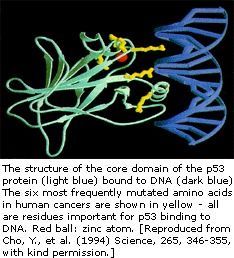
The p53 gene like the Rb gene, is a tumor suppressor gene, i.e., its activity stops the formation of tumors. If a person inherits only one functional copy of the p53 gene from their parents, they are predisposed to cancer and usually develop several independent tumors in a variety of tissues in early adulthood. This condition is rare, and is known as Li-Fraumeni syndrome. However, mutations in p53 are found in most tumor types, and so contribute to the complex network of molecular events leading to tumor formation.
The p53 gene has been mapped to chromosome 17. In the cell, p53 protein binds DNA, which in turn stimulates another gene to produce a protein called p21 that interacts with a cell division-stimulating protein (cdk2). When p21 is complexed with cdk2 the cell cannot pass through to the next stage of cell division. Mutant p53 can no longer bind DNA in an effective way, and as a consequence the p21 protein is not made available to act as the ‘stop signal’ for cell division. Thus cells divide uncontrollably, and form tumors.
Help with unraveling the molecular mechanisms of cancerous growth has come from the use of mice as models for human cancer, in which powerful ‘gene knockout’ techniques can be used. The amount of information that exists on all aspects of p53 normal function and mutant expression in human cancers is now vast, reflecting its key role in the pathogenesis of human cancers. It is clear that p53 is just one component of a network of events that culminate in tumor formation.