Every day, hundreds of thousands of new COVID-19 cases and thousands of new deaths are still being reported worldwide, creating a need for drugs that can combat the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2.
Now, new research led by investigators at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital points to a well-known and widely available drug called disulfiram (marketed as Antabuse) as a possible treatment for COVID-19.
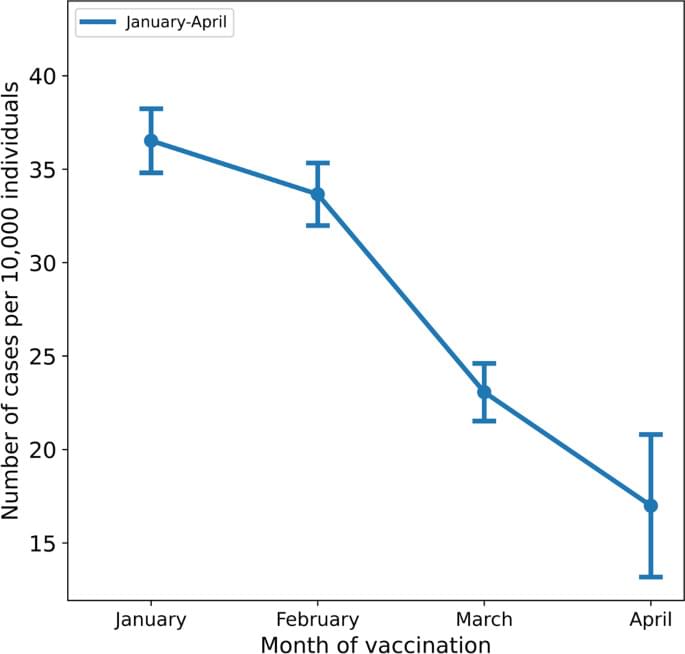
In the retrospective study, published Oct. 28 in PLOS ONE, patients taking disulfiram for alcoholism were less likely to become infected with SARS-CoV-2, and those who did get infected were less likely to die from COVID-19 than those not taking the drug.
New research points to a well-known and widely available drug called disulfiram (marketed as Antabuse) as a possible treatment for COVID-19.