As we approach two full years of the COVID-19 pandemic, we now know it spreads primarily through airborne transmission. The virus rides inside tiny microscopic droplets or aerosol ejected from our mouths when we speak, shout, sing, cough, or sneeze. It then floats within the air, where it can be inhaled by and transmitted.
This inspired researchers in India to explore how we can better understand and engineer airflow to mitigate the transmission of COVID-19. To do this, they used their knowledge of airflow around aircraft and engines to tailor the airflow within indoor spaces.
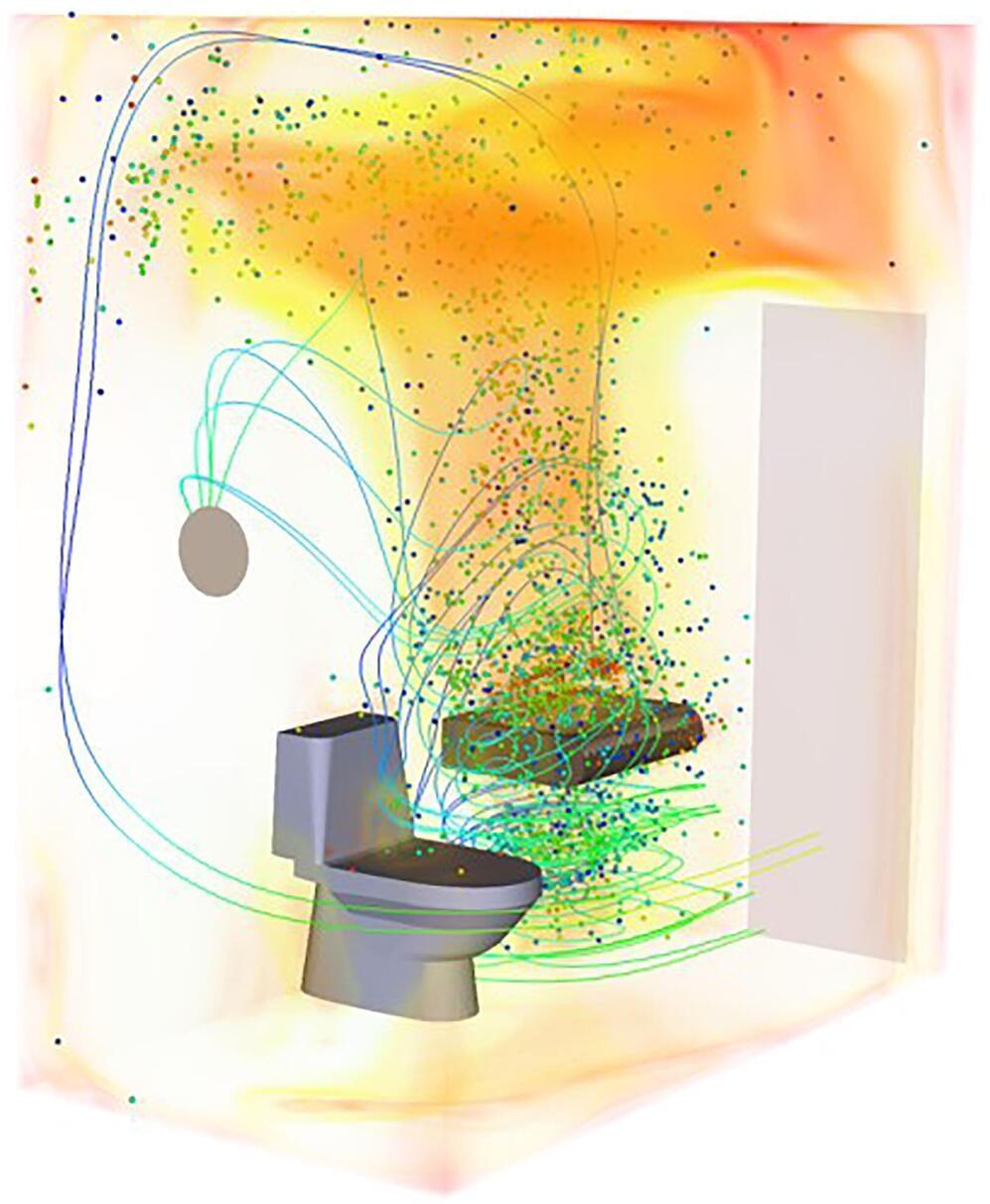
In Physics of Fluids, they report computer simulations of airflow within a public washroom showing infectious aerosols in dead zones can linger up to 10 times longer than the rest of the room. These dead zones of trapped air are frequently found in corners of a room or around furniture.