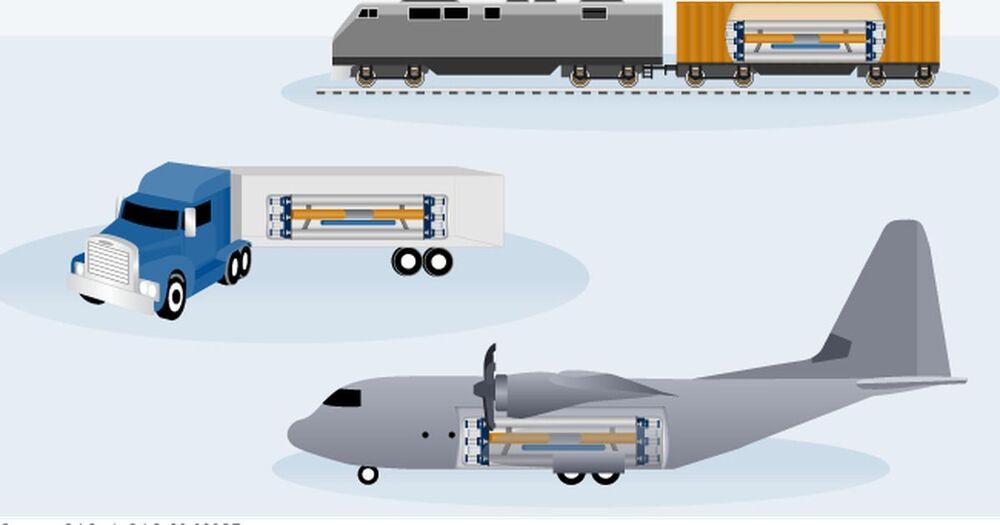
The two companies, along with Westinghouse Government Services, were each given preliminary contracts of less than $15 million in March 2020 to begin design work. The final design is due to the Strategic Capabilities Office in 2022, at which point the Defense Department will make a decision on whether to move forward with testing the systems.
“We are thrilled with the progress our industrial partners have made on their designs,” Jeff Waksman, Project Pele’s program manager, said in a statement. “We are confident that by early 2022 we will have two engineering designs matured to a sufficient state that we will be able to determine suitability for possible construction and testing.”
The Pentagon has long eyed nuclear power as a potential way to reduce both its energy cost and its vulnerability in its dependence on local energy grids. According to a news release, the Defense Department uses “approximately 30 Terawatt-hours of electricity per year and more than 10 million gallons of fuel per day.”