Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Papers referenced in the video:
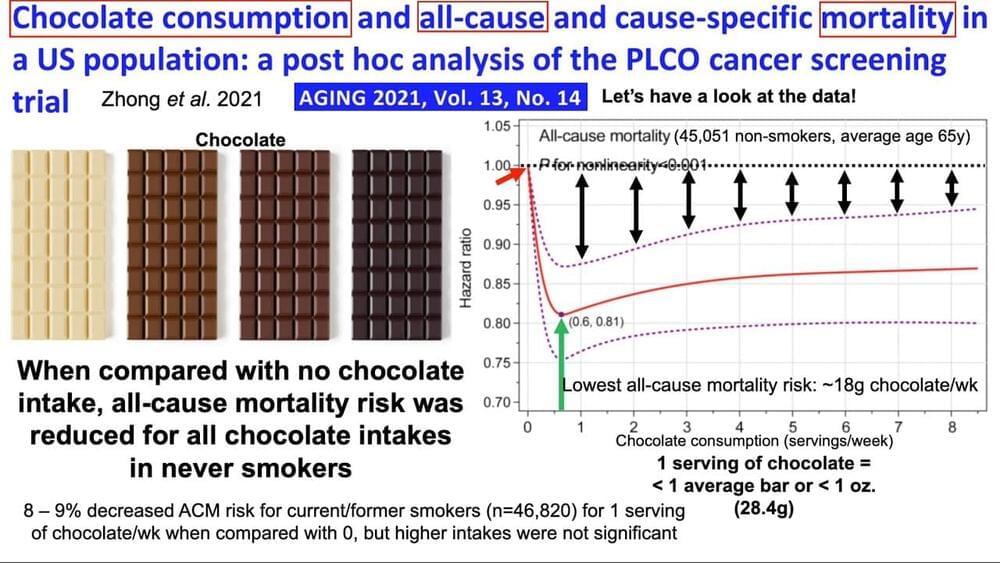
Chocolate consumption and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in a US population: a post hoc analysis of the PLCO cancer screening trial.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34329196/
Short-term administration of dark chocolate is followed by a significant increase in insulin sensitivity and a decrease in blood pressure in healthy persons.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15755830/
Other RCTs for the effect of chocolate on health:
Sub-Chronic Consumption of Dark Chocolate Enhances Cognitive Function and Releases Nerve Growth Factors: A Parallel-Group Randomized Trial.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31744119/
Habitual cocoa intake reduces arterial stiffness in postmenopausal women regardless of intake frequency: a randomized parallel-group study.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27881914/
High Flavonoid Cocoa Supplement Ameliorates Plasma Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Levels While Improving Mobility and Quality of Life in Older Subjects: A DoubleBlind Randomized Clinical Trial.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31056655/
Dietary epicatechin improves survival and delays skeletal muscle degeneration in aged mice.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30096038/