To achieve interstellar travel, the Kline Directive instructs us to be bold, to explore what others have not, to seek what others will not, to change what others dare not. To extend the boundaries of our knowledge, to advocate new methods, techniques and research, to sponsor change not status quo, on 5 fronts:
1. Legal Standing. 2. Safety Awareness. 3. Economic Viability. 4. Theoretical-Empirical Relationship. 5. Technological Feasibility.
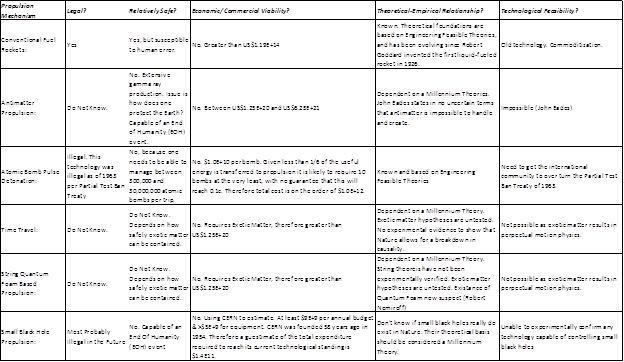
In this post I will explore Economic Viability. I have proposed the Interstellar Challenge Matrix (ICM) to guide us through the issues so that we can arrive at interstellar travel sooner, rather than later. Let us review the costs estimates of the various star drives just to reach the velocity of 0.1c, as detailed in previous blog posts:
Interstellar Challenge Matrix (Partial Matrix)
Note Atomic Bomb numbers were updated on 10/18/2012 after Robert Steinhaus commented that costs estimates “are excessively high and unrealistic”. I researched the topic and found Project Orion details the costs, of $2.6E12 to $25.6E12, which are worse than my estimates.
These costs are humongous. The Everly Brothers said it the best.
Let’s step back and ask ourselves the question, is this the tool kit we have to achieve interstellar travel? Are we serious? Is this why DARPA — the organization that funds many strange projects — said it will take more than a 100 years? Are we not interested in doing something sooner? What happened to the spirit of the Kline Directive?
From a space exploration perspective economic viability is a strange criterion. It is not physics, neither is it engineering, and until recently, the space exploration community has been government funded to the point where realistic cost accountability is nonexistent.
Don’t get me wrong. This is not about agreeing to a payment scheme and providing the services as contracted. Government contractors have learned to do that very well. It is about standing on your own two feet, on a purely technology driven commercial basis. This is not an accounting problem, and accountants and CFOs cannot solve this. They would have no idea where to start. This is a physics and engineering problem that shows up as an economic viability problem that only physicists and engineers can solve.
The physics, materials, technology and manufacturing capability has evolved so much that companies like Planetary Resources, SpaceX, Orbital Sciences Corp, Virgin Galactic, and the Ad Astra Rocket Company are changing this economic viability equation. This is the spirit of the Kline Directive, to seek out what others would not.
So I ask the question, whom among you physicist and engineers would like to be engaged is this type of endeavor?
But first, let us learn a lesson from history to figure out what it takes. Take for example DARPA funding of the Gallium Arsenide. “One of DARPA’s lesser known accomplishments, semiconductor gallium arsenide received a push from a $600-million computer research program in the mid-1980s. Although more costly than silicon, the material has become central to wireless communications chips in everything from cellphones to satellites, thanks to its high electron mobility, which lets it work at higher frequencies.”
In the 1990s Gallium Arsenide semiconductors were so expensive that “silicon wafers could be considered free”. But before you jump in and say that is where current interstellar propulsion theories are, you need to note one more important factor.
The Gallium Arsenide technology had a parallel commercially proven technology in place, the silicon semiconductor technology. None of our interstellar propulsion technology ideas have anything comparable to a commercially successful parallel technology. (I forgot conventional rockets. Really?) A guesstimate, in today’s dollars, of what it would cost to develop interstellar travel propulsion given that we already had a parallel commercially proven technology, would be $1 billion, and DARPA would be the first in line to attempt this.
Given our theoretical physics and our current technological feasibility, this cost analysis would suggest that we require about 10 major technological innovations, each building on the other, before interstellar travel becomes feasible.
That is a very big step. Almost like reaching out to eternity. No wonder Prof Adam Franks in his July 24, 2012 New York Times Op-Ed, Alone in the Void, wrote “Short of a scientific miracle of the kind that has never occurred, our future history for millenniums will be played out on Earth”.
Therefore, we need to communicate to the theoretical physics community that they need get off the Theory of Everything locomotive and refocus on propulsion physics. In a later blog posting I will complete the Interstellar Challenge Matrix (ICM). Please use it to converse with your physicist colleagues and friends about the need to focus on propulsion physics.
In the spirit of the Kline Directive — bold, explore, seek & change — can we identify the 10 major technological innovations? Wouldn’t that keep you awake at night at the possibility of new unthinkable inventions that will take man where no man has gone before?
PS. I was going to name the Interstellar Challenge Matrix (ICM), the Feasibility Matrix for Interstellar Travel (FMIT), then I realized that it would not catch on at MIT, and decided to stay with ICM.
Previous post in the Kline Directive series.
Next post in the Kline Directive series.
—————————————————————————————————
Benjamin T Solomon is the author & principal investigator of the 12-year study into the theoretical & technological feasibility of gravitation modification, titled An Introduction to Gravity Modification, to achieve interstellar travel in our lifetimes. For more information visit iSETI LLC, Interstellar Space Exploration Technology Initiative.
Solomon is inviting all serious participants to his LinkedIn Group Interstellar Travel & Gravity Modification.