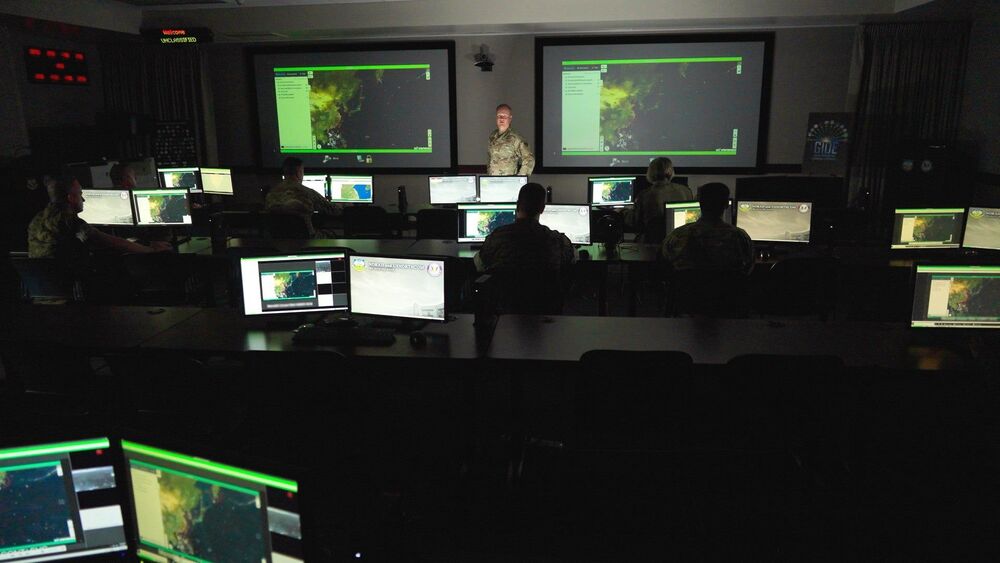
The US military’s AI experiments are growing particularly ambitious. The Drive reports that US Northern Command recently completed a string of tests for Global Information Dominance Experiments (GIDE), a combination of AI, cloud computing and sensors that could give the Pentagon the ability to predict events “days in advance,” according to Command leader General Glen VanHerck. It’s not as mystical as it sounds, but it could lead to a major change in military and government operations.
The machine learning-based system observes changes in raw, real-time data that hint at possible trouble. If satellite imagery shows signs that a rival nation’s submarine is preparing to leave port, for instance, the AI could flag that mobilization knowing the vessel will likely leave soon. Military analysts can take hours or even days to comb through this information — GIDE technology could send an alert within “seconds,” VanHerck said.
The most recent dry run, GIDE 3, was the most expansive yet. It saw all 11 US commands and the broader Defense Department use a mix of military and civilian sensors to address scenarios where “contested logistics” (such as communications in the Panama Canal) might pose a problem. The technology involved wasn’t strictly new, the General said, but the military “stitched everything together.”