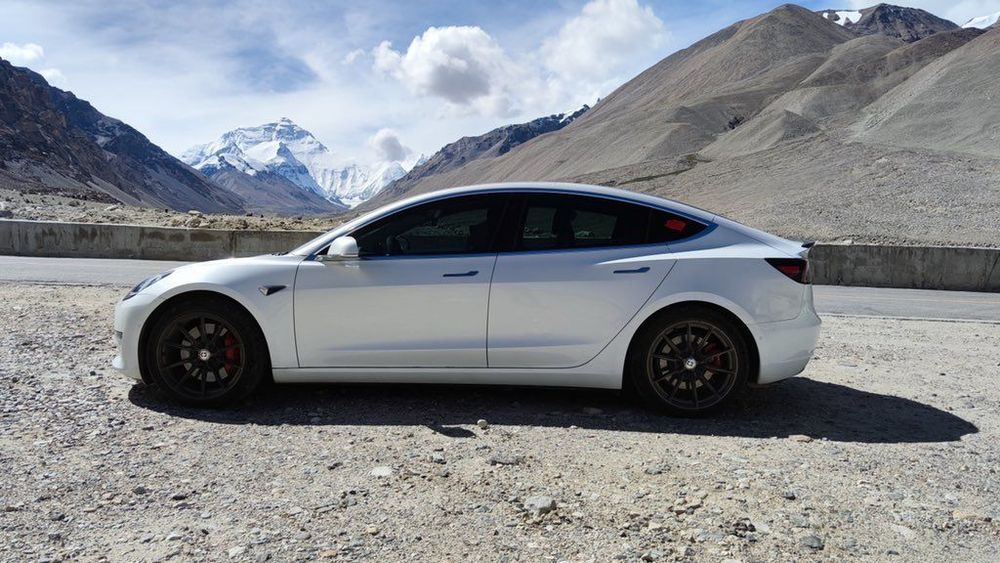
A Tesla Model 3 from China has recently gone where no other Model 3 has gone before. In an epic 5,500 km (3,400-mile) road trip, a white Tesla Model 3 Dual Motor AWD started a long journey from Shenzhen all the way to the base camp of Mt. Everest. What’s more remarkable was that over the long trip, the Tesla owner remarked that he experienced no range anxiety at all, despite his extremely remote destination.
Driving to the base camp of Mt. Everest is no joke, and it is hardly something that is considered relaxing and convenient. Needless to say, any trip that involves one of the highest and most dangerous mountains in the world is not something that is taken lightly. Some who drive to Everest’s base camp even utilize support vehicles just to be on the safe side. The Model 3 owner, for his part, took on the journey alone.