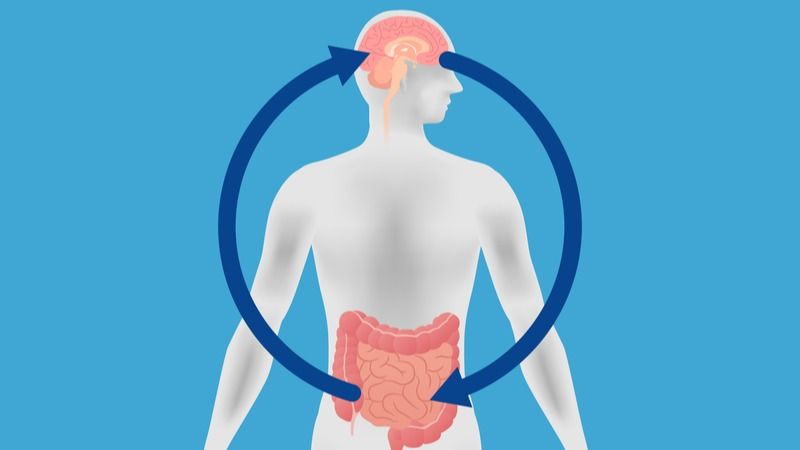
In a recent study, a team from the Neurobiota Research Center in Korea has discovered that reducing gut dysbiosis partially alleviates the cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer’s disease. This may seem puzzling, as the gut and the brain are separate and relatively distant organs, but this research makes sense in the context of chronic inflammation.
Inflammaging
Under normal circumstances, inflammation is a short-term measure in response to infection: immune cells are directed towards the inflamed area and handle the infection, and then the inflammation dies down. However, chronic inflammation causes harm to our organs; it is the main form of altered intercellular communication, which is one of the hallmarks of aging. The protein complex NF-kB, the master regulator of inflammation, is the main culprit of inflammaging, and it is specifically discussed in this paper.