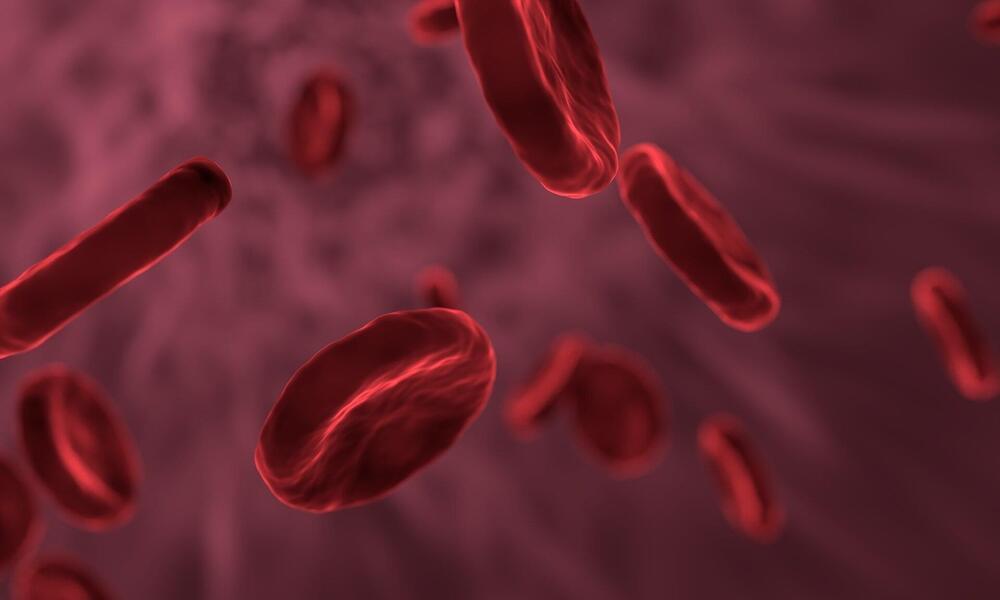
Red blood cells are the most abundant cell type in blood, carrying oxygen throughout the human body. In blood circulation, they repetitively encounter various levels of oxygen tension. Hypoxia, a low oxygen tension condition, is a very common micro-environmental factor in physiological processes of blood circulation and various pathological processes such as cancer, chronic inflammation, heart attacks and stroke. In addition, an interplay between poor cellular deformability and impaired oxygen delivery is found in various pathological processes such as sickle cell disease. Sickle red blood cells simultaneously undergo drastic mechanical deformation during the sickling and unsickling process.
The interactions between hypoxia and cell biomechanics and the underlying biochemical mechanisms of the accelerated damage in diseased red blood cells are well understood, however, the exact biomechanical consequences of hypoxia contributing to red blood cell degradation (aging) remains elusive.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s College of Engineering and Computer Science, in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), sought to identify the role of hypoxia on red blood cell aging via the biomechanical pathways. In particular, they examined hypoxia-induced impairment of red blood cell deformability at the single cell level, compared the differences between non-cyclic hypoxia and cyclic hypoxia, and documented any cumulative effect vs. hypoxia cycles, such as aspects that have not been studied quantitatively. Red blood cell deformability is an important biomarker of its functionality.






 Even new innovative recycled toilet paper is a new concept but someday even vital chemicals will not be wasted with these new reclaiming systems.
Even new innovative recycled toilet paper is a new concept but someday even vital chemicals will not be wasted with these new reclaiming systems.