An aging/longevity/junk dna link.
~~~
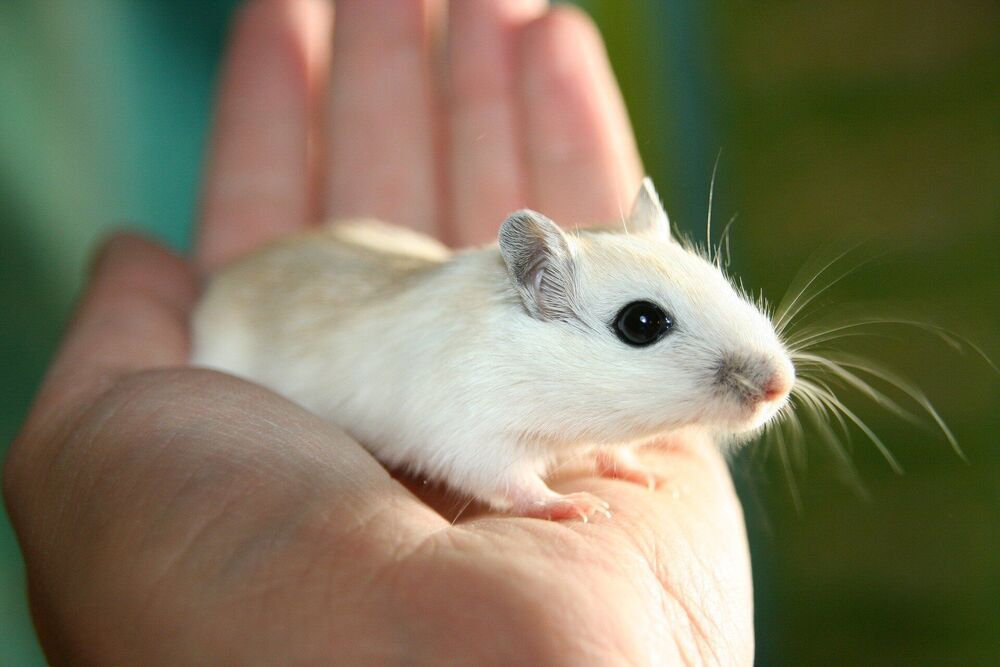
The human body is essentially made up of trillions of living cells. It ages as its cells age, which happens when those cells eventually stop replicating and dividing. Scientists have long known that genes influence how cells age and how long humans live, but how that works exactly remains unclear. Findings from a new study led by researchers at Washington State University have solved a small piece of that puzzle, bringing scientists one step closer to solving the mystery of aging.
A research team headed by Jiyue Zhu, a professor in the College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, recently identified a DNA region known as VNTR2-1 that appears to drive the activity of the telomerase gene, which has been shown to prevent aging in certain types of cells. The study was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The telomerase gene controls the activity of the telomerase enzyme, which helps produce telomeres, the caps at the end of each strand of DNA that protect the chromosomes within our cells. In normal cells, the length of telomeres gets a little bit shorter every time cells duplicate their DNA before they divide. When telomeres get too short, cells can no longer reproduce, causing them to age and die. However, in certain cell types—including reproductive cells and cancer cells —the activity of the telomerase gene ensures that telomeres are reset to the same length when DNA is copied. This is essentially what restarts the aging clock in new offspring but is also the reason why cancer cells can continue to multiply and form tumors.