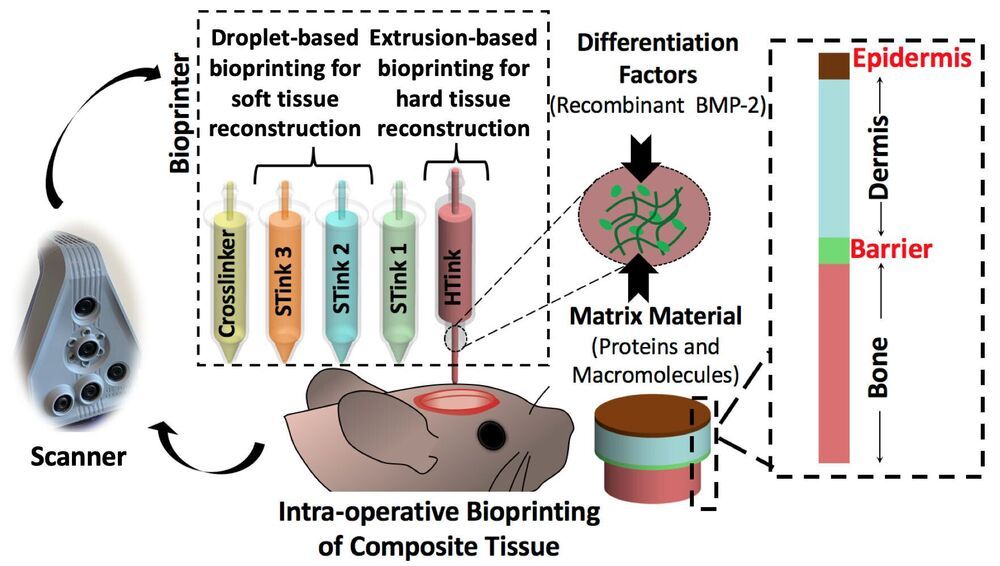
Fixing traumatic injuries to the skin and bones of the face and skull is difficult because of the many layers of different types of tissues involved, but now, researchers have repaired such defects in a rat model using bioprinting during surgery, and their work may lead to faster and better methods of healing skin and bones.
“This work is clinically significant,” said Ibrahim T. Ozbolat, Hartz Family Career Development Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics, Biomedical Engineering and Neurosurgery, Penn State. “Dealing with composite defects, fixing hard and soft tissues at once, is difficult. And for the craniofacial area, the results have to be esthetically pleasing.”
Currently, fixing a hole in the skull involving both bone and soft tissue requires using bone from another part of the patient’s body or a cadaver. The bone must be covered by soft tissue with blood flow, also harvested from somewhere else, or the bone will die. Then surgeons need to repair the soft tissue and skin.