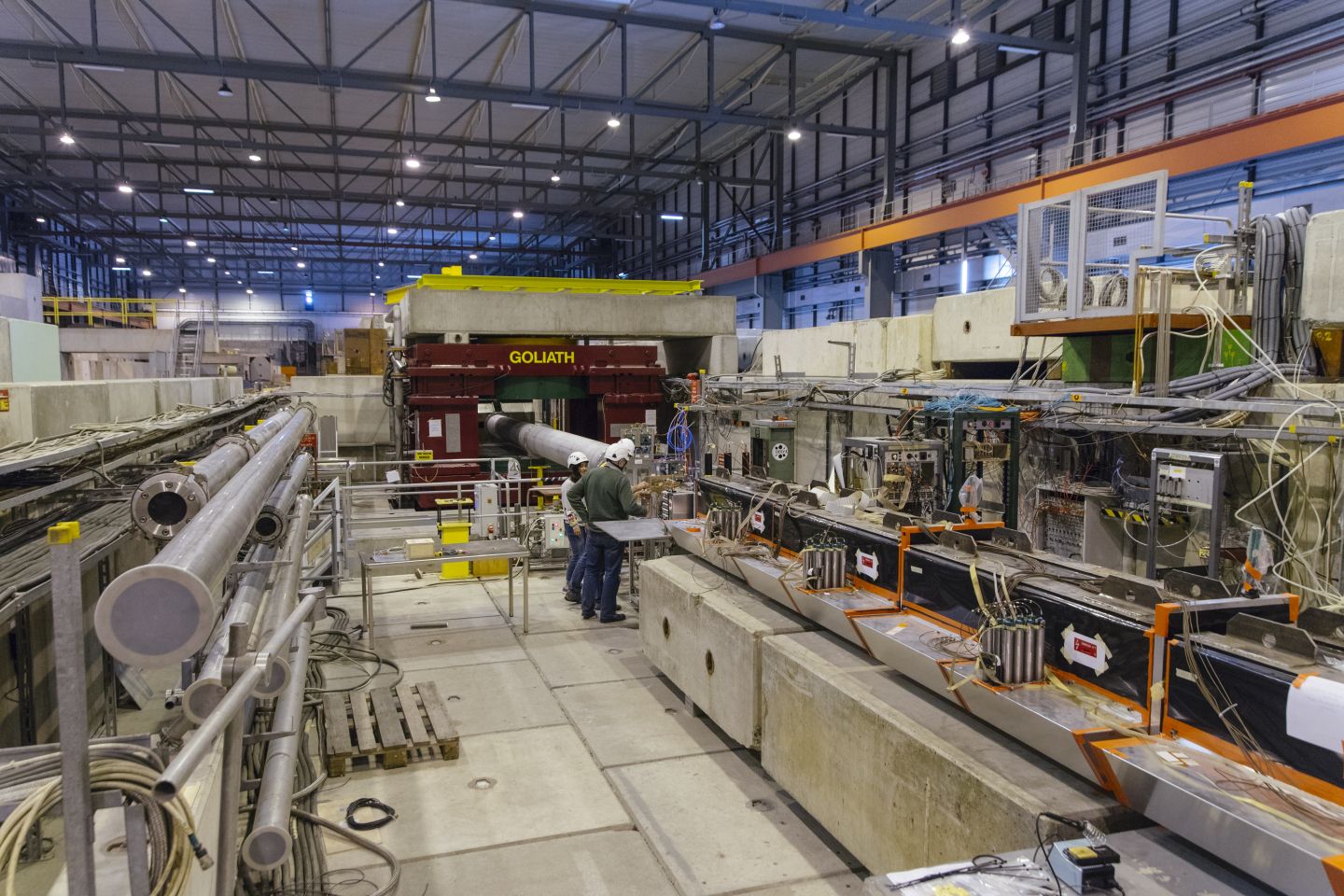
One of the biggest puzzles in physics is that eighty-five percent of the matter in our universe is “dark”: it does not interact with the photons of the conventional electromagnetic force and is therefore invisible to our eyes and telescopes. Although the composition and origin of dark matter are a mystery, we know it exists because astronomers observe its gravitational pull on ordinary visible matter such as stars and galaxies.
Some theories suggest that, in addition to gravity, dark matter particles could interact with visible matter through a new force, which has so far escaped detection. Just as the electromagnetic force is carried by the photon, this dark force is thought to be transmitted by a particle called “dark” photon which is predicted to act as a mediator between visible and dark matter.
“To use a metaphor, an otherwise impossible dialogue between two people not speaking the same language (visible and dark matter) can be enabled by a mediator (the dark photon), who understands one language and speaks the other one,” explains Sergei Gninenko, spokesperson for the NA64 collaboration.
Read more