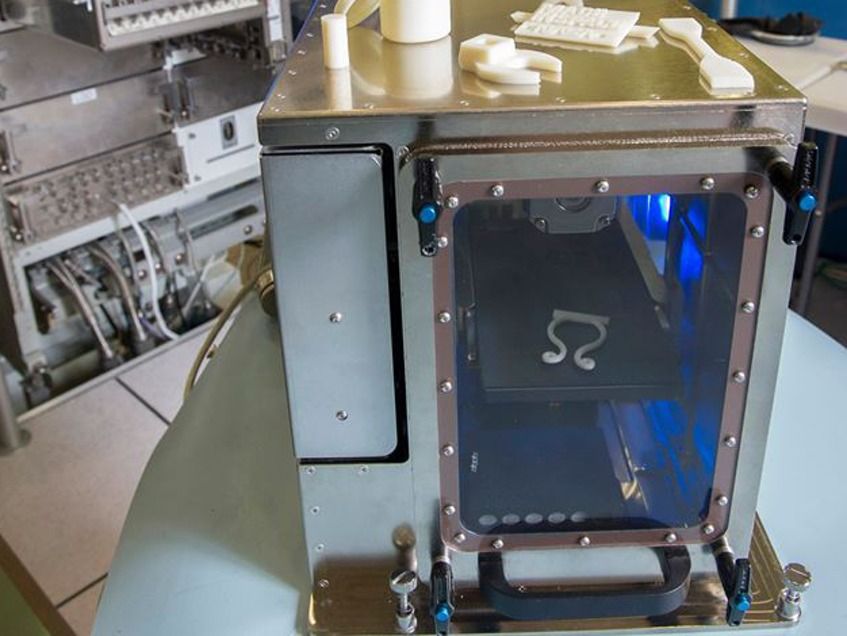
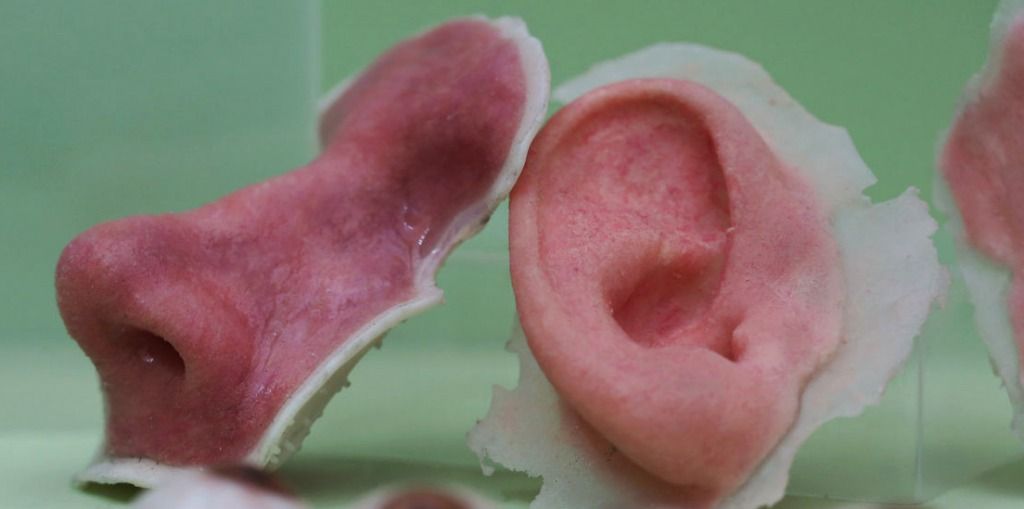
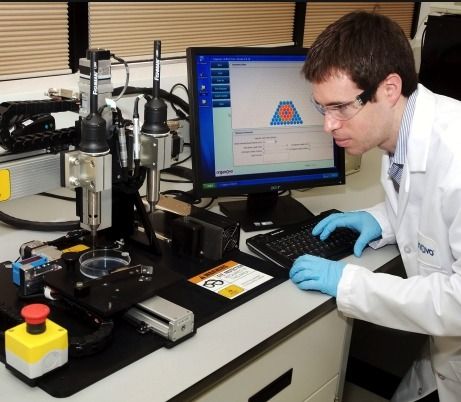
How 3D printing is changing the way we manufacture and produce is already a fact, step by step, in different areas, from aerospace to the medical areas.
How will this impact the established processes, the economy, the patient …
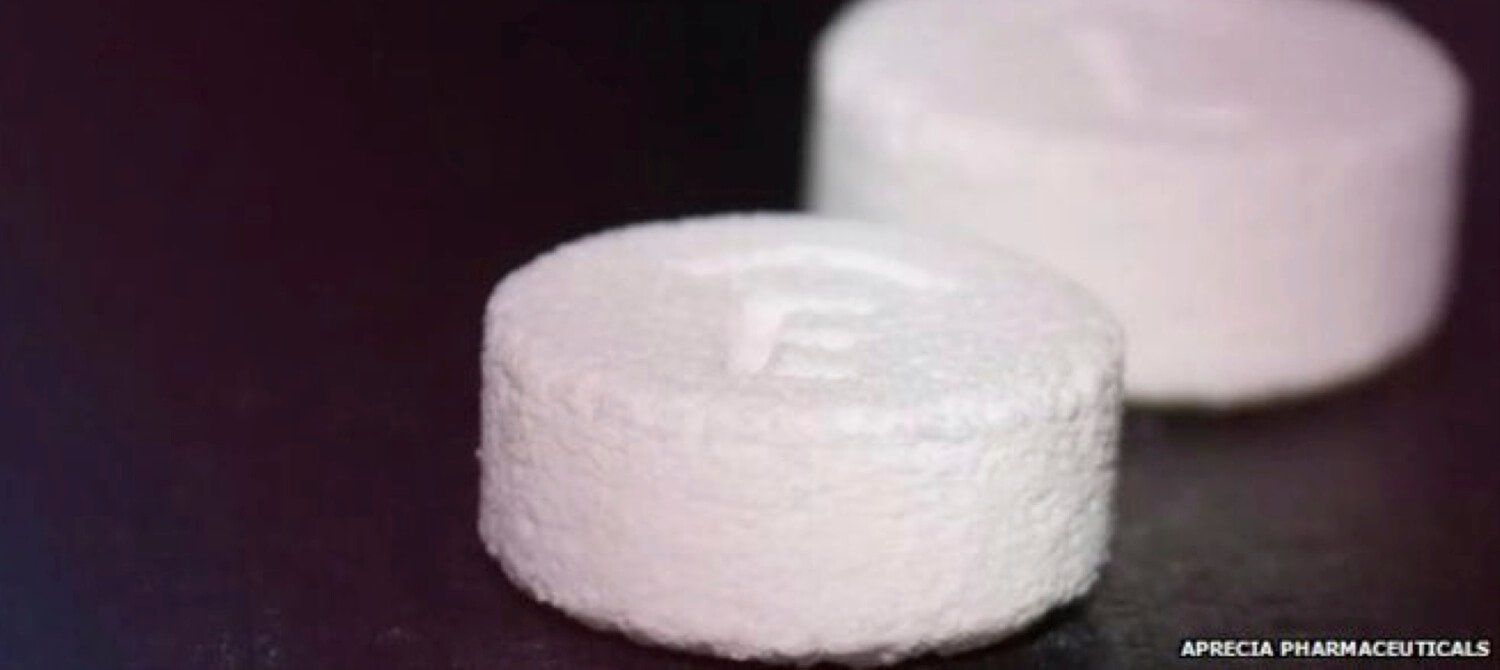
Is this the dawn of personalized medicine? patients will be able to print their own pills at home? Will 3D printing represent an enhancement to distribution processes?
Exciting but at the same time other questions are if following a cheap driver is really safe…
“Would the FDA be able to oversee personal pill printing? Should they? If an automated pill printer goes out of whack and misprints medication, would the blame fall on the machine’s manufacturers or the operators (i.e., the patients)? What if the machines were hacked? If people can reverse engineer patented drugs through 3D printing, how can those patents be protected? Will it be a detriment to drug development?
will people be able to hijack pill printers to manufacture illicit drugs?” This is the same situation we have now with RPAS/UAS (Remote Piloted Aircrafts/Unmanned Aircraft Systems) and cyberthreats ..
Read more at http://singularityhub.com/2015/08/14/first-3d-printed-drug-ushers-in-era-of-downloadable-medicine/