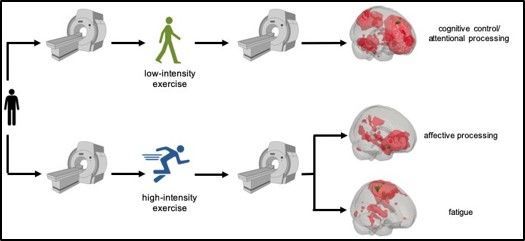
Walking and running may affect the functional connectivity of brain networks in different ways, according to a new study.


Why could the mongoose Rikki Tikki Tavi attack deadly snakes with impunity in Kipling’s “Jungle Book?” Because he has a uniquely mutated receptor for a brain neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The toxins in many snake venoms, including that of cobras, bind to the acetylcholine receptors of their victims, blocking nerve-muscle communications. Molecular biologist Sara Fuchs and her colleagues found that the acetylcholine receptor in mongooses—like that in the snakes themselves—is slightly mutated so that the venom simply bounces off the muscle cells, causing them no harm.

Braintree founder Bryan Johnson, MBA’07, invests in bold ventures on the next frontier.
Bryan Johnson is determined to explore the depths of your mind and help save humanity from its direst threats.
“The biggest revolutions that have happened over the past couple of decades have largely been done on silicon—the transistors we build, the computers we have, the internet, our smartphones,” said Johnson, MBA’07. “The next great revolutions will be evolving our cognition and predictably engineering atoms, molecules, organisms and complex systems.”

Today (11am PST / 2pm EST / 7pm GMT) — Carboncopies JOURNAL CLUB with Dr. Michael Cerullo presenting work by Hilary Putnam: “Minds and Machines”. Continuing our theme on consciousness and personal identity. The Journal Club is open, you are very welcome to join at http://call.carboncopies.org/
The livestream (see our Youtube channel) will also be recorded for later viewing.


Have always been fascinated with architecture, design, space, travel, and technology.
Big windows, fresh fruit and regular phone calls home help manage the mental health of astronauts on the International Space Station. But missions to Mars on beyond will require a whole new approach to how spaceships are designed.
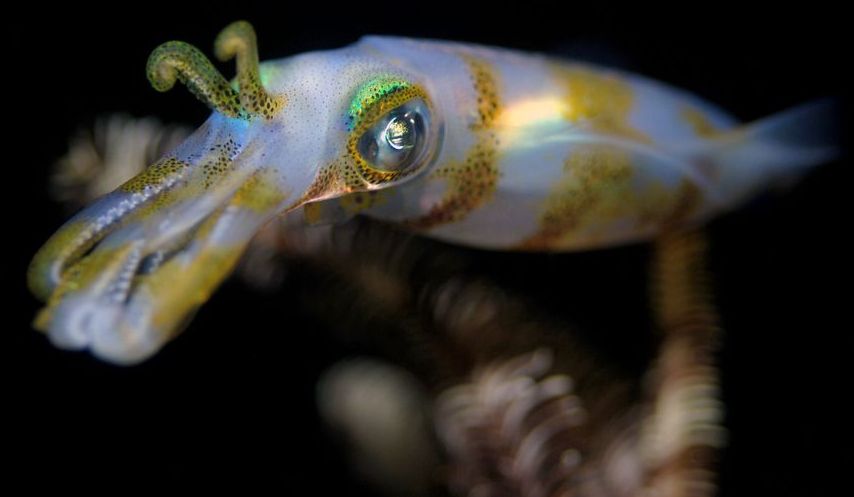


New research led by Wen-Sung Chung and Justin Marshall of the University of Queensland is shedding new light on the complexity of squid brains. Using MRI scanning to examine the brain of the of the reef squid Sepioteuthis lessoniana, the researchers have produced a new map of neural connections that improves our understanding of their behavior.
The cephalopods are widely recognized as the most intelligent of mollusks, but how do they rate when they are competing against something other than clams? Cephalopods show all sorts of complex behavior, like being able to recognize patterns, solve problems, communicate through signals, and camouflage themselves in different textures and colors, despite being colorblind.
“We can see that a lot of neural circuits are dedicated to camouflage and visual communication,” says Chung. “Giving the squid a unique ability to evade predators, hunt and conspecific communicate with dynamic color change.”