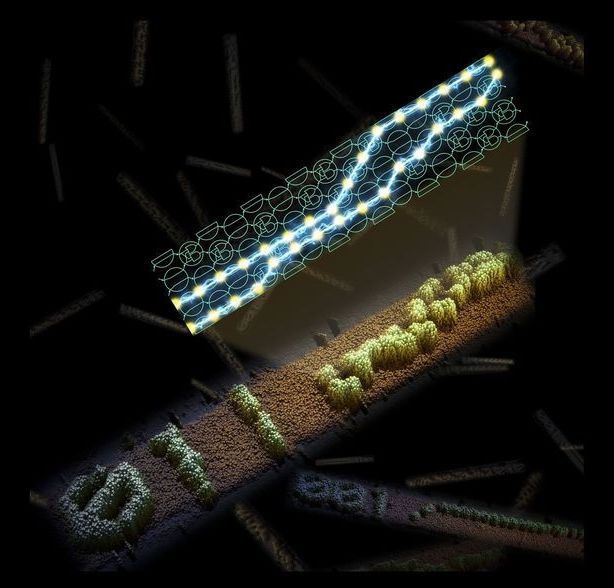
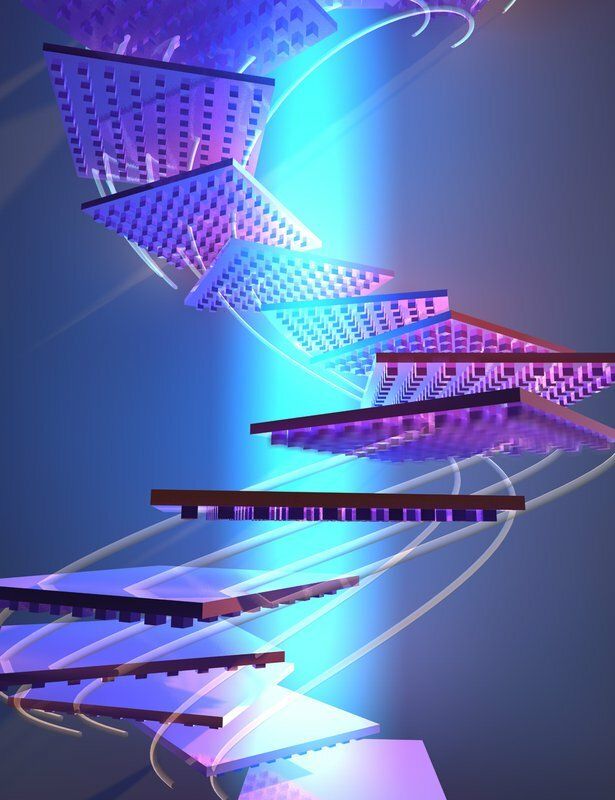
Electrochemical energy systems—processes by which electrical energy is converted to chemical energy—are at the heart of establishing more efficient generation and storage of intermittent energy from renewable sources in fuel cells and batteries.
The powerhouse substances known as catalysts, which are used to accelerate chemical reactions, are key players in these systems. The size and efficiency of fuel cells, for example, could greatly benefit from using high-performance catalysts.
Producing better catalysts is easier said than done, however. A catalyst’s usefulness is partially based on the amount and quality of its active sites, due to the sites’ specific geometry and electronic properties. Engineering these sites can be an arduous, inefficient process.