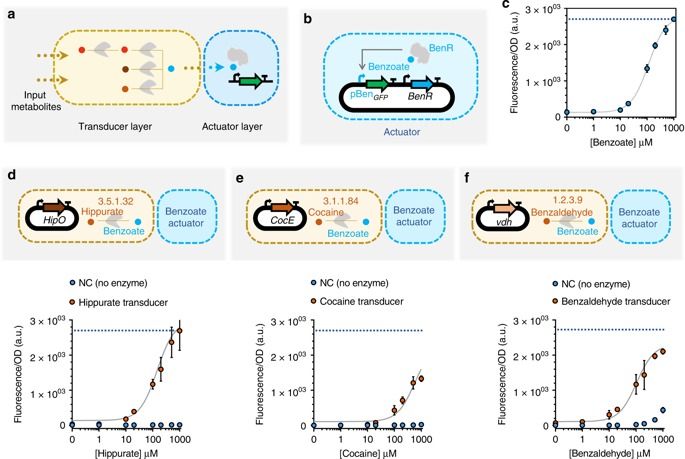
Synthetic biological circuits are promising tools for developing sophisticated systems for medical, industrial, and environmental applications. So far, circuit implementations commonly rely on gene expression regulation for information processing using digital logic. Here, we present a different approach for biological computation through metabolic circuits designed by computer-aided tools, implemented in both whole-cell and cell-free systems. We first combine metabolic transducers to build an analog adder, a device that sums up the concentrations of multiple input metabolites. Next, we build a weighted adder where the contributions of the different metabolites to the sum can be adjusted. Using a computational model fitted on experimental data, we finally implement two four-input perceptrons for desired binary classification of metabolite combinations by applying model-predicted weights to the metabolic perceptron. The perceptron-mediated neural computing introduced here lays the groundwork for more advanced metabolic circuits for rapid and scalable multiplex sensing.