Musk recently sold approximately $7 billion in Tesla stock, which skyrocketed in value during the pandemic and made him the world’s richest man.
Category: biotech/medical
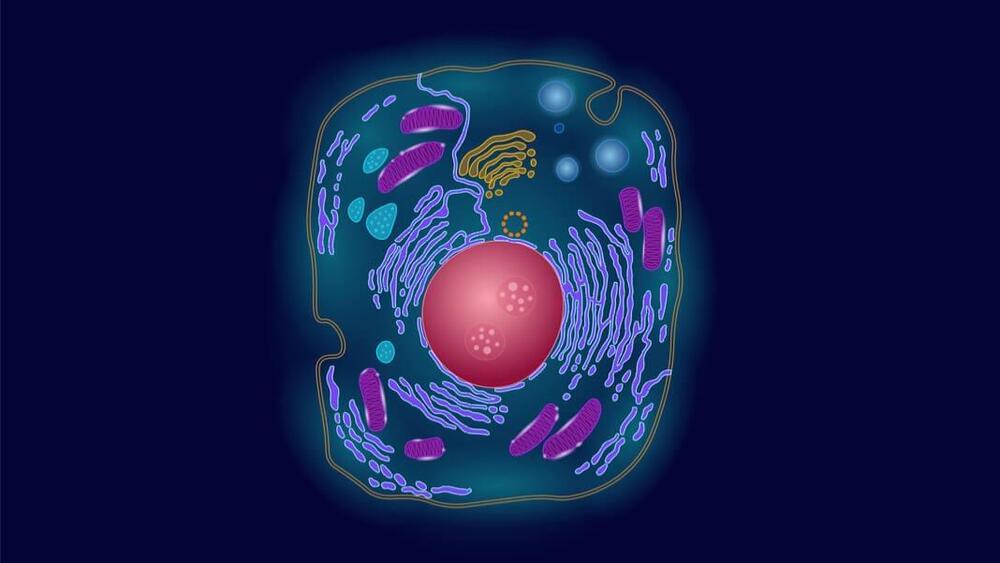
In an unprecedented atlas, researchers begin to map how genes are turned on or off in different cells, a step toward better understanding the connections between genetics and disease.
Researchers at University of California San Diego have produced a single-cell chromatin atlas for the human genome. Chromatin is a complex of DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).
And it can be hacked.
The authors of a new study in Nature Catalysis reprogrammed these blobs—called exosomes—into an army of living nanobioreactors. It’s a seemingly simple process of mix and match: each blob is filled with a different chemical that’s involved in a biological reaction. By bringing two together, the blobs merge into a single squishy container, allowing the two chemicals to react.
The results were explosive. The tiny bioreactors pumped out energy molecules, called ATP, inside living cells. The burst of energy saved injured cells, providing them with a boost of power to fight back against dangerous molecules that otherwise lead to cell death.
𝙎𝙥𝙤𝙣𝙜𝙚 𝙂𝙚𝙣𝙚𝙨 𝙃𝙞𝙣𝙩 𝙖𝙩 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙊𝙧𝙞𝙜𝙞𝙣𝙨 𝙤𝙛 𝙉𝙚𝙪𝙧𝙤𝙣𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙊𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙧 𝘾𝙚𝙡𝙡𝙨
A new study of gene expression in sponges reveals the complex diversity of their cells as well as some possibly ancient connections between the nervous, immune and digestive systems.
Great video of vital biomolecular processes.
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines deliver directions to make a protein that educates our immune system, so it will neutralize the virus in future encounters. The mRNA-containing lipid particles are taken up by specialized immune system cells. See more: COVIDVaccineAnswers.org
Animation created by and for the Vaccine Makers Project.
Copyright © 2021, Medical History Pictures, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Vaccine Makers Project (VMP) is the classroom-based program of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (VEC at CHOP). The Center’s team is composed of scientists, physicians, mothers and fathers devoted to the study and prevention of infectious diseases. The Center was launched in October 2000 to provide accurate, comprehensive and up-to-date information about vaccines and the diseases they prevent. The VMP program is committed to public education about vaccine science via scientifically supported, historically accurate, and emotionally compelling content.
In one of the mysteries of mammalian development, every cell in the early female embryo shuts down one of its two copies of the X chromosome, leaving just one functional. For years, the mechanics behind this X chromosome inactivation have been murky, but scientists from the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have now taken a major step forward in understanding the process.
Their findings, based on research on mouse stem cells, upend previous assumptions about how X inactivation is initiated in female embryos and could lead to new ways to treat some genetic disorders, as well as a better understanding of how genes on other chromosomes are silenced.
“X inactivation is one of the most fundamentally important processes in development, and I think this study is a slam dunk in finally understanding it,” said Kathrin Plath, a professor of biological chemistry and senior author of the paper, published in the journal Cell.
‘Shark Tank’ star Kevin O’Leary defends Elon Musk’s nearly $300 billion fortune — and predicts many workers won’t return to offices
Posted in biotech/medical, Elon Musk | Leave a Comment on ‘Shark Tank’ star Kevin O’Leary defends Elon Musk’s nearly $300 billion fortune — and predicts many workers won’t return to offices
“Shark Tank” investor Kevin O’Leary defended Tesla CEO Elon Musk’s massive fortune in an interview on “Real Time with Bill Maher” on Saturday.
The O’Leary Funds boss — whose nickname is “Mr Wonderful” — also attributed the recent surge in asset prices to aggressive fiscal stimulus, and predicted that many people who worked from home during the pandemic won’t return to their companies’ offices.
Taking a daily multivitamin for 3 years is associated with a 60% slower cognitive aging, with the effects particularly pronounced in patients with cardiovascular (CVD) disease, new research suggests.
In addition to testing the effect of a daily multivitamin on cognition, the COSMOS-Mind study also examined the effect of cocoa flavonols, but showed no beneficial effect.
The results “may have important public health implications, particularly for brain health, given the availability of multivitamins and minerals and their low cost and safety,” said research researcher Laura D. Baker, PhD, professor, Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
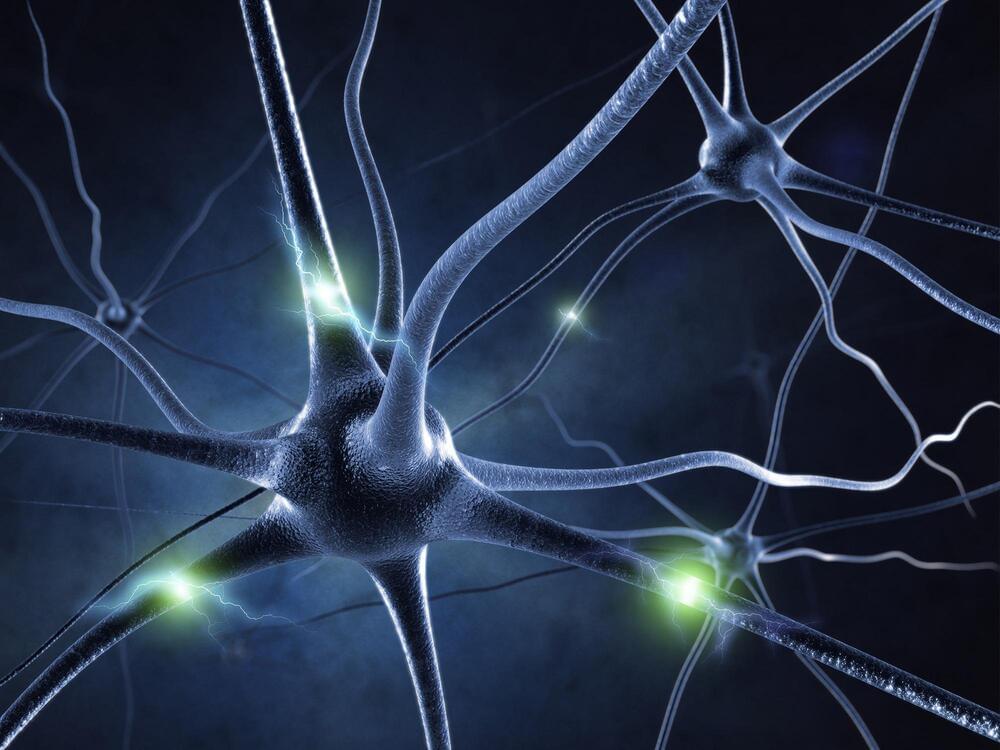
Unusual clusters on neurons are calcium-signaling “hotspots” that activate gene transcription, allowing neurons to produce crucial proteins.
For 30 years, mysterious clusters of proteins found on the cell body of neurons in the hippocampus, a part of the brain, both intrigued and baffled James Trimmer.
Now, the distinguished professor of physiology and membrane biology at the UC Davis School of Medicine may finally have an answer. In a new study published in PNAS, Trimmer and his colleagues reveal these protein clusters are calcium signaling “hotspots” in the neuron that play a crucial role in activating gene transcription.
With advancements in the field of robotics, scientists have created smart soft robots that can mimic any animal in terms of movement and behaviour. This may be the future of robotics since any kind of animals, whether it’s a robot dog, cat or fish can easily be built to perform complex movements and actions to help researchers and people in need of a social companion or pet.
Soft robotics is the specific sub-field of robotics dealing with constructing robots from highly compliant materials, similar to those found in living organisms.
Soft robotics draws heavily from the way in which living organisms move and adapt to their surroundings. In contrast to robots built from rigid materials, soft robots allow for increased flexibility and adaptability for accomplishing tasks, as well as improved safety when working around humans. These characteristics allow for its potential use in the fields of medicine and manufacturing.
–
If you enjoyed this video, please consider rating this video and subscribing to our channel for more frequent uploads. Thank you! smile
–
TIMESTAMPS:
00:00 How Robots have gotten more real.
00:48 Current robotic companions.
02:45 What are these new “Soft Robots”?
04:34 What these new Robots can accomplish.
06:55 Last Words.
–
#robots #robotics #animals