Advance could make flow batteries cheaper and easier to build.
Category: energy

Cambridge Physicists Find Wormhole Proof
Calculations show that if the wormhole’s throat is orders of magnitude longer then the width of its mouth, it does indeed create Casimir energy at its centre.
Cambridge Physicists Find Wormhole Proof:-Physicists at the University of Cambridge have established a theoretical groundwork for the reality of wormholes, which are pipes that join two different points in space-time. If a part of information or physical object could pass through the wormhole, it might open the door to time travel or immediate communication through huge distances. “But there’s a problem: Einstein’s wormholes are extremely unsteady, and they don’t stay open long enough for something to pass over.” In 1988, physicists reached the deduction that a type of negative energy called Casimir energy might keep wormholes open.
The hypothetical solution established at Cambridge has to do with the properties of quantum energy, which conveys that even vacuums are teaming by means of waves of energy. If you visualize two metal plates in a vacuum, some waves of energy would be excessively big enogh to fit between the plates, meaning that the space-time among the plates would have negative energy. “Under the right circumstances, could the tube-like shape of the wormhole itself generate Casimir energy? Calculations show that if the wormhole’s throat is orders of magnitude longer then the width of its mouth, it does indeed create Casimir energy at its centre.”
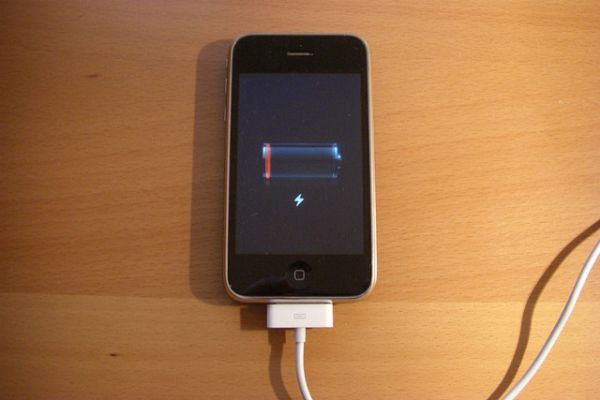

This new battery charges to 70% in two minutes, and lasts for 20 years
Sick of waiting an hour for your phone to charge before you leave the house? Researchers at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore have come up with the best solution yet — a lithium ion battery that charges to 70 percent in just two minutes.
Even better, it also lasts for 20 years, and will reportedly be available to the public within two years.
Rechargeable lithium ion batteries are already common in our mobile phones, tablets and laptops — but most only last around 500 recharge cycles, which is around two to three years of typical use. And at the moment batteries take around two hours to fully charge.
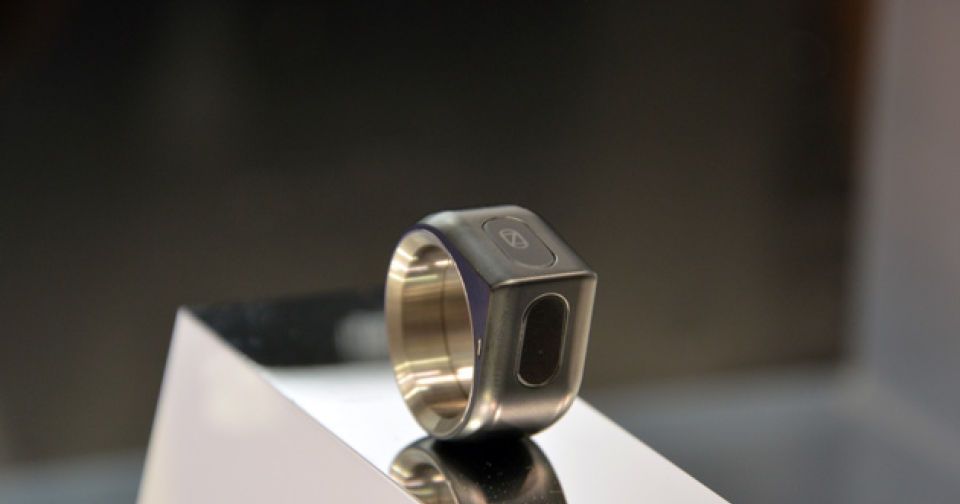

The one (gesture control) ring to rule them all
While many companies are tinkering with lasers, ultrasound and even arm muscles for touchless gesture control on portable devices and desktop PCs, Japan’s 16Lab just wants to put a pretty ring on you. The yet-to-be-named titanium wearable is designed by the award-winning Manabu Tago, and it features ALPS Electric’s tiny module (5.05 x 5.65 x 2.5 mm) that somehow manages to pack Bluetooth Smart radio, movement sensor, environment sensor plus antennas — there’s a video demo after the break. Despite its custom-made 10mAh lithium polymer cell, 16Lab is aiming for at least 20 hours of battery life. This is possible mainly because you have to place your thumb on the top pad (with the ring’s wedge pointing away from the user) to enable the sensors — upon which point the ring vibrates to confirm that it’s active. It’s then just a matter of waving and tilting your hand until you’re done.
Gallery | 13 Photos.
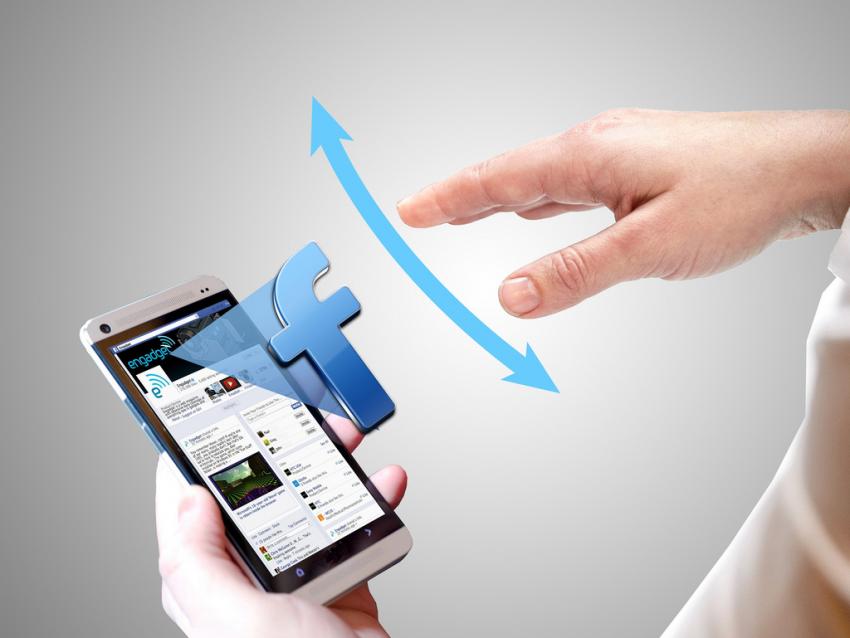

Elliptic Labs powers up ultrasound for touchless gesturing
Touchless gestures powered by ultrasound has become a mark of distinction for Elliptic Labs. The company has new “Multi Layer Interaction” technology designed to bring users intuitive device interactions.
Without touching the device, the person’s hand moves towards the smartphone, the screen lights up and information is displayed. As the person continues moving the hand closer, different information is revealed. With users constantly, frequently, eagerly reaching for their devices throughout the day, Elliptic Labs aims to make a difference in its easy and fast way to get information, from playing games to navigating maps, to using social media, to watching videos. A promotional video says the user can interact above, in front, underneath, double-tapping anywhere around the device, easily turning the device on and off as well. There is an SDK kit for applications. How it works: Ultrasound signals sent through the air from speakers integrated in smartphones and tablets bounce against the hand and are recorded by microphones integrated in the devices. As such, the technology recognizes hand gestures and uses them to move objects on the screen, similar to how bats use echolocation to navigate.
The company also talks about range-gating capabilities, saying that their touchless gesturing technology can easily separate foreground from background, for separating finger motion from wrist, and hand motion from movements or reflections from the body. This prevents unwanted and accidental gestures from being recognized. Overall, the company believes that “Ultrasound offers the best combination of high resolution, 180-degree interaction space, and low power consumption compared to camera or other sensing technologies.” They use an ultra-low power audio SoC for ultrasound processing such as Wolfson audio hubs. They have formed partnerships with Murata Manufacturing and Wolfson Microelectronics.

German Scientists Create Lithium Ion Battery that Can Charge an Electric Car for 27 Years
German scientists have developed technology that makes lithium-ion batteries last for 10,000 charging and discharging cycles while still retaining 85% of their original capacity.

Intel wireless charging in a bowl coming sooner than later
When vendors send out announcements of long battery life and juicing strategies for electronic gadgets, interest is assured; the bad news is that interest is assured because consumers are still eagerly looking for less bother and less time needed to keep their smartphones and other mobile gadgets up and running. Intel is aware of the challenge, what with wearables on tap in an assortment of form factors. To be sure, Intel would like to be in the frontlines of technology giants providing the buying public with finer solutions.
“What’s New with Wireless Charging?” Intel asked in July. Intel’s answer, “If you’ve been keeping up with trade shows and tech blogs, you might think that some new breakthrough in wireless energy transfer has taken place in the past year. It hasn’t.” Nikola Tesla worked on wireless power transmission before the turn of the 20th century; his inductive charging techniques would see a renaissance some five decades after his death in 1943, said Intel. That has not stopped technologists, however, from asking what comes next. Today, said Intel, the idea and the technology is gaining momentum.
This week’s news headlines of Intel saying its charging bowl will be available by the end of this year will no doubt interest readers and will please those who saw the bowl earlier this year at the Consumer Electronics show, and kept sending e-mails to Intel asking when it will be ready. Earlier this year, it was clear that Intel was working on a day not too distant in the future when people in PC environments could enjoy docking and charging activities as a wire-free experience. Intel revealed at the Computex trade show in Taipei, via an Intel demonstration by Kirk Skaugen, Intel’s senior vice president and general manager of the PC Client Group, that the chipmaker was in fact working on wireless technologies to help deliver a new normal. Skaugen demonstrated how wireless technology could be integrated into a table that could simultaneously charge a laptop, phone, headset and tablet. In January, the company had really whetted appetites for changes in showing a wireless charging bowl at CES. The bowl looks like the standard bowl one might place on a table at home to hold keys, loose coins, or other items.

‘Cool-Burning’ Space Flames Could Make Greener Cars
Astronauts typically try to avoid starting fires in space, but new research on the behavior of flames in orbit could have benefits closer to home. In fact, this fiery research could lead to more-efficient car engines that contribute less pollution to the environment, according to a new study.
A series of experiments aboard the orbiting complex is investigating “cool-burning” flames in space — a type of fire that burns at lower temperatures than ordinary flames on Earth. Blazes on this planet typically burn at between 2,240 degrees and 3,140 degrees Fahrenheit (1,225 degrees and 1,725 degrees Celsius). Cooler flames produced in microgravity burn at temperatures of between 440 degrees and 980 degrees Fahrenheit (227 degrees and 527 degrees Celsius).
In the space station experiments, researchers ignited droplets of heptane fuel. These types of fires are possible on Earth, but they are typically short-lived, flickering out almost immediately, the researchers said. In microgravity, though, the flames burned for several minutes. [7 Everyday Things that Happen Strangely In Space].
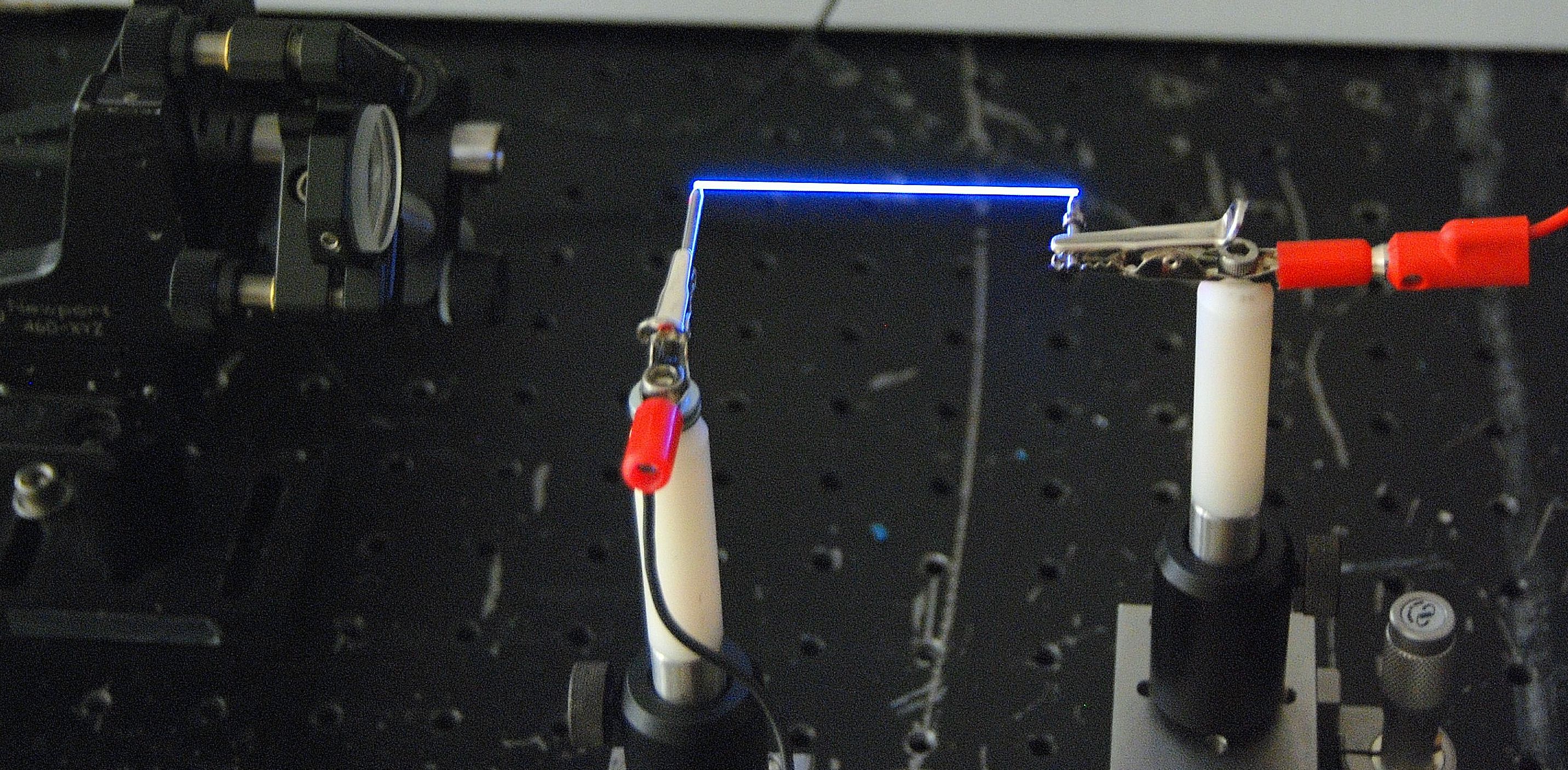
Laser ‘Lightning rods’ channel electricity through thin air
By zapping the air with a pair of powerful laser bursts, researchers at the University of Arizona have created highly focused pathways that can channel electricity through the atmosphere.
The new technique can potentially direct an electrical discharge up to 10 meters (33 feet) away or more, shattering previous distance records for transmitting electricity through air. It also raises the intriguing possibility of one day channeling lightning with laser power.
Described in a paper published in The Optical Society’s new open-access journal Optica, the current system may have near-term, lifesaving applications in areas such as the remote detonation of land mines, the researchers speculate. The laser system could easily pinpoint an active land mine and then carry an electric pulse strong enough to safely discharge harmful explosives from afar.
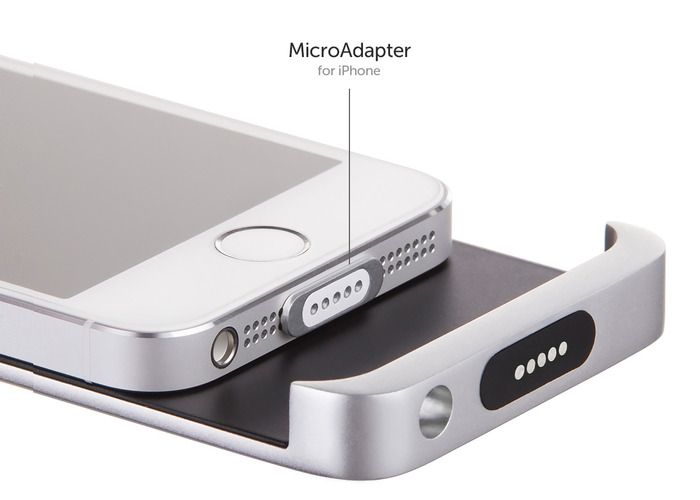

Kickstarter campaign bringing magnetic charging to iPhone
If you’ve got an iPhone, there is a good chance you also have a MacBook. The MagSafe charger on Apple’s laptop offerings is easy to use, leading some to want an iPhone with the same functionality. A recently funded Kickstarter is attempting to bring it to us, and even slaps in a battery pack for good measure.
The draw for Cabin is twofold: the magnetic charging, and the battery pack. The battery pack slips onto the rear of the device, much like we see with the Case+ lineup from Logitech. Aluminum, Cabin is relying on your sensitivity to style for the battery pack. At 2200mAh, it’ll charge you up more than once, too.
The magnetic charging is a bit more adapter than anything else. By taking a lightning connector and working a pinned magnetic charger on the end, we get simple, easy, and (hopefully) effective charging. What you won’t be able to do is use your MacBook charger. Cabin includes a Lightning adapter and dock (if you spend a touch more), though.