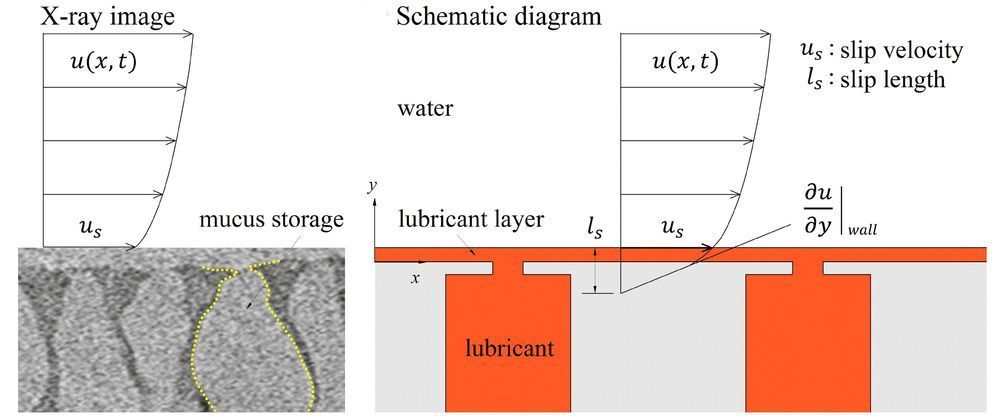
Long-distance cargo ships lose a significant amount of energy due to fluid friction. Looking to the drag reduction mechanisms employed by aquatic life can provide inspiration on how to improve efficiency.
Fish and seaweed secrete a layer of mucus to create a slippery surface, reducing their friction as they travel through water. A potential way to mimic this is by creating lubricant-infused surfaces covered with cavities. As the cavities are continuously filled with the lubricant, a layer is formed over the surface.
Though this method has previously been shown to work, reducing drag by up to 18%, the underlying physics is not fully understood. In the journal Physics of Fluids, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology and Pohang University of Science and Technology conducted simulations of this process to help explain the effects.