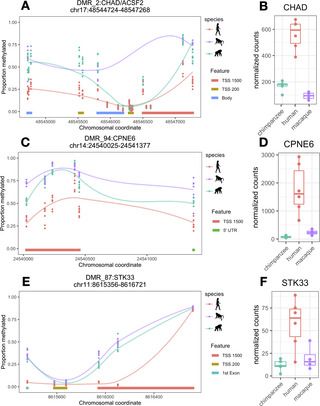
Humans are distinguished from other species by several aspects of cognition. While much comparative evolutionary neuroscience has focused on the neocortex, increasing recognition of the cerebellum’s role in cognition and motor processing has inspired considerable new research. Comparative molecular studies, however, generally continue to focus on the neocortex. We sought to characterize potential genetic regulatory traits distinguishing the human cerebellum by undertaking genome-wide epigenetic profiling of the lateral cerebellum, and compared this to the prefrontal cortex of humans, chimpanzees, and rhesus macaque monkeys. We found that humans showed greater differential CpG methylation–an epigenetic modification of DNA that can reflect past or present gene expression–in the cerebellum than the prefrontal cortex, highlighting the importance of this structure in human brain evolution. Humans also specifically show methylation differences at genes involved in neurodevelopment, neuroinflammation, synaptic plasticity, and lipid metabolism. These differences are relevant for understanding processes specific to humans, such as extensive plasticity, as well as pronounced and prevalent neurodegenerative conditions associated with aging.
Citation: Guevara EE, Hopkins WD, Hof PR, Ely JJ, Bradley BJ, Sherwood CC (2021) Comparative analysis reveals distinctive epigenetic features of the human cerebellum. PLoS Genet 17: e1009506. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.
Editor: Takashi Gojobori, National Institute of Genetics, JAPAN.