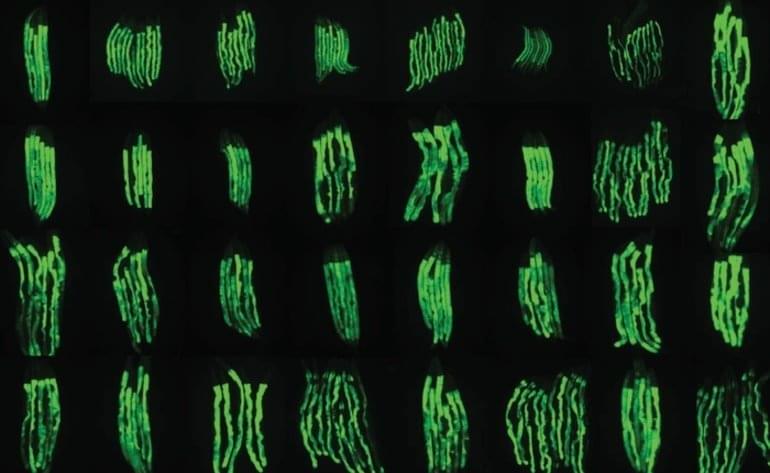
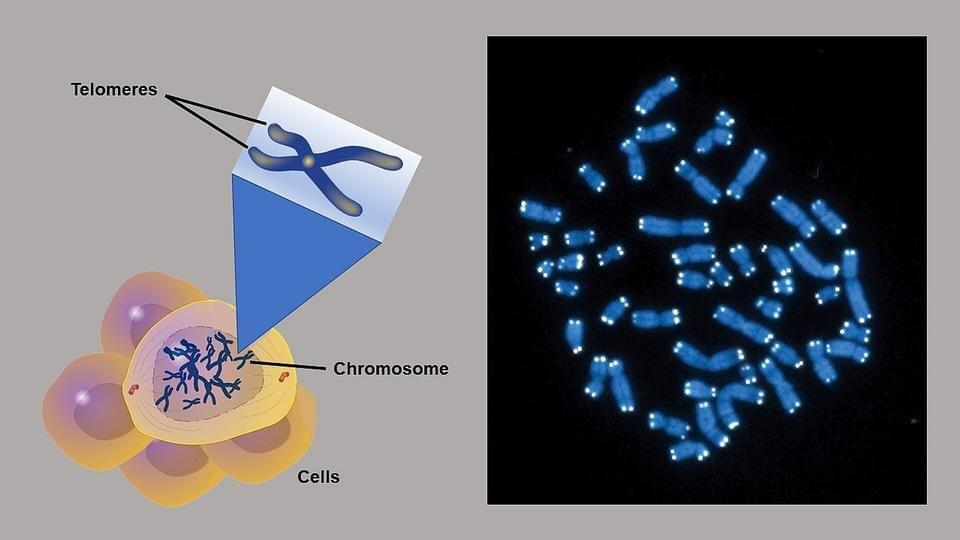
In this video Dr. Katcher reveals his thought on the future of aging if E5 is fulfils on its promise.
Dr Katcher’s book is on Amazon.
The Illusion of Knowledge: The paradigm shift in aging research that shows the way to human rejuvenation.
https://amzn.to/3jJ5deD
Dr Harold Katcher is one of the discovers of the human breast cancer gene BRCA1, and has thousands of citations in the scientific literature with publications ranging from protein structure to bacteriology, bioinformatics and biochemistry. He was the Academic Director for Natural Sciences of the University of Maryland Global Campus and is now the Chief Scientific Officer at Yuvan Research Inc, a company working on the development of rejuvenation treatments.
Dr Katcher’s new book, the Illusion of Knowledge, the paradigm shift in aging research that shows the way to human rejuvenation will be launched on 4th September 2021 and is already available in electronic form. The book launch will take place at The Book Passage in the Ferry Building in San Francisco at 3:00 pm Pacific Time.
************************************************************
Health claims Disclosure: Information provided on this video is not a substitute for direct, individual medical treatment or advice. Please consult with your doctor first. Products or services mentioned in this video are not a recommendation.
Audio Copyright Disclaimer:
Please note that we have full authorization to the music that we used in our videos as they were created using the service WeVideo which provides the rights to the music. The rights are detailed in the terms of use that can be reviewed here https://www.wevideo.com/terms-of-use and any following inquiries should be addressed to [email protected].