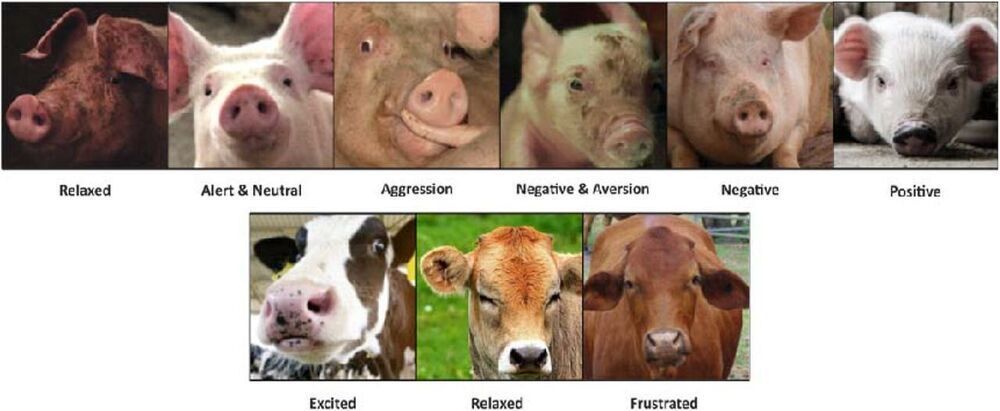
An animal scientist with Wageningen University & Research in the Netherlands has created an artificial-intelligence-based application that can gauge the emotional state of farm animals based on photographs taken with a smartphone. In his paper uploaded to the bioRxiv preprint server, Suresh Neethirajan describes his app and how well it worked when tested.
Prior research and anecdotal evidence has shown that farm animals are more productive when they are not living under stressful conditions. This has led to changes in farming practices, such as shielding cows’ eyes from the spike that is used to kill them prior to slaughter to prevent stress hormones from entering the meat. More recent research has suggested that it may not be enough to shield farm animals from stressful situations—adapting their environment to promote peacefulness or even playfulness can produce desired results, as well. Happy cows or goats, for example, are likely to produce more milk than those that are bored. But as Neethirajan notes, the emotional state of an animal can be quite subjective, leading to incorrect conclusions. To address this problem, he adapted human face recognition software for use in detecting emotions in cows and pigs.
The system is called WUR Wolf and is based on several pieces of technology: the YOLO Object Detection System, the YOLOv4 that works with a convolution neural network and Faster R-CNN, which also allows for detection of objects, but does so with different feature sets. For training, he used the Nvidia GeForece GTX 1080 Ti GRP running on a CUDA 9.0 computer. The data consisted of thousands of images of cows and pigs taken with a smartphone from six farms located in several countries with associated classification labels indicating which physical features could be associated with which mood—raised ears on a cow, for example, generally indicate the animal is excited.

 XPENG MOTORS — Follow China’s leading smart EV automaker on Facebook at https://www.facebook.com/XpengMotorsGlobal.
XPENG MOTORS — Follow China’s leading smart EV automaker on Facebook at https://www.facebook.com/XpengMotorsGlobal.