Batteries with high energy densities could enable the creation of a wider range of electric vehicles, including flying vehicles that can transport humans in urban environments. Past studies predict that to support the operation of vehicles capable of take-off and landing, batteries require energy densities of approximately 400 Wh kg-1 at the cell level, which is approximately 30% higher than the energy density of most existing lithium-ion (Li-ion) cells.
In addition to powering flying vehicles, high-energy cells (i.e., single units within a battery that convert chemical into electrical energy) could increase the distance that electric cars can travel before they need to be charged again. They may also reduce overall fabrication costs for electric vehicles, as similar results could be achieved using fewer but better-performing cells.
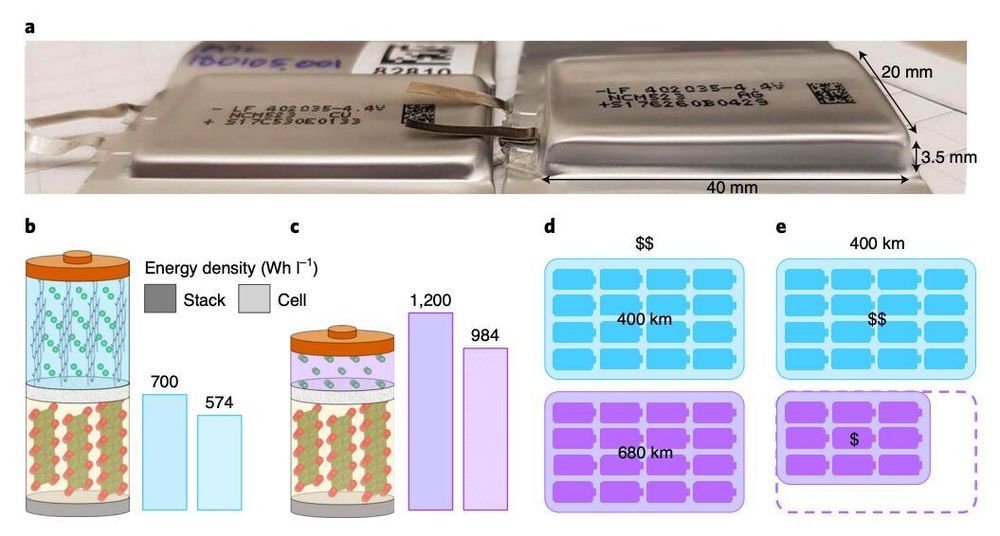
Anode-free lithium metal cells are particularly promising for creating batteries with higher energy densities. While they use the same cathode as Li-ion cells, these cells store energy via an electroplated lithium metal instead of a graphite host, and they can have energy densities that are 60% greater than those of Li-ion cells.