For all that neural networks can accomplish, we still don’t really understand how they operate. Sure, we can program them to learn, but making sense of a machine’s decision-making process remains much like a fancy puzzle with a dizzying, complex pattern where plenty of integral pieces have yet to be fitted.
If a model was trying to classify an image of said puzzle, for example, it could encounter well-known, but annoying adversarial attacks, or even more run-of-the-mill data or processing issues. But a new, more subtle type of failure recently identified by MIT scientists is another cause for concern: “overinterpretation,” where algorithms make confident predictions based on details that don’t make sense to humans, like random patterns or image borders.
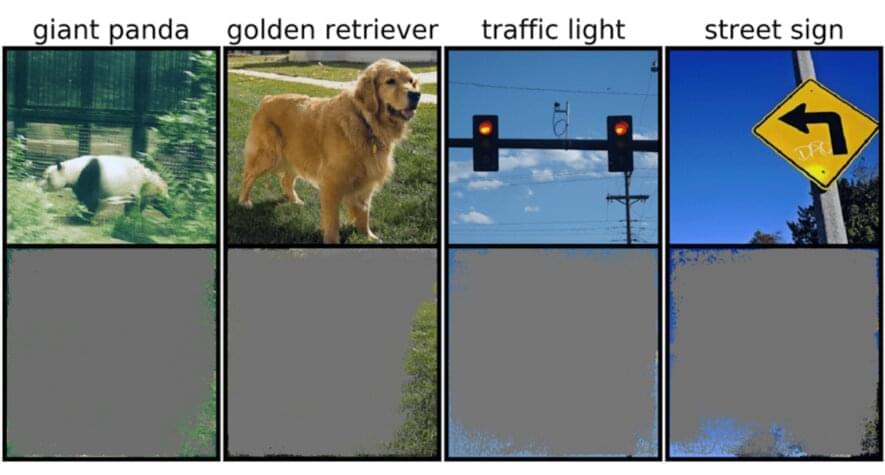
This could be particularly worrisome for high-stakes environments, like split-second decisions for self-driving cars, and medical diagnostics for diseases that need more immediate attention. Autonomous vehicles in particular rely heavily on systems that can accurately understand surroundings and then make quick, safe decisions. The network used specific backgrounds, edges, or particular patterns of the sky to classify traffic lights and street signs—irrespective of what else was in the image.