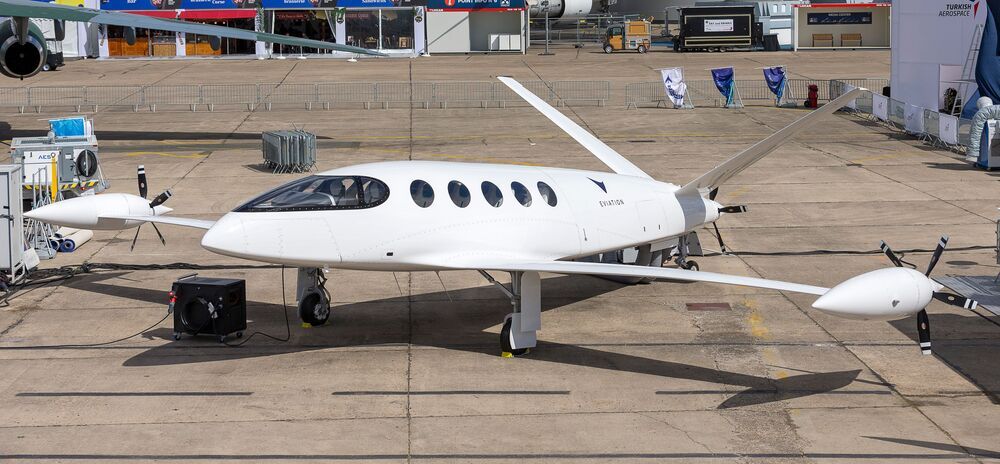
Israeli/American company Eviation is preparing for the first test flights of its gorgeous Alice, an all-electric 11-seat luxury plane with an impressive 506-mile (814-km) range from a single charge of its huge 820-kWh battery pack.
The company says it’s just taken delivery of its first electric motor, one of three Magnix Electric Propulsion Units the Alice will use to power its three variable pitch pusher props, one on a pod at the end of each wing and a third on the tail. The latter is designed to accelerate fast-moving air around the fuselage and turn the whole body into a bonus wing surface for extra lift.
The prototype is certainly a striking looking aircraft, all space-age looking with its big v-tail and that tastefully squashed high-lift fuselage. Once everything’s all hooked up, it’ll carry two crew and nine passengers at cruise speeds up to 253 mph (407 km/h), and Eviation says the low noise output of its electric powertrain will make a solid contribution to the comfort factor in the back.