New potential drug combo for kids with brain cancer found using BenevolentAI.


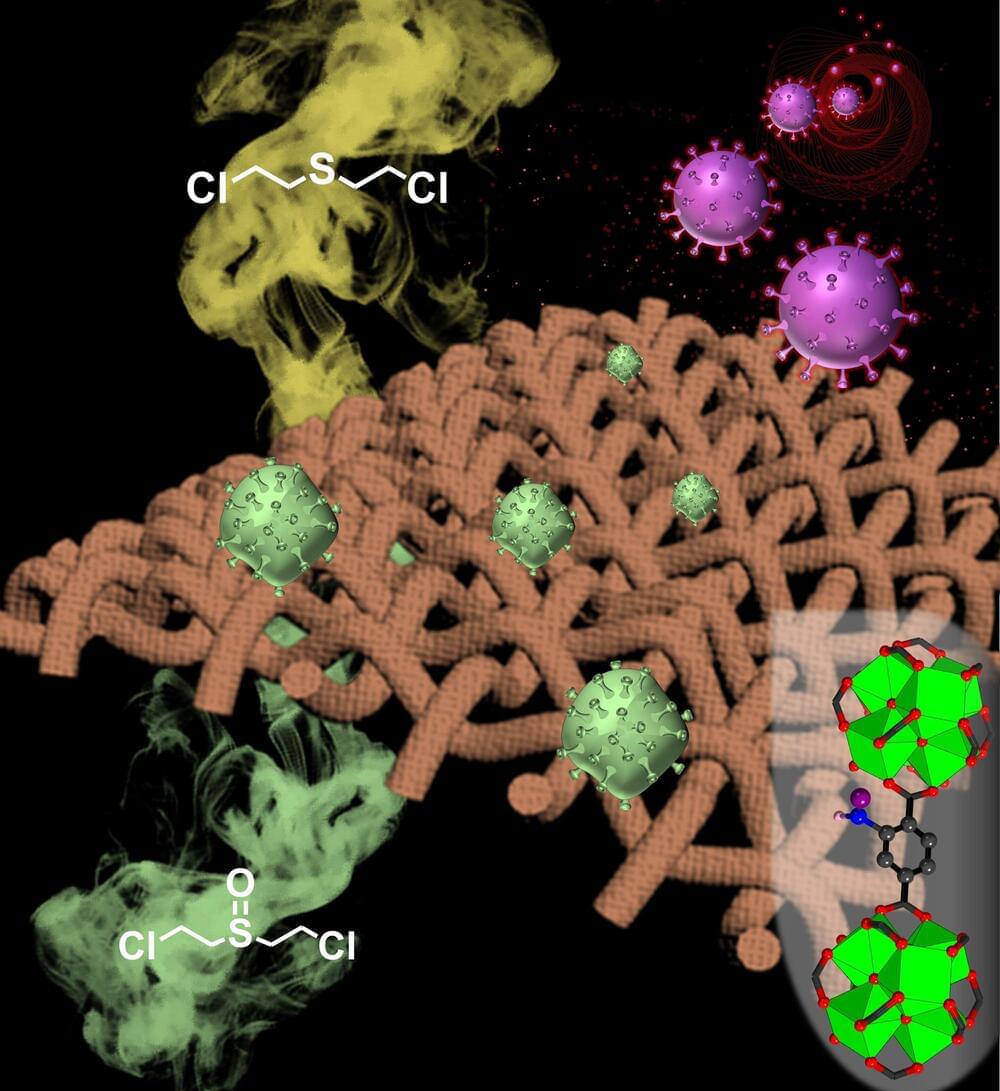
A Northwestern University research team has developed a versatile composite fabric that can deactivate both biological threats, such as the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19, and chemical threats, such as those used in chemical warfare. A material that is effective against both classes of threats is rare.
The material also is reusable. It can be restored to its original state after the fabric has been exposed to threats by a simple bleach treatment. The promising fabric could be used in face masks and other protective clothing.
“Having a bifunctional material that has the ability to deactivate both chemical and biological toxic agents is crucial since the complexity to integrate multiple materials to do the job is high,” said Northwestern’s Omar Farha, an expert in metal-organic frameworks, or MOFs, which is the basis for the technology.
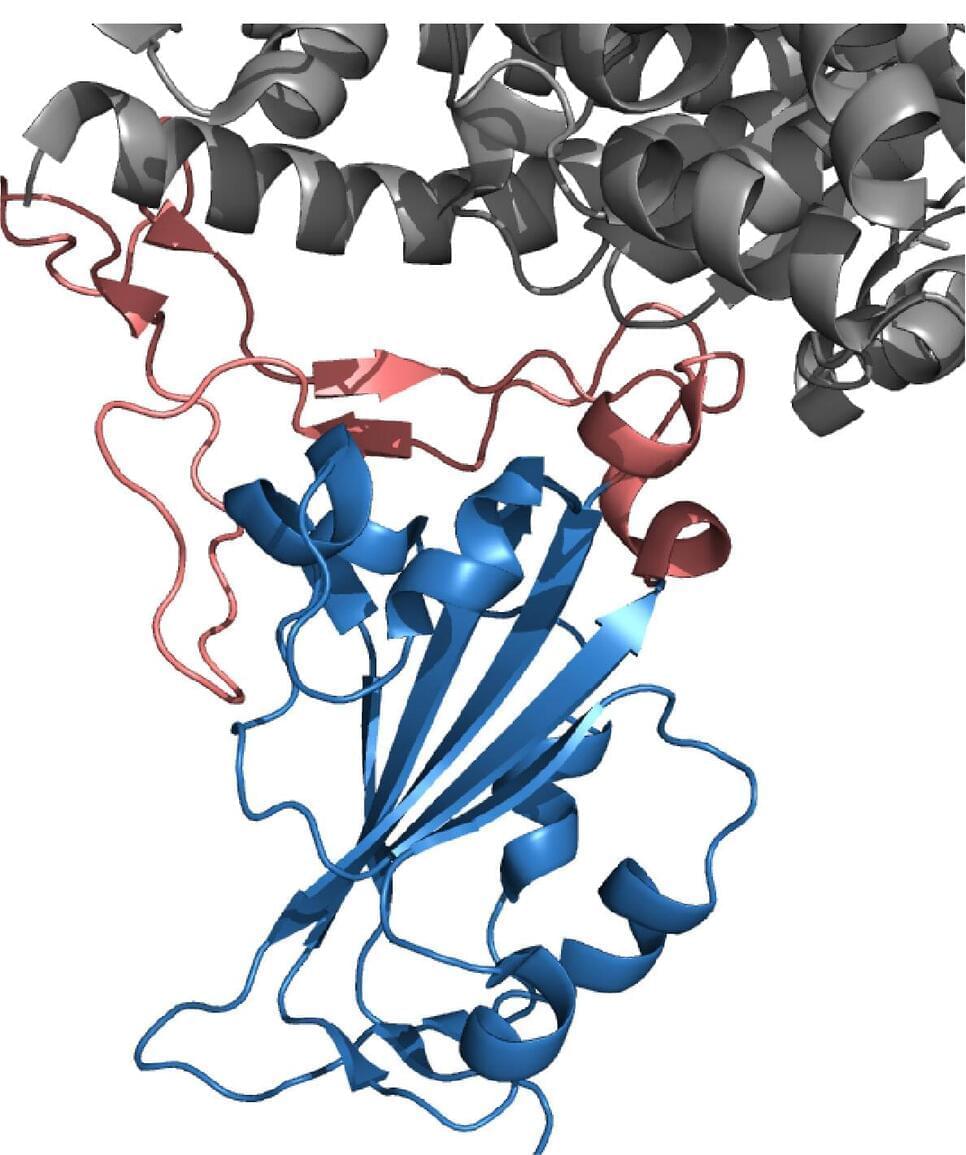
Researchers in Japan have developed a vaccination strategy in mice that promotes the production of antibodies that can neutralize not only SARS-CoV-2 but a broad range of other coronaviruses as well. If successfully translated to humans, the approach, to be published October 8 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, could lead to the development of a next-generation vaccine capable of preventing future coronavirus pandemics.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19 enters human cells by using its spike protein to bind to a cell surface receptor called ACE2. The receptor-binding domain of the spike protein consists of two parts: a “core” region that is very similar in all coronaviruses, and a more specialized “head” region that mediates binding to ACE2.
Antibodies that recognize the head region of the spike receptor-binding domain can block the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into cells but offer little protection against other coronaviruses, such as the SARS-CoV-1 virus responsible for the severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak of 2002. Antibodies that recognize the core region of the spike receptor-binding domain, in contrast, can prevent the entry of various coronaviruses into human cells. Unfortunately, however, individuals exposed to the viral spike protein tend to produce lots of antibodies against the head region but few, if any, antibodies that recognize the core region.



After raising almost $3 billion, Ginkgo Bioworks has built the world’s largest DNA factory in a bid to alter the code behind life and replace traditional manufacturing with biology.
#Science #HelloWorld #BloombergQuicktake.
——-
Like this video? Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/Bloomberg?sub_confirmation=1
Become a Quicktake Member for exclusive perks: http://www.youtube.com/bloomberg/join.
QuickTake Originals is Bloomberg’s official premium video channel. We bring you insights and analysis from business, science, and technology experts who are shaping our future. We’re home to Hello World, Giant Leap, Storylines, and the series powering CityLab, Bloomberg Businessweek, Bloomberg Green, and much more.
Subscribe for business news, but not as you’ve known it: exclusive interviews, fascinating profiles, data-driven analysis, and the latest in tech innovation from around the world.
Visit our partner channel QuickTake News for breaking global news and insight in an instant.

It sounds like a scene from a spy thriller. An attacker gets through the IT defenses of a nuclear power plant and feeds it fake, realistic data, tricking its computer systems and personnel into thinking operations are normal. The attacker then disrupts the function of key plant machinery, causing it to misperform or break down. By the time system operators realize they’ve been duped, it’s too late, with catastrophic results.
The scenario isn’t fictional; it happened in 2,010 when the Stuxnet virus was used to damage nuclear centrifuges in Iran. And as ransomware and other cyberattacks around the world increase, system operators worry more about these sophisticated “false data injection” strikes. In the wrong hands, the computer models and data analytics—based on artificial intelligence—that ensure smooth operation of today’s electric grids, manufacturing facilities, and power plants could be turned against themselves.
Purdue University’s Hany Abdel-Khalik has come up with a powerful response: To make the computer models that run these cyberphysical systems both self-aware and self-healing. Using the background noise within these systems’ data streams, Abdel-Khalik and his students embed invisible, ever-changing, one-time-use signals that turn passive components into active watchers. Even if an attacker is armed with a perfect duplicate of a system’s model, any attempt to introduce falsified data will be immediately detected and rejected by the system itself, requiring no human response.








The Chinese government is developing biological weapons that can attack #DNA strands specific to targeted racial groups. According to Gordon Chang, author of “The Coming Collapse of China,” these “ethnic-specific pathogens” could amount to “civilization killers,” and leave China as the world’s “only viable #civilization.” This development is happening as China amasses the largest collection of American DNA profiles, even larger than what the United States has, through the purchase of DNA sequencing companies. We sat down with Gordon Chang to learn more about why these developments necessitate the immediate attention of the U.S. #government, and of governments around the world.
–
Follow EpochTV on social media
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/EpochTVus.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/EpochTVus.
Rumble: https://rumble.com/c/EpochTV
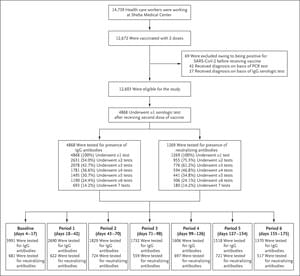
Despite high vaccine coverage and effectiveness, the incidence of symptomatic infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has been increasing in Israel. Whether the increasing incidence of infection is due to waning immunity after the receipt of two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine is unclear.
As the rollout of vaccines against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)1,2 is expanding worldwide, data on the durability of protection are limited. A randomized, controlled trial and real-world studies have shown vaccine efficacy of 94 to 95% with the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer–BioNTech) and vaccine effectiveness in preventing symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) 7 days or more after receipt of the second dose of vaccine.1,3–5 Real-world effectiveness and immunogenicity data describing the antibody kinetics over time after vaccination are beginning to appear, but a complete picture of the duration of immunity is not yet available. We recently reported that breakthrough infection in BNT162b2-vaccinated persons was correlated with neutralizing antibody titers.6 However, a threshold titer that can predict breakthrough infection has not been defined.
The BNT162b2 vaccine elicits high IgG and neutralizing antibody responses 7 to 14 days after receipt of the second dose. Lower antibody levels have been shown to develop in older persons, men, and persons with an immunosuppressed condition, which suggests that antibody titers in these populations may decrease earlier than in other populations.7,8 A decrease in anti-spike (S) antibody levels by a factor of two was observed from the peak (at 21 to 40 days) to 84 days after receipt of the second dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine among 197 vaccinated persons.9 Here, we report the results of a large-scale, real-world, longitudinal study involving health care workers that was conducted to assess the kinetics of immune response among persons with different demographic characteristics and coexisting conditions throughout the 6-month period after receipt of the second dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine.