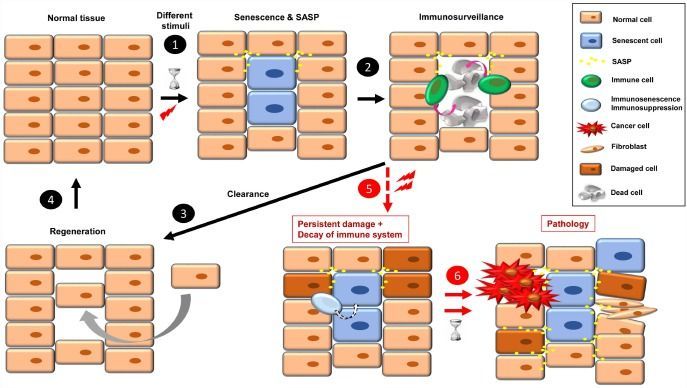
Cellular senescence is a hallmark of aging, whose onset is linked to a series of both cell and non-cell autonomous processes, leading to several consequences for the organism. To date, several senescence routes have been identified, which play a fundamental role in development, tumor suppression and aging, among other processes. The positive and/or negative effects of senescent cells are directly related to the time that they remain in the organism. Short-term (acute) senescent cells are associated with positive effects; once they have executed their actions, immune cells are recruited to remove them. In contrast, long-term (chronic) senescent cells are associated with disease; they secrete pro-inflammatory and pro-tumorigenic factors in a state known as senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). In recent years, cellular senescence has become the center of attention for the treatment of aging-related diseases. Current therapies are focused on elimination of senescent cell functions in three main ways: i) use of senolytics; ii) inhibition of SASP; and iii) improvement of immune system functions against senescent cells (immunosurveillance). In addition, some anti-cancer therapies are based on the induction of senescence in tumor cells. However, these senescent-like cancer cells must be subsequently cleared to avoid a chronic pro-tumorigenic state. Here is a summary of different scenarios, depending on the therapy used, with a discussion of the pros and cons of each scenario.
Keywords: cellular senescence, senolytics, senomorphics, immunosurveillance, anti-aging therapies.
Cellular senescence is a stress response mechanism induced by different types of insults such as telomere attrition, DNA damage, and oncogenic mutations, among others [1]. First described in cultured human diploid fibroblasts after successive rounds of division [2], its main hallmarks are irreversible growth arrest, alterations of cell size and morphology, increased lysosomal activity, expression of anti-proliferative proteins, resistance to apoptosis, activation of damage-sensing signaling routes. Another important characteristic is the regulated secretion of interleukins (ILs), inflammatory factors, chemokines, proteases and growth factors, termed the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) [3].