😳!
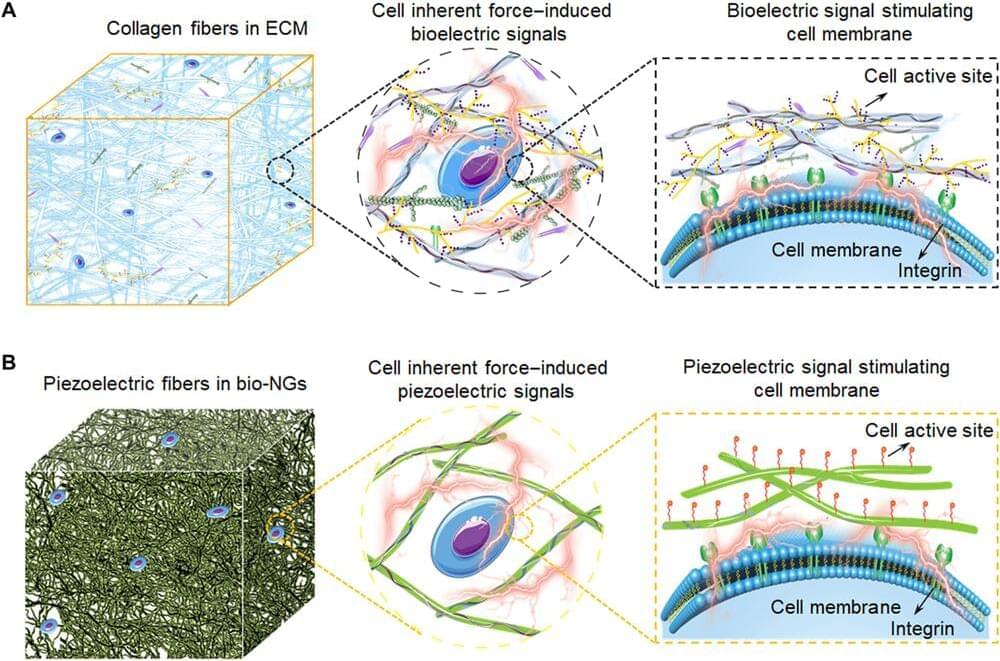
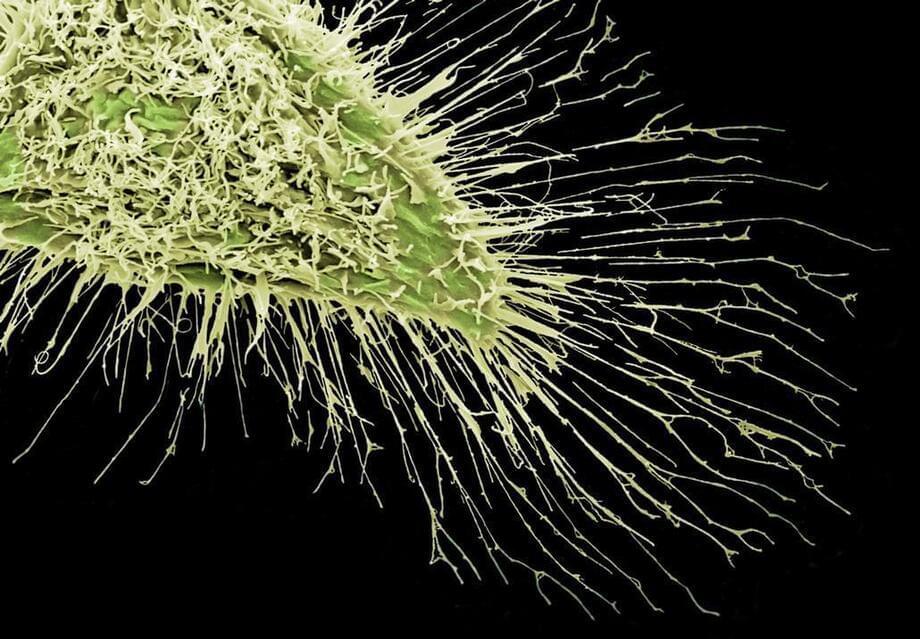
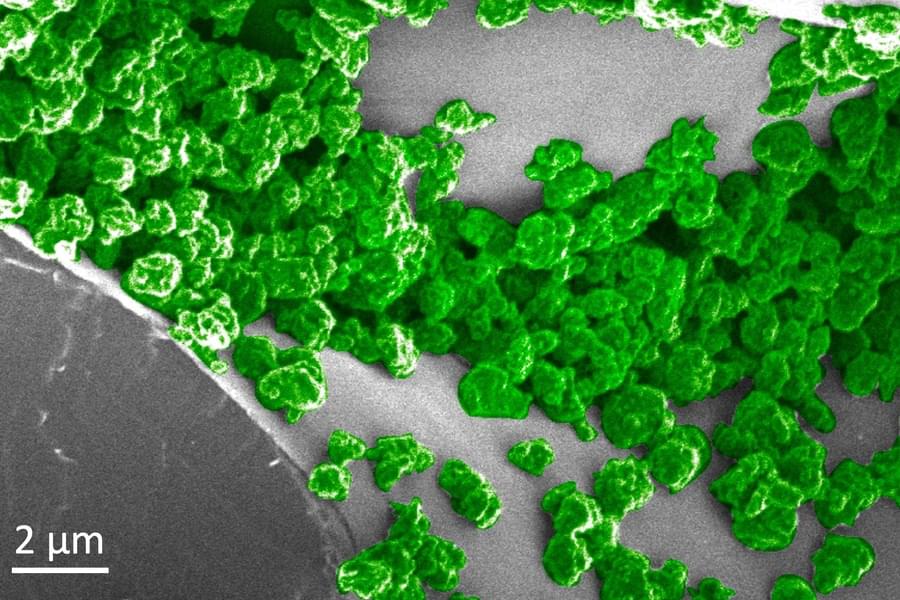
The extracellular matrix (ECM) including three-dimensional (3D) network and bioelectricity can profoundly influence cell development, migration, and functional expression. In a new report now published on Science Advances, Tong Li and a research team in chemistry, nanotechnology, bioelectronics and advanced materials in China, developed an electromechanical coupling bio-nanogenerator abbreviated bio-NG inspired by biophysical cues of the extracellular matrix. The device contained highly discrete piezoelectric fibers to generate piezo potential of up to millivolts to provide in situ electrical stimulation for living cells.