Micro aerial vehicles (MAVs) could have numerous useful applications, for instance, assisting humans in completing warehouse inventories or search and rescue missions. While many companies worldwide have already started producing and using MAVs, some of these flying robots still have considerable limitations.
To work most effectively, MAVs should be supported by an efficient pose estimation system. This is a system or method that can calculate a drone’s position and attitude, which can then be used to control its flight, adjust its speed and aid its navigation while it is operating autonomously and when controlled remotely.
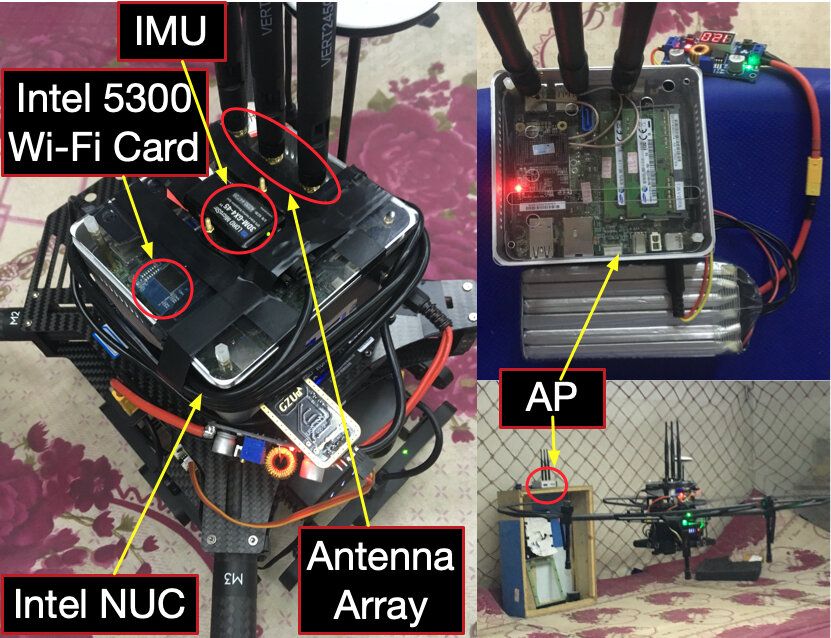
Researchers at Huazhong University of Science and Technology in China have recently developed a new system for the pose estimation of MAVs in indoor environments. Their new approach, outlined in a paper pre-published on arXIv and set to be published in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, leverages existing WiFi infrastructure to enable more effective navigation in small and agile drones.