Smoothing out a material used in desalination filters could help combat worldwide water shortages.
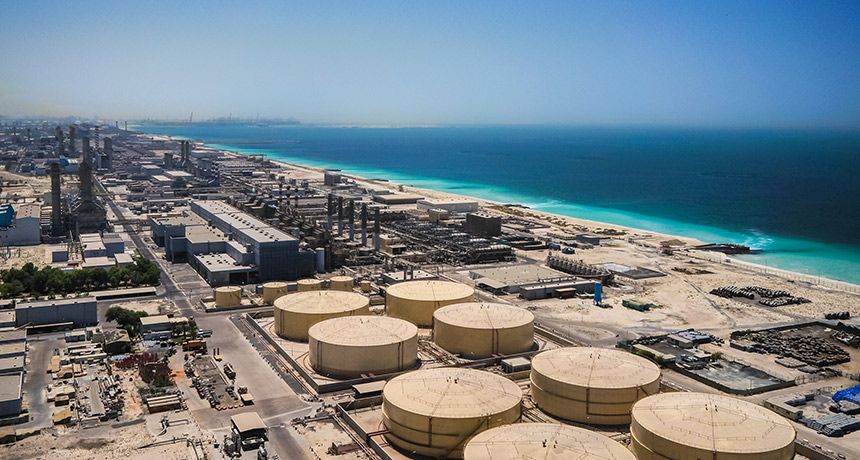


Smoothing out a material used in desalination filters could help combat worldwide water shortages.
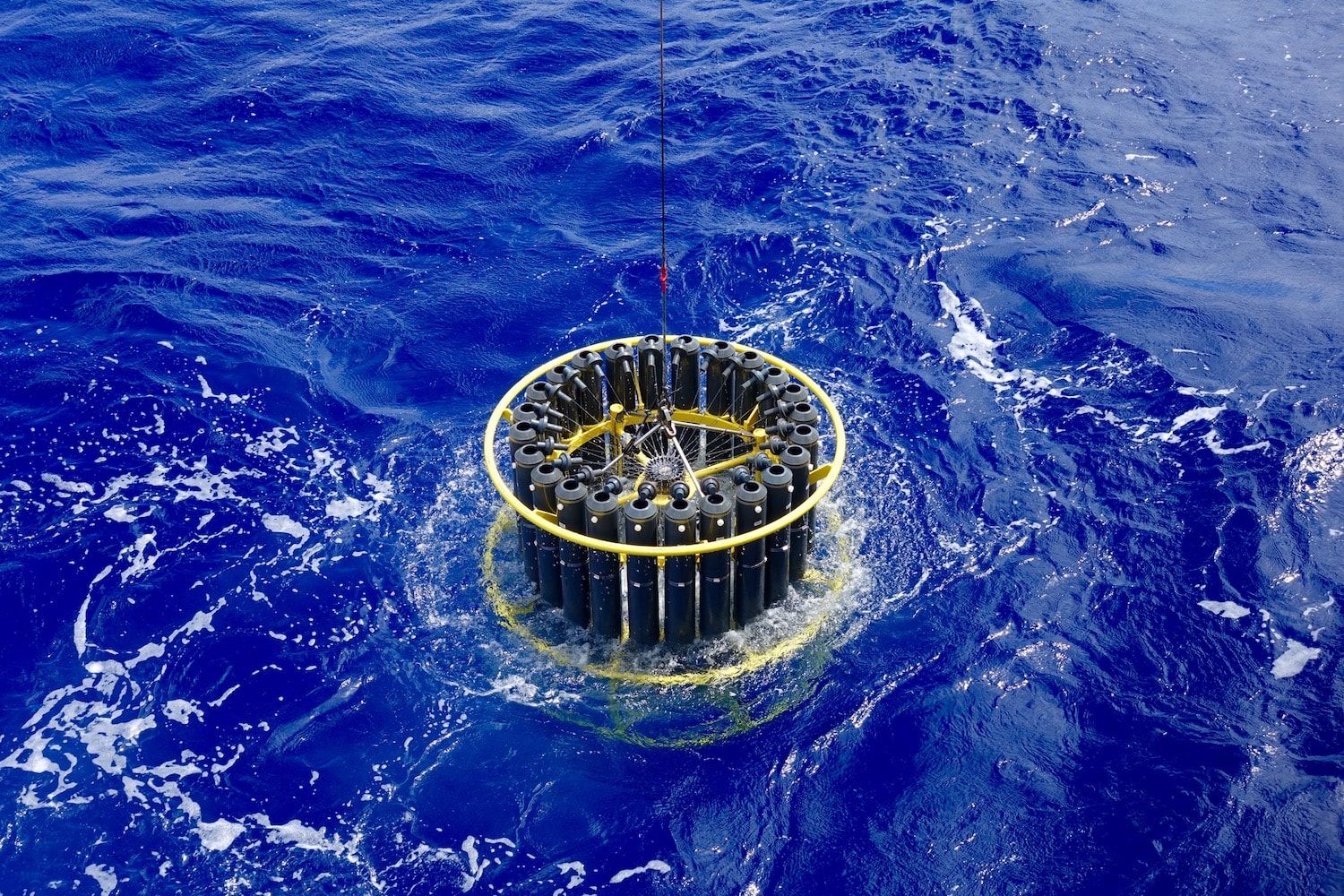

Half of the planet’s oxygen comes from tiny plants under the ocean’s surface—phytoplankton.

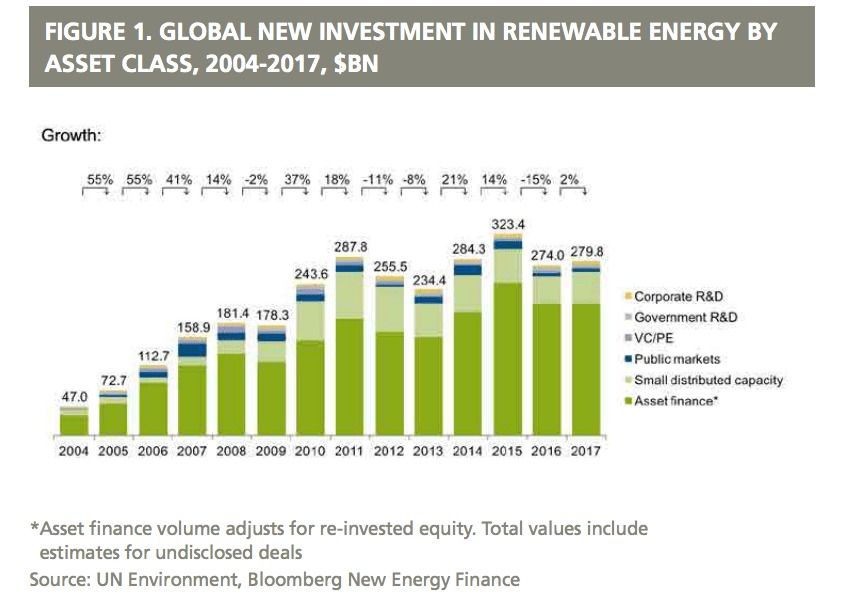
Global investment in renewable energy (Solar, Wind, Hydro and biofuel) edged up 2% in 2017 to $279.8 billion, taking cumulative investment since 2010 to $2.2 trillion. The level of global renewable power spending has been virtually flat for seven years. There has been an increase in overall installed renewable power each year because of the dropping prices. A 2% increase in spending has resulted in 10% increase in global installations from 2016 to 2017.
A record 157 gigawatts of renewable power capacity was commissioned in 2017, up from 143GW in 2016. This was more than the 70GW of net fossil fuel generating capacity added last year. However, the installed fossil fuel power generates more kilowatt hours because of the low capacity factors of solar and wind power.

It may seem off-putting to some, but human waste is full of nutrients that can be recycled into valuable products that could promote agricultural sustainability and better economic independence for some developing countries.
Cities produce and must manage huge quantities of wastewater. Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have developed a model to clarify what parts of the world may benefit most from re-circulation of human-waste-derived nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus from cities and back into farm fields. They report their findings in the journal Nature Sustainability.
“We grow our crops in the field, apply nutrient-rich fertilizers, eat the crops, excrete all of the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and then those nutrients end up at the wastewater treatment plant,” said Jeremy Guest, a civil and environmental engineering professor and study co-author. “It is a very linear, one-directional flow of resources. Engineering a more circular nutrient cycle would create opportunities that could benefit the environment, economy and agriculture.”
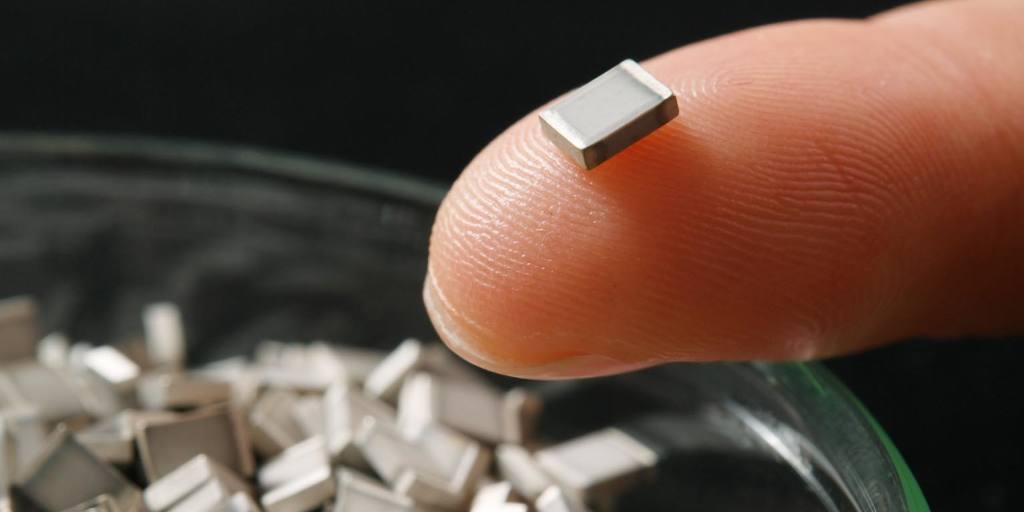

TOKYO — Imagine electric cars that can travel 700km to 800km on a single charge, twice as far as they do today. Imagine batteries that are smaller, safer and pack more punch than the lithium-ion cells that power our gadgets now.
Such is the promise of solid-state batteries. Capable of holding more electricity and recharging more quickly than their lithium-ion counterparts, they could do to lithium-ion power cells what transistors did to vacuum tubes: render them obsolete.
As their name implies, solid-state batteries use solid rather than liquid materials as an electrolyte. That is the stuff through which ions pass as they move between the poles of a battery as it is charged and discharged. Because they do not leak or give off flammable vapor, as lithium-ion batteries are prone to, solid-state batteries are safer. They are also more energy-dense and thus more compact.
Energy use in industrial buildings continues to skyrocket, contributing to the negative impact on global warming and Earth’s natural resources. An EU initiative introduced a disruptive system that’s able to reduce electricity consumption in the industrial sector.
Using energy efficiently helps industry save money, conserve resources and tackle climate change. ISO 50001 supports companies in all sectors to use energy more efficiently through the development of an energy management system. It calls on the industrial sector to integrate energy management into their overall efforts for improving quality and environmental management. Companies can perform several actions to successfully implement this new international standard, including creating policies for more efficient energy use, identifying significant areas of energy consumption and targeting reductions.
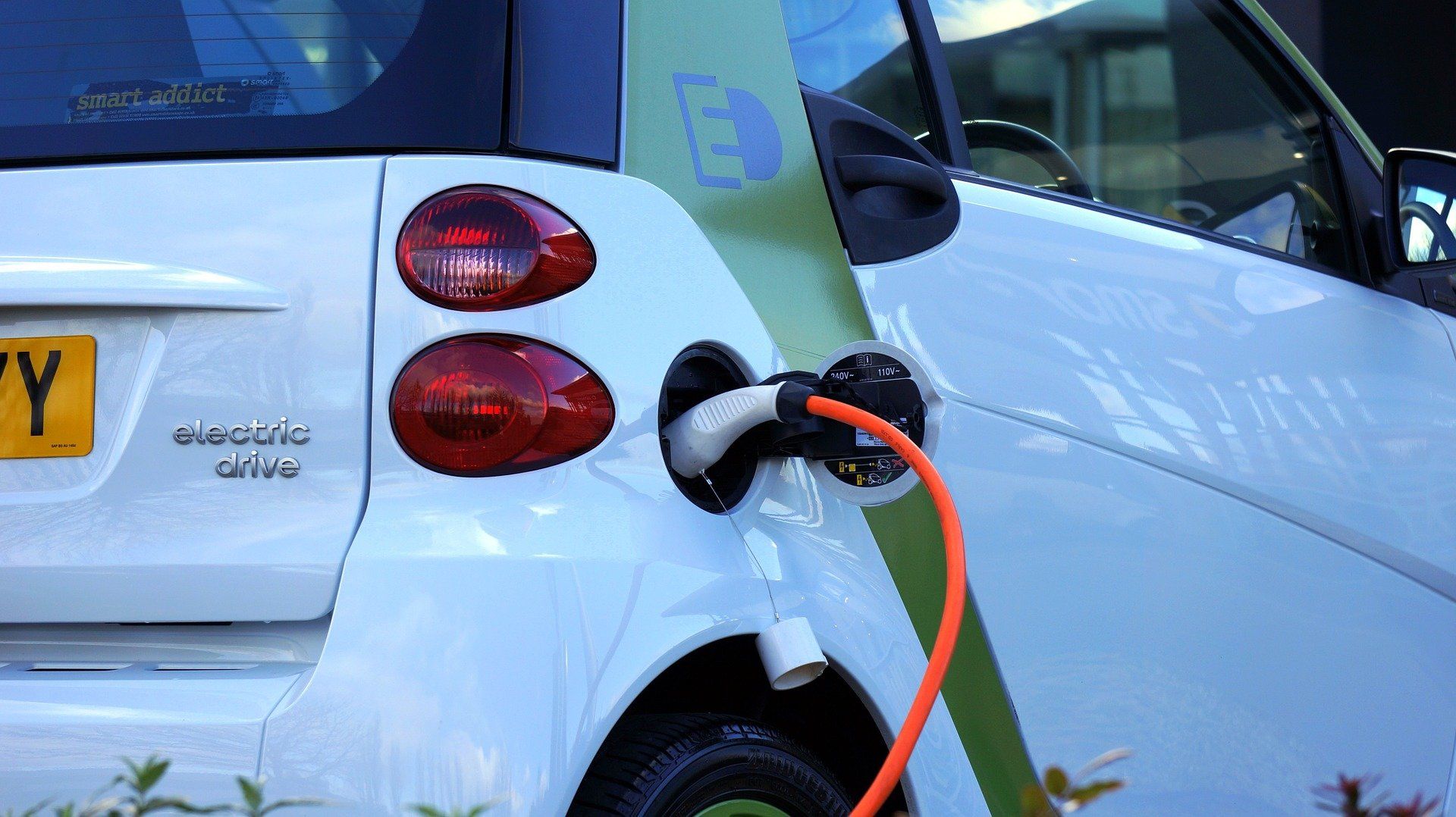

A new type of energy storage system could revolutionise energy storage and drop the charging time of electric cars from hours to seconds.
In a new paper published today in the journal Nature Chemistry, chemists from the University of Glasgow discuss how they developed a flow battery system using a nano-molecule that can store electric power or hydrogen gas giving a new type of hybrid energy storage system that can be used as a flow battery or for hydrogen storage.
Their ‘hybrid-electric-hydrogen’ flow battery, based upon the design of a nanoscale battery molecule can store energy, releasing the power on demand as electric power or hydrogen gas that can be used a fuel. When a concentrated liquid containing the nano-molecules is made, the amount of energy it can store increases by almost 10 times. The energy can be released as either electricity or hydrogen gas meaning that the system could be used flexibly in situations that might need either a fuel or electric power.
The aquaculture sector is growing, with fish farming being a key way to ensure Europe gets the quality food it needs without exploiting marine resources further. One key problem the industry faces is how to get the immature fish though their first few months – one EU project may be about to smooth the way.
Aquaculture is a growing market within the EU, bringing employment and providing a sustainable source of fish at a time when our marine life is under pressure. The main bottle-neck for the production of marine fish is the juvenile phase, especially during the time in which live diets are used. Even the established species, sea bream and sea bass, have a very low survival rate with an average of 25 percent. For new species in aquaculture, such as amberjack and tuna, the mortality is even higher.
The natural first feed for most fish larvae is crustacean nauplii, the offspring of many types of crustacean zooplankton. Fish larvae is evolutionary adapted to such a diet, and it is believed that this type of prey fulfils the fish larva’s nutritional requirements.

The German engineering company Geltz Umwelt-Technologie has successfully developed an advanced recycling plant for obsolete or ageing solar panels.
As sales of solar power increase, there is a looming problem that is quite often overlooked: disposing waste from outdated or destroyed solar panels. A surge in solar panel disposal is expected to take place in the early 2030s, given the design life of solar energy systems installed around the millennium.
To address this problem before this big disposal wave, the EU has funded the ELSi project. With strong competencies in plant manufacturing and wastewater treatment including recycling, the Geltz Umwelt-Technologie firm has built a test and treatment facility at a large disposal firm to retrieve reusable materials from solar modules.

Imagine something similar to the Great Depression of 1929 hitting the world, but this time it never ends.
Economic modelling suggests this is the reality facing us if we continue emitting greenhouse gases and allowing temperatures to rise unabated.
Economists have largely underestimated the global economic damages from climate change, partly as a result of averaging these effects across countries and regions, but also because the likely behaviour of producers and consumers in a climate change future isn’t usually taken into consideration in climate modelling.