DNA has the capacity to store large amounts of information for very long durations. This protocol describes encoding of digital files as DNA and the error-free retrieval of the stored data from the sequenced data.



Know Labs’ glucose monitors are both powered by its Body-Radio Frequency Identification, or Bio-RFID, technology. The Bio-RFID sensors emit radio waves to measure specific molecular signatures in the blood through the skin, calculated using spectroscopy.
“We know that not all people with diabetes are looking for a wearable continuous glucose monitoring device to manage their diabetes. Some simply want to replace the painful, inconvenient and expensive fingersticks they currently rely on,” said CEO Phil Bosua, who invented the Bio-RFID technology. “The Bio-RFID sensor we currently use for our internal product testing fits in your pocket and is ready for final use, so we decided to create the KnowU as a portable, affordable and convenient alternative requiring no disposable items, such as test strips and lancets.”
In vitro tests have found that the radiofrequency sensor technology was able to measure glucose levels with accuracy comparable to that of Abbott’s Freestyle Libre continuous glucose monitor, which uses a sensor attached to the back of the arm for up to two weeks at a time. According to a 2018 study (PDF) comparing the two, 97% of the UBand’s readings were within 15% of the values calculated by Abbott’s device.
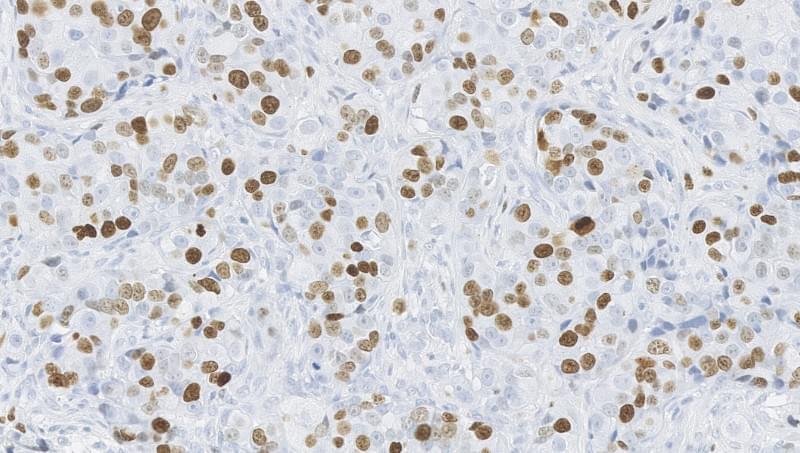
Dowsett’s algorithm was recently published in npj Breast Cancer, a Nature Partner Journal supported by the Breast Cancer Research Foundation. It is intended to help physicians triage postmenopausal women with ER+ HER2–breast cancers, which represent around 70% of breast cancer cases.1 During the pandemic, many within this patient group were prescribed neoadjuvant endocrine therapy (NeoET), rather than surgery, as a disease management strategy.
Analysis of biomarkers in biopsies helps identify breast cancer patients in need of urgent surgery or chemotherapy during COVID-19 pandemic.

Summary: Mouse study reveals chronic stress affects neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus.
Source: Tokyo University of Science.
Depression is a serious medical condition that plagues modern society. Several theories have been proposed to explain the physiological basis of depression, of which the “neurogenic hypothesis of depression” has garnered much attention.

Back in 2,014 the World Health Organization (WHO) warned that within a decade, antibiotic-resistant bacteria could make routine surgery, organ transplantation, and cancer treatment life-threateningly risky — and spell the end of modern medicine as we know it.
Antibiotics are a cornerstone of modern medicine, used to treat infections and to protect vulnerable patients undergoing surgery or chemotherapy. The world desperately needs new antibiotics, and Covid-19 has only exacerbated the problem.
In our search for new antibiotics, we have focused on fungi, especially those found only in Aotearoa New Zealand. Our latest research describes the discovery of fungal compounds able to kill Mycobacteria, a family of slow-growing bacteria that includes another important global airborne killer — Mycobacterium tuberculosis — which causes the lung disease tuberculosis and kills thousands of people around the world each day.

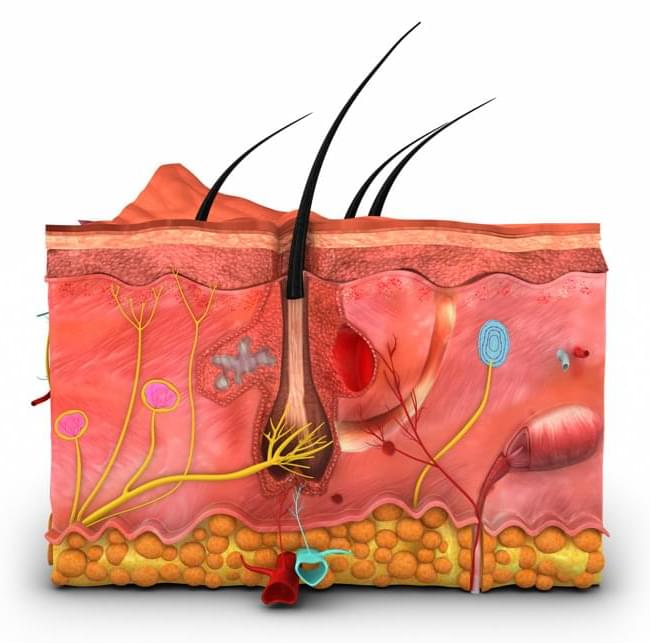
PHILADELPHIA – Treating obese mice with the cytokine known as TSLP led to significant abdominal fat and weight loss compared to controls, according to new research published Thursday in Science from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Unexpectedly, the fat loss was not associated with decreased food intake or faster metabolism. Instead, the researchers discovered that TSLP stimulated the immune system to release lipids through the skin’s oil-producing sebaceous glands.
“This was a completely unforeseen finding, but we’ve demonstrated that fat loss can be achieved by secreting calories from the skin in the form of energy-rich sebum,” said principal investigator Taku Kambayashi, MD, PhD, an associate professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at Penn, who led the study with fourth-year medical student Ruth Choa, PhD. “We believe that we are the first group to show a non-hormonal way to induce this process, highlighting an unexpected role for the body’s immune system.”
The animal model findings, Kambayashi said, support the possibility that increasing sebum production via the immune system could be a strategy for treating obesity in people.
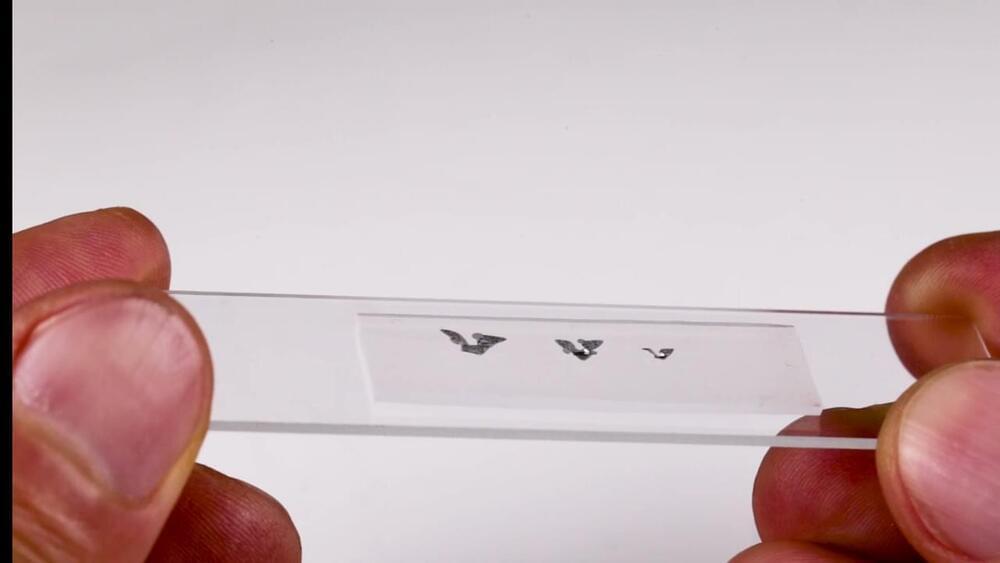


The size of a grain of sand, dispersed microfliers could monitor air pollution, airborne disease, and environmental contamination.
Northwestern University engineers have added a new capability to electronic microchips: flight.
About the size of a grain of sand, the new flying microchip (or “microflier”) does not have a motor or engine. Instead, it catches flight on the wind — much like a maple tree’s propeller seed — and spins like a helicopter through the air toward the ground.