Researchers in the US have identified the two main culprits in rechargeable battery degradation, which could lead to longer-lasting phone, laptop and electric car batteries.
Category: energy
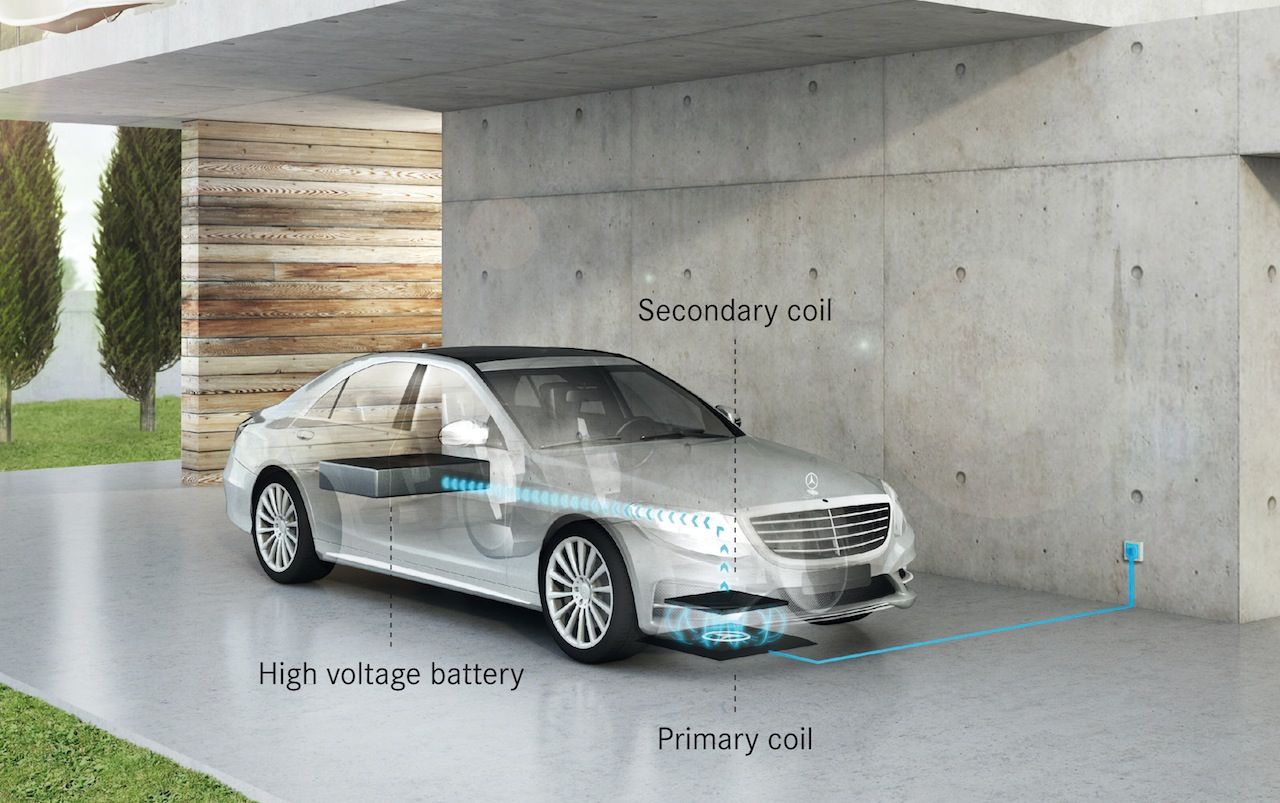
BMW and Mercedes team on wireless car charging
BMW and Mercedes-Benz are teaming up on wireless car charging, pushing a super-efficient way of refueling EVs like the BMW i8 and the Mercedes S500 Plug-In Hybrid simply by parking over a certain spot on your driveway. The system, which the two German marques hope to get accepted as the de-facto standard for wireless car recharging, promises a cut in charge times without the hassle of having to regularly plug in: BMW says the batteries in its i8 supercar, for instance, can be topped up in under two hours.
As with other such systems we’ve seen, Mercedes-Benz and BMW use a pair of coils to transmit power wirelessly. A primary coil is mounted in a floor plate, and connects with a secondary coil in the vehicle floor: an alternating magnetic field is created by the former and tracked by the latter.
However, the new system uses a circular coil which the two companies claim makes for a more productive magnetic field, with more than 90-percent efficiency. The charging rate is initially 3.6 kW, but could be ramped up to as much as 7 kW, in preparation for the next generation of higher-powered EV drivetrains car firms envisage.
Sand-based batteries could soon power your mobile phone
Researchers at the University of California, Riverside in the US have developed lithium-ion batteries that substitute graphite with silicon extracted from sand and last three times longer than current products.
The negative side of lithium-ion batteries, or anode, is made with graphite, and scientists have been trying to find a substitute material that could make batteries last longer. One of the options is silicon, which can store up to 10 times more energy than current materials, but it’s expensive and hard to produce in large quantities.
But then a very simple but brilliant option revealed itself to graduate student Zachary Favors. As Gizmag reports, Favors was relaxing after surfing when he noticed something quite special: sand. Sand is made of quartz, or silicon dioxide, and other materials, so Favors thought he could extract the silicon and use it to make batteries.
For more innovative ideas, visit our website at
http://www.engineeringbuddies.com/channels/innovative-ideas/
The Engineering Buddies Team
www.EngineeringBuddies.com

Tesla’s Powerwall home battery is coming to Australia in 2015
The Powerwall, a rechargeable lithium ion home battery from the makers of the Tesla Model S car, will be on sale in Australia by the end of the year.
Powerwall will be available in Australia in late 2015 through a variety of Tesla Energy partners who are yet to be announced, Business Insider reported.

World’s first all-electric propulsion satellite goes on line
Boeing has announced that the first satellite with all-electric propulsion is now fully operational. Launched last March, the ABS-3A 702SP (small platform) satellite was formally handed over to its owner, Bermuda-based telecommunications company ABS, on August 31. It will provide communications services to the Americas, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa.
ABS-3A launched on March 1 atop a Falcon 9 rocket from SpaceX’s Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida along with EUTELSAT 115 West B. The geosynchronous comsat’s key technology is its Xenon Ion Propulsion System (XIPS). Previously, hybrid systems that use a mix of chemical and ion propellants have been sent into orbit, but this is the first time a satellite has been deployed with an all-electric drive.
Boeing says that the technology is based on 210,000 hours of ion propulsion flight experience and is 10 times more efficient than liquid-fueled rockets. Four 25-cm (9.8-in) thrusters using xenon as a propellant allow the 702SP satellite to maintain stationkeeping while using only 5 kg (11 lb) of fuel per year. This is a great saving because the satellite needs less fuel and smaller thrusters, which reduces launch costs.
3D Printed Solar Cells Could Provide 1.3 Billion People with Electricity
Solar power has been gaining more and more popularity worldwide since the efficiency of solar panels has significantly increased during the recent years, along with the dramatic decrease in the costs. However, its popularity is not only due its affordability to a wider audience but also to the growing awareness about the benefits of clean sources of energy. Yet, the costs of transportation and production often make it extremely difficult to implement solar technology in developing countries. Printed solar cells could offer a solution to this problem.
Thanks to the advances in printed solar cell technology during the past few years, its energy efficiency has increased from 3% to 20%.
“Its success is due to its cost-effectiveness and simplicity. A 10×10 cm solar cell film is enough to generate as much as 10–50 watts per square meter,” said Scott Watkins from the Korean company Kyung-In Synthetic.
No More Air Conditioners: This “Skin” For Buildings Keeps The Inside Cool With Zero Energy
The facade works with no power at all—not even solar panels—and keeps the temperature comfortable and light bright inside.
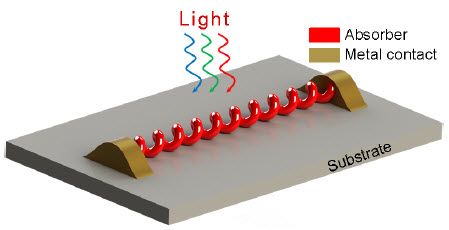
How curly nanowires can absorb more light to power nanoscale electronic circuits
This illustration shows a prototype device comprising bare nanospring photodetectors placed on a glass substrate, with metal contacts to collect charges (credit: Tural Khudiyev and Mehmet Bayindir/Applied Optics)
Researchers from Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey, have shown that twisting straight nanowires into springs can increase the amount of light the wires absorb by up to 23 percent. Absorbing more light is important because one application of nanowires is turning light into electricity, for example, to power tiny sensors instead of requiring batteries.
If nanowires are made from a semiconductor like silicon, light striking the wire will dislodge electrons from the crystal lattice, leaving positively charged “holes” behind. Both the electrons and the holes move through the material to generate electricity. The more light the wire absorbs; the more electricity it generates. (A device that converts light into electricity can function as either a solar cell or a photosensor.)