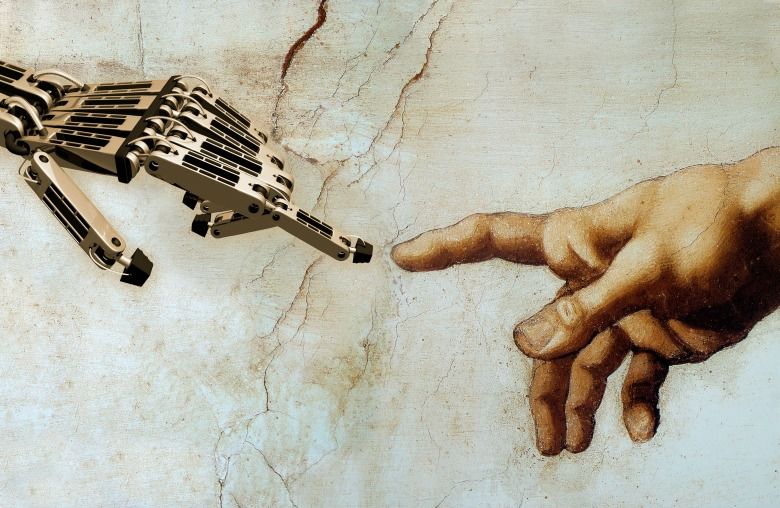
Facts of life, even for passionate seperation of church and state advocates like me: Religious #transhumanism is growing.
WASHINGTON – A Christian pastor from Florida is promoting acceptance of some forms of transhumanism, saying believers should be open to finding an “ethical alternative” to the complete rejection of the scientific, technical and philosophical transhumanist movement that has already begun.
Rev. Christopher Benek, associate pastor of family ministries and mission at First Presbyterian Church in Fort Lauderdale, writes in the Christian Post that it’s time for the development of “Christian transhumanism.”
“If you have read the The American Conservative’s recent postings about the evolving transhumanist movement, you have likely developed reasonable concerns,” Benek wrote. “People should be dismayed at Zoltan Istvan’s misguided article in TAC from two weeks ago entitled: ‘The Growing World of Libertarian Transhumanism.’ And, if one believes that Istvan’s transhumanism represents all transhumanists, then Kai Weiss’ follow-up piece “Transhumanism is Not Libertarian, It’s an Abomination,” is correct and appropriately titled. But these two depictions do not represent the majority of transhumanist thought. As such I would request: Please folks do not throw the transhumanist-baby out with Zoltan Istvan’s bathwater. There is an ethical transhumanist alternative: Christian Transhumanism.”
Benek says “Christians can make a positive moral impact” on the debate over transhumanism rather than throw the baby out with the bathwater.