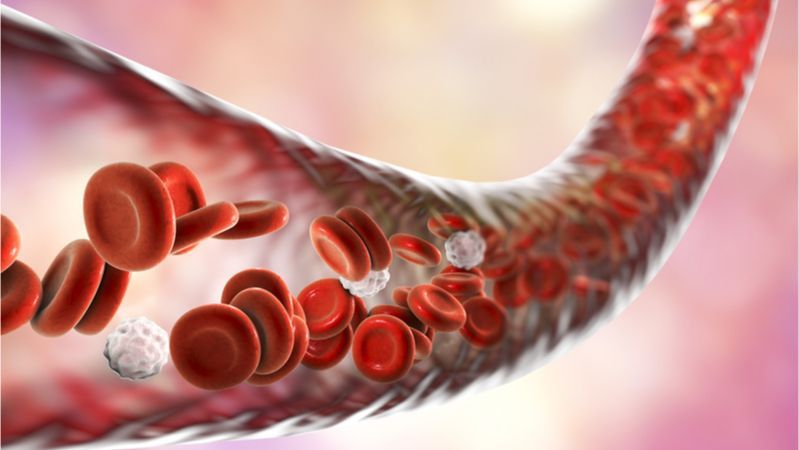
Age-related changes to the signals sent and received by our cells travelling via the bloodstream are one of the hallmarks of aging. A team of researchers, including Drs. Irina and Michael Conboy, has published the results of a new study suggesting that rejuvenation might be achieved by the calibration of these signals found in the blood [1].
The search for rejuvenation
The Conboys had done earlier research in joining of the circulatory systems between young and old animals, a process known as parabiosis, and they showed that tissue aging was not a one-way street and could be rapidly reversed in a matter of weeks, given access to the beneficial signaling from the younger animal [2].