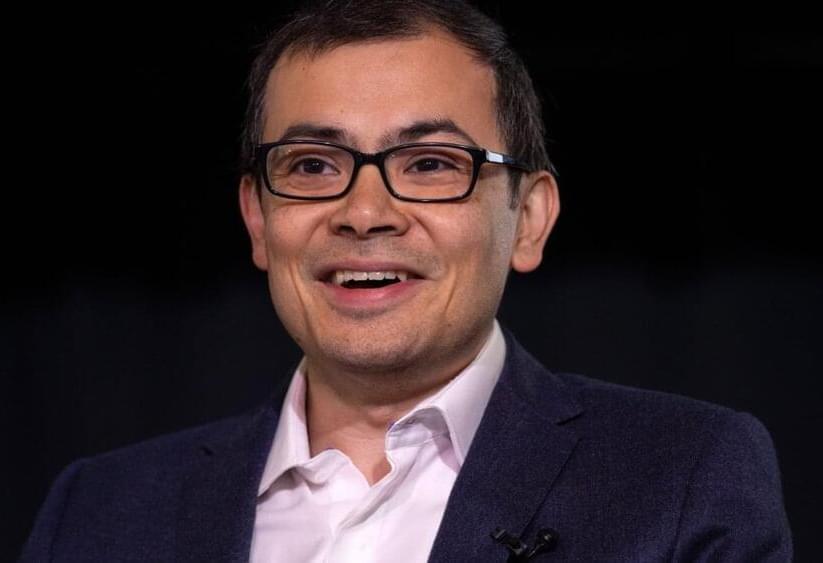
Alphabet has launched a new drug discovery company called Isomorphic Labs that will be led by DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis.
Category: biotech/medical
The issue facing the world today is not simply “THE supply chain,” the issue is that nearly every single link in the supply chain is compromised. Human talent is less available and manufacturers fear this will become a permanent reality, even after the pandemic. Extreme weather events occur every month and the ongoing pandemic is also causing shortages of direct and indirect materials. In turn, shipping costs have risen sharply. The status of sheet metal, computer chips and all food ingredients are up in the air. Constraints on the supply of raw materials, including those needed for semiconductors, PPE and various plastics, have led to factory shutdowns. A chronic lack of truck drivers has every neighborhood filled empty store shelves staring back at its citizens. And, to no surprise, Inflation was just reported at 5.4%, which is a 13 year high.
Now consider that only 4% of supply chain leaders believe their operations are future ready. We are at the precipice of either complete disaster, or a brave new world.
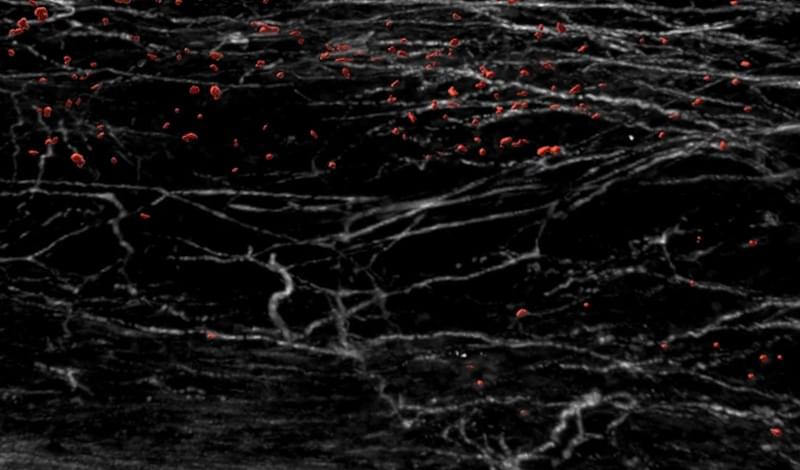
Scientists have found a way to deactivate DDR1, a molecule that forms a barrier ‘like barbed wire’ in tumours. By removing this barrier, anti-tumour immune cells could target aggressive forms of breast cancer.
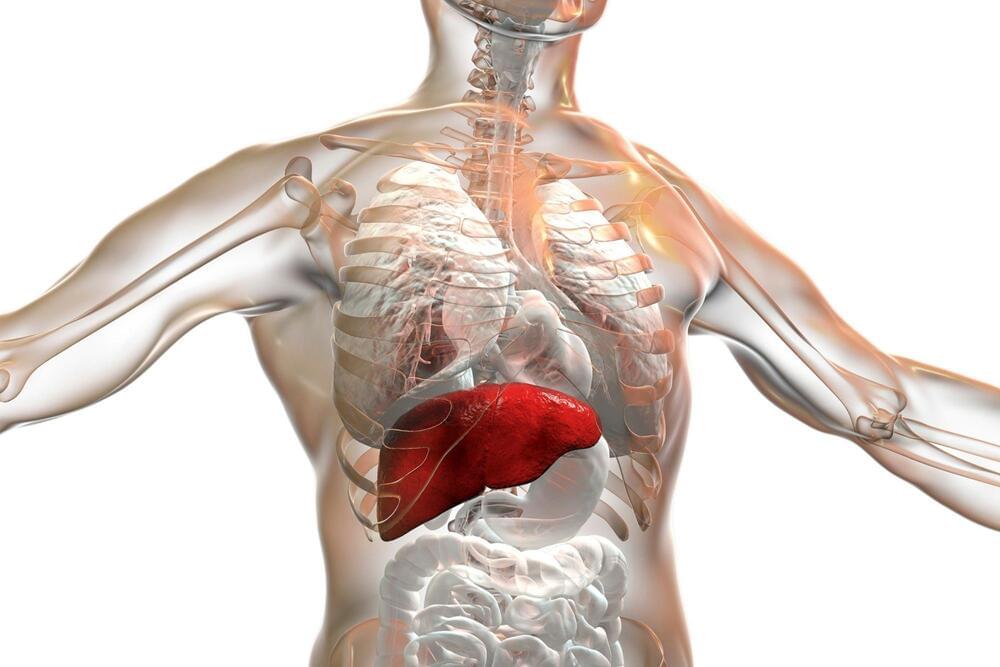
About 80 million Americans have fatty liver disease unrelated to alcohol abuse. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with obesity and diabetes, and can lead to more severe liver damage such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis and liver cancer. Cardiovascular disease, colorectal cancer and breast cancer actually are the major causes of death in patients with fatty liver disease.
Several drugs in advanced stages of development have failed because of the complexity of the disease, low efficacy, or the toxicity of drugs. Although several clinical trials were conducted in past decades, currently there is no FDA-approved pharmaceutical therapy for NASH.
To understand the complexity of the progression of fatty liver disease, a team of USC.
Plans Of A Technocratic Elite: ‘The Great Reset’ Is Not A Conspiracy Theory
Posted in 3D printing, biotech/medical, genetics, information science, internet, nanotechnology, quantum physics, Ray Kurzweil, robotics/AI, singularity, transhumanism | Leave a Comment on Plans Of A Technocratic Elite: ‘The Great Reset’ Is Not A Conspiracy Theory
According to Klaus Schwab, the founder and executive chair of the World Economic Forum (WEF), the 4-IR follows the first, second, and third Industrial Revolutions—the mechanical, electrical, and digital, respectively. The 4-IR builds on the digital revolution, but Schwab sees the 4-IR as an exponential takeoff and convergence of existing and emerging fields, including Big Data; artificial intelligence; machine learning; quantum computing; and genetics, nanotechnology, and robotics. The consequence is the merging of the physical, digital, and biological worlds. The blurring of these categories ultimately challenges the very ontologies by which we understand ourselves and the world, including “what it means to be human.”
The specific applications that make up the 4-R are too numerous and sundry to treat in full, but they include a ubiquitous internet, the internet of things, the internet of bodies, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, 3D printing, nanotechnology, biotechnology, materials science, energy storage, and more.
While Schwab and the WEF promote a particular vision for the 4-IR, the developments he announces are not his brainchildren, and there is nothing original about his formulations. Transhumanists and Singularitarians (or prophets of the technological singularity), such as Ray Kurzweil and many others, forecasted these and more revolutionary developments,. long before Schwab heralded them. The significance of Schwab and the WEF’s take on the new technological revolution is the attempt to harness it to a particular end, presumably “a fairer, greener future.”
A team of physicists has discovered how DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).
SRI Newsletter, a report from IAC2021 Dubaiby Prof. Bernard Foing, SRI President, and.
Paramount important too, space philosophy and humanities are now well recognized and accepted by the space community. The first IAF Congress I attended, 1998 at Melbourne, was dramatically void of philosophy, yet participants already were missing it. I saw many young people at IAC2021, scientists, designers, economists, scholars of various disciplines, including philosophy. And, heartwarming indeed, Space Renaissance had a great enthusiastic welcome. The space people know us (and know me!), many people which I didn’t know personally shook my hand, asked me for comments and short talks, were enthusiast about the Space Renaissance… All of that is for sure due to the big work we made for our recent congress, and of course to the great world-wide influence of our new President, Prof. Bernard Foing. Yet, there is something deeper, in the feeling of this peculiar sub-assembly of humankind, that was looking ahead enough to dedicate their life to human expansion into outer space. The last two years – characterized by the Covid pandemics — have worked hard, to shape and forge space leaders, raising the awareness of the urgency to kick-off the civilian space development. And it is now maybe a general acknowledge that the space philosophers were right, when they were rushing for an acceleration of the enabling technologies, low cost access to space, space tourism, space safety, … The need to get rid of space debris was well present in several speeches, even if only a few dare to target space debris as a huge source of business development, when we’ll start capturing and reusing them.
Simple sponges contain cells that appear to send signals to digestive chambers, a communication system that offer hints about how brains evolved.
Professor Stefan Lorenz Sorgner talks about his new book, ‘We Have Always Been Cyborgs’. Find out more about the book: https://bristoluniversitypress.co.uk/we-have-always-been-cyborgs.
“With an encyclopaedic knowledge of transhumanism and a deep philosophical grounding, especially in Nietzschean thought, Stefan Sorgner tackles some of the most challenging ethical issues currently discussed, including gene editing, digital data collection, and life extension, with uncommon good sense and incisive conclusions. This study is one of the most detailed and comprehensive analyses available today. Highly recommended for anyone interested in transhumanist/posthumanist ideas and in these issues generally.” N. Katherine Hayles, University of California, Los Angeles.
“An eye-opening, wide-ranging and all-inclusive study of transhumanism. Sorgner’s account avoids both the utopian trap and the bogeyman spectre. He makes a compelling case for placing ourselves on the transhuman spectrum. How we continue to use technologies is in our hands. Sorgner’s book is both a comprehensive introduction to transhumanist thought and a clear-sighted vision for its future realisation.” Julian Savulescu, University of Oxford.
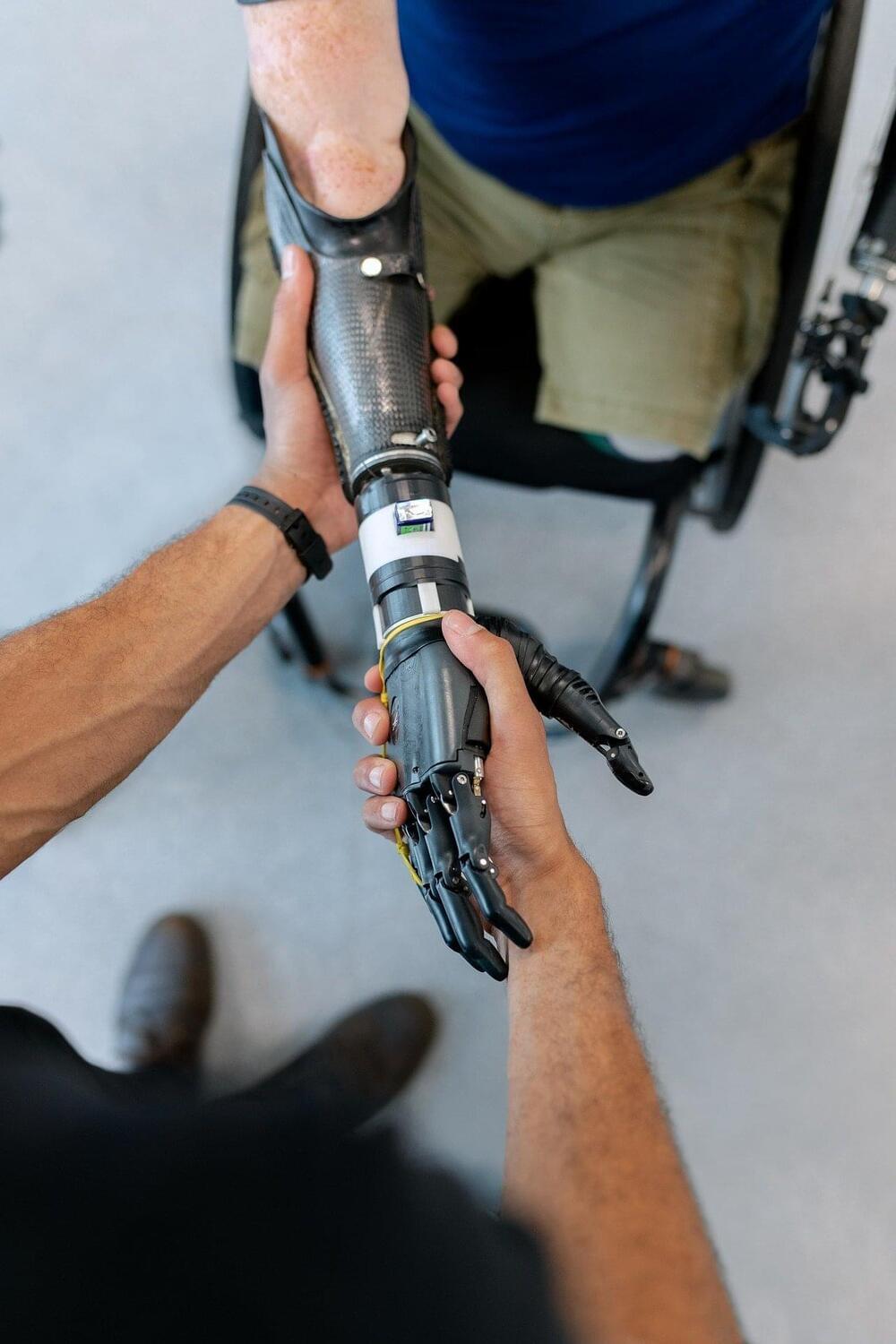
A system to control robotic arms based on augmented reality and a brain-computer interface
Posted in augmented reality, bioengineering, biotech/medical, cyborgs, robotics/AI, transhumanism | Leave a Comment on A system to control robotic arms based on augmented reality and a brain-computer interface
For people with motor impairments or physical disabilities, completing daily tasks and house chores can be incredibly challenging. Recent advancements in robotics, such as brain-controlled robotic limbs, have the potential to significantly improve their quality of life.
Researchers at Hebei University of Technology and other institutes in China have developed an innovative system for controlling robotic arms that is based on augmented reality (AR) and a brain-computer interface. This system, presented in a paper published in the Journal of Neural Engineering, could enable the development of bionic or prosthetic arms that are easier for users to control.
“In recent years, with the development of robotic arms, brain science and information decoding technology, brain-controlled robotic arms have attained increasing achievements,” Zhiguo Luo, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “However, disadvantages like poor flexibility restrict their widespread application. We aim to promote the lightweight and practicality of brain-controlled robotic arms.”