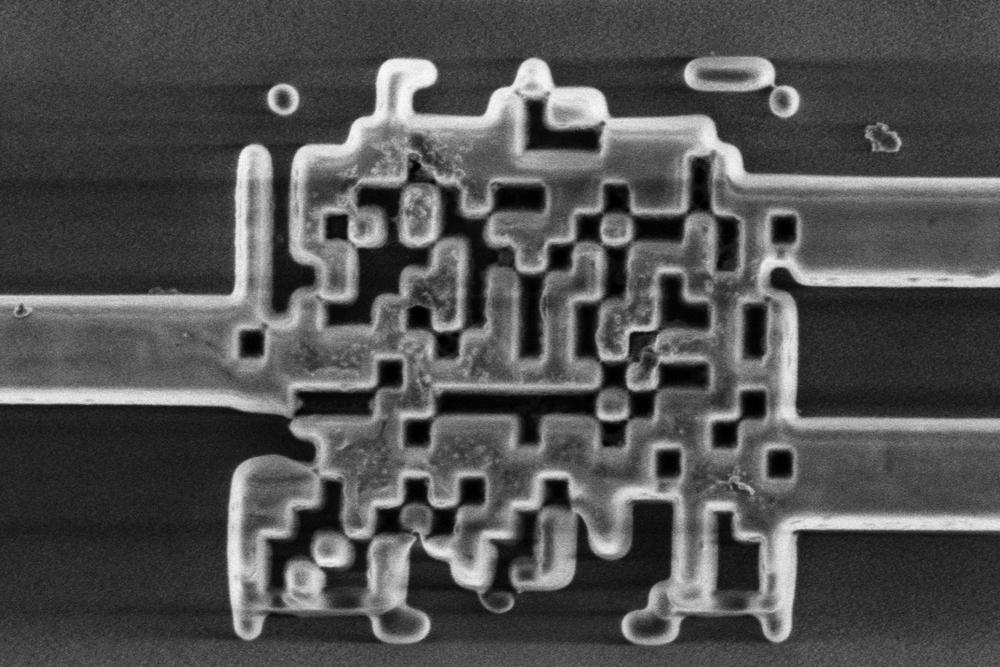
Circa 2015
University of Utah engineers have taken a step forward in creating the next generation of computers and mobile devices capable of speeds millions of times faster than current machines.
The Utah engineers have developed an ultracompact beamsplitter—the smallest on record—for dividing light waves into two separate channels of information. The device brings researchers closer to producing silicon photonic chips that compute and shuttle data with light instead of electrons. Electrical and computer engineering associate professor Rajesh Menon and colleagues describe their invention today in the journal Nature Photonics.
Silicon photonics could significantly increase the power and speed of machines such as supercomputers, data center servers and the specialized computers that direct autonomous cars and drones with collision detection. Eventually, the technology could reach home computers and mobile devices and improve applications from gaming to video streaming.