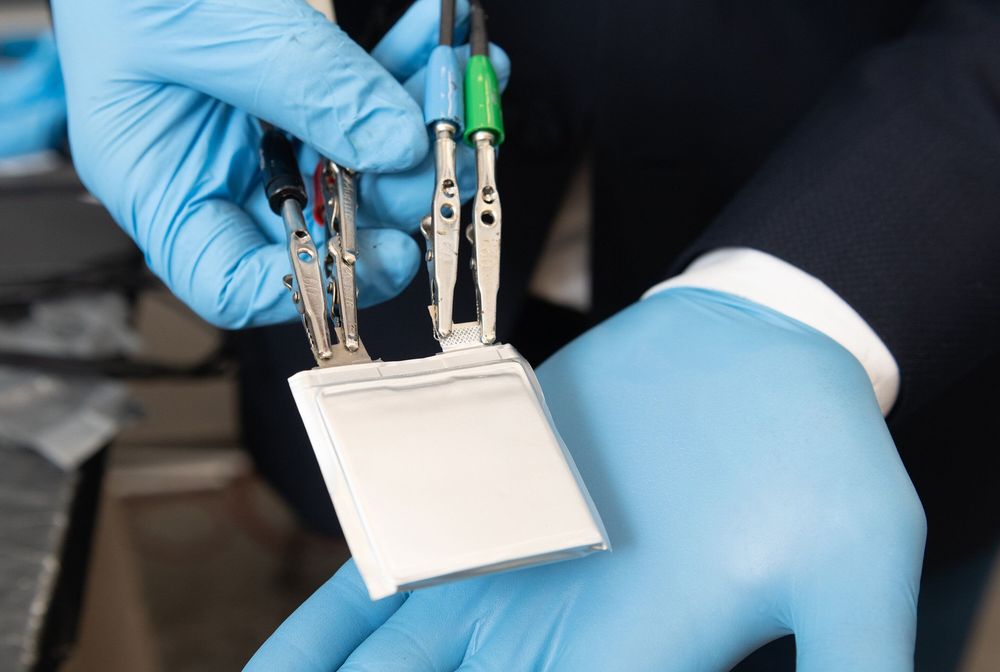
The growing popularity of lithium-ion batteries in recent years has put a strain on the world’s supply of cobalt and nickel—two metals integral to current battery designs—and sent prices surging.
In a bid to develop alternative designs for lithium-based batteries with less reliance on those scarce metals, researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have developed a promising new cathode and electrolyte system that replaces expensive metals and traditional liquid electrolyte with lower cost transition metal fluorides and a solid polymer electrolyte.
“Electrodes made from transition metal fluorides have long shown stability problems and rapid failure, leading to significant skepticism about their ability to be used in next generation batteries,” said Gleb Yushin, a professor in Georgia Tech’s School of Materials Science and Engineering. “But we’ve shown that when used with a solid polymer electrolyte, the metal fluorides show remarkable stability—even at higher temperatures—which could eventually lead to safer, lighter and cheaper lithium-ion batteries.”