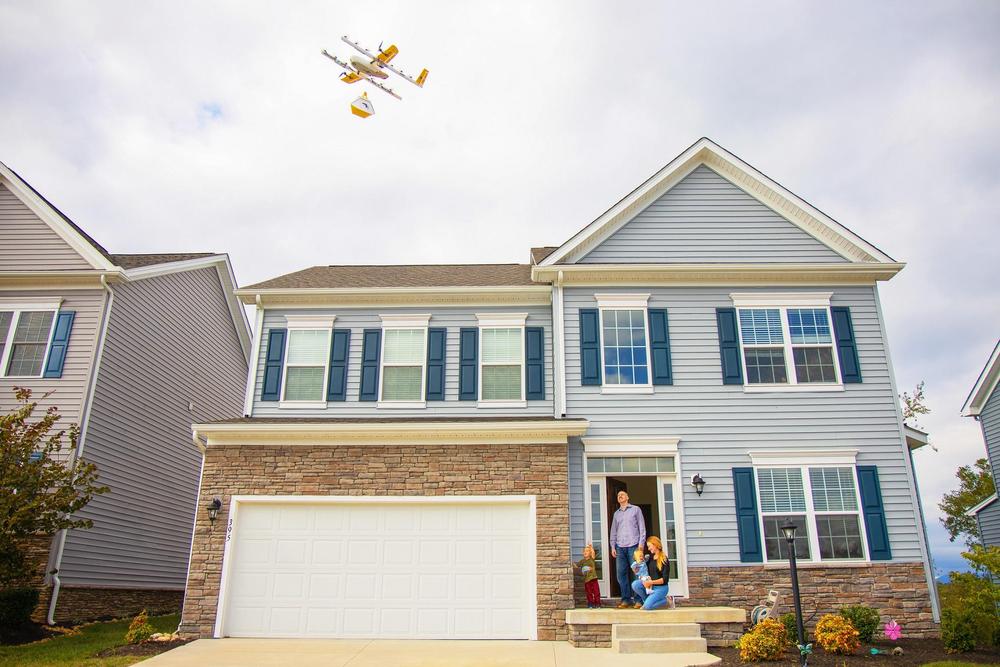
Forced to stay at home amid the coronavirus pandemic, more residents of Christianburg, Virginia, are ordering from a pilot drone residential delivery service run by Google parent Alphabet. The most popular items: Coffee, toilet paper and cookies.



NEW DELHI: For the last four years, it was used for crop dusting. But now, it has a new name and purpose. Chennai-based startup Garuda Aerospace’s drone is spraying disinfectant all over locked down cities in its new avatar of Corona Killer-100.
Garuda has deployed 300 drones across 26 Indian cities, including Varanasi, Raipur and many in Tamil Nadu, at the behest of state governments and municipal bodies that are looking for ways to disinfect their areas with as little human intervention as possible. “We spray in public areas, hospitals, bus stations — anywhere Covid-19 can spread,” says Agnishwar Jayaprakash, the founder and president of the startup. Commercial pilot volunteers are steering these drones.
Across the country, startups are utilising the lockdown period to innovate and add to the state’s arsenal to fight the coronavirus pandemic. Their work has resulted in disinfectant-spraying drones, drones that make public announcements or shoo away crowds during a lockdown, disinfectant trucks, new kinds of sanitisers and even robotic dispensers.

Get all the latest news on coronavirus and more delivered daily to your inbox. Sign up here.
As authorities enforce social distancing in the battle against coronavirus, don’t be surprised if you hear reminders coming from the sky.
Police departments in Florida and New Jersey have drones with pre-recorded warnings that will be deployed if crowds are not following COVID-19 guidelines.
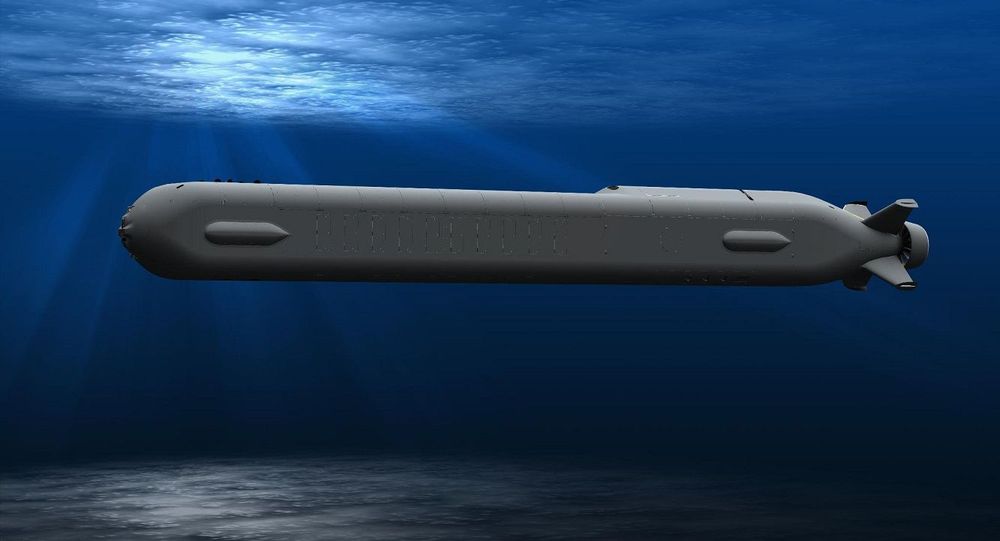

Graphene hematene batteries eternal sea power.
What’s better than an underwater drone? An underwater drone that can remain at sea forever, or at least for long periods.
By Michael Peck

#Technology in #medicine: What will the #future #healthcare be like? https://www.neurozo-innovation.com/post/future-health Technologies have made many great impacts on our medical system in recent years. The article will first give a thorough summarization of them, and then the expectations and potential problems regarding future healthcare will be discussed. #AI #5G #VR #AR #MR #3DPrinting #BrainComputerInterface #telemedicine #nanotechnology #drones #SelfDriving #blockchain #robotics #innovation #trend
Technology has many beneficial effects on modern people’s lives, and one of them is to prolong our lifespan through advancing the medical field. In the past few years, new techniques such as artificial intelligence, robots, wearable tech, and so on have been used to improve the quality of our healthcare system, and some even newer innovations such as flying vehicles and brain computer interface are also considered valuable to the field. In this article, we will first give a thorough discussion about how these new technologies will shape our future healthcare, and then some upcoming problems that we may soon face will be addressed.

As we enter our third decade in the 21st century, it seems appropriate to reflect on the ways technology developed and note the breakthroughs that were achieved in the last 10 years.
The 2010s saw IBM’s Watson win a game of Jeopardy, ushering in mainstream awareness of machine learning, along with DeepMind’s AlphaGO becoming the world’s Go champion. It was the decade that industrial tools like drones, 3D printers, genetic sequencing, and virtual reality (VR) all became consumer products. And it was a decade in which some alarming trends related to surveillance, targeted misinformation, and deepfakes came online.
For better or worse, the past decade was a breathtaking era in human history in which the idea of exponential growth in information technologies powered by computation became a mainstream concept.

The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), based at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, has delivered what it says is the Air Force’s first high-energy laser weapon for battlefield use against drones.
AFRL has set up the laser weapon system overseas for a 12-month field assessment. The Air Force Strategic Development Planning & Experimentation (SDPE) Office located at Wright-Patt is leading the project, AFRL said in a statement Monday.

The biggest change worldwide in the last decade was probably the smartphone revolution, but overall, cities themselves still look pretty much the same. In the decade ahead, cities will change a lot more. Most of our regular readers probably think I am referring to how autonomous vehicles networks will start taking over and how owning a car will start to become closer to owning a horse. However, the real answer isn’t just the autonomous vehicles on the roads — they will likely also compete with autonomous eVTOL aircraft carrying people between hubs.
Today, the European Union is moving one step closer to making this second part a reality. Together with Daedalean, an autonomous flight company we have covered in the past, EASA published a new joint report covering “The Learning Assurance for Neural Networks.”
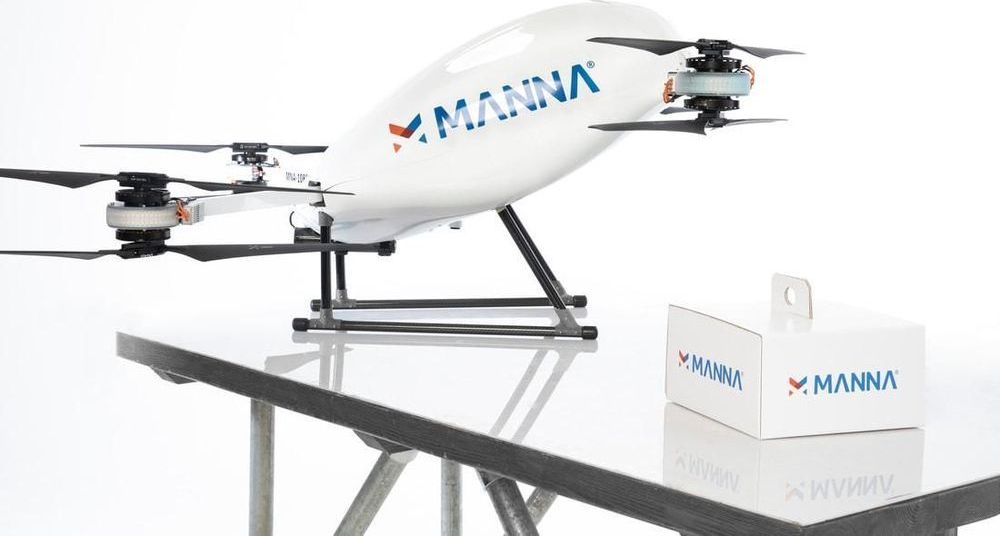

Coronavirus is sending in the drones. In what’s being billed as a “world first,” startup Manna Aero has begun a drone delivery service in Moneygall, Ireland. Delivering medicine to vulnerable people locked in their homes, it provides yet another strong example of how technology is helping the world adjust to life in the shadow of the coronavirus.
Having received authorisation from the Irish Aviation Authority, Manna Aero’s service began last Friday as a pilot in Moneygall, which was previously best known as Barack Obama’s ancestral village. However, if the trial is successful, the service will be rolled out throughout Ireland, and could also be used to deliver food.
The drones will deliver prescription orders for medicine to around a dozen households. As Manna Zero’s founder Bobby Healy told the Irish Independent, the drones ensure “zero human-contact” and can execute deliveries “in ways normal delivery can’t.”
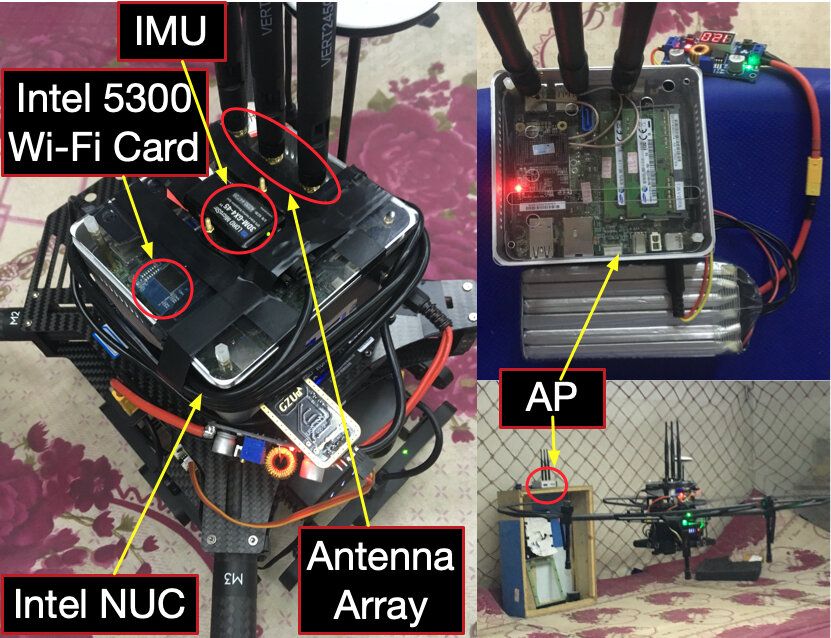
Micro aerial vehicles (MAVs) could have numerous useful applications, for instance, assisting humans in completing warehouse inventories or search and rescue missions. While many companies worldwide have already started producing and using MAVs, some of these flying robots still have considerable limitations.
To work most effectively, MAVs should be supported by an efficient pose estimation system. This is a system or method that can calculate a drone’s position and attitude, which can then be used to control its flight, adjust its speed and aid its navigation while it is operating autonomously and when controlled remotely.
Researchers at Huazhong University of Science and Technology in China have recently developed a new system for the pose estimation of MAVs in indoor environments. Their new approach, outlined in a paper pre-published on arXIv and set to be published in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, leverages existing WiFi infrastructure to enable more effective navigation in small and agile drones.