An Australian hospital is building a facility dedicated to 3D-Printing organs.
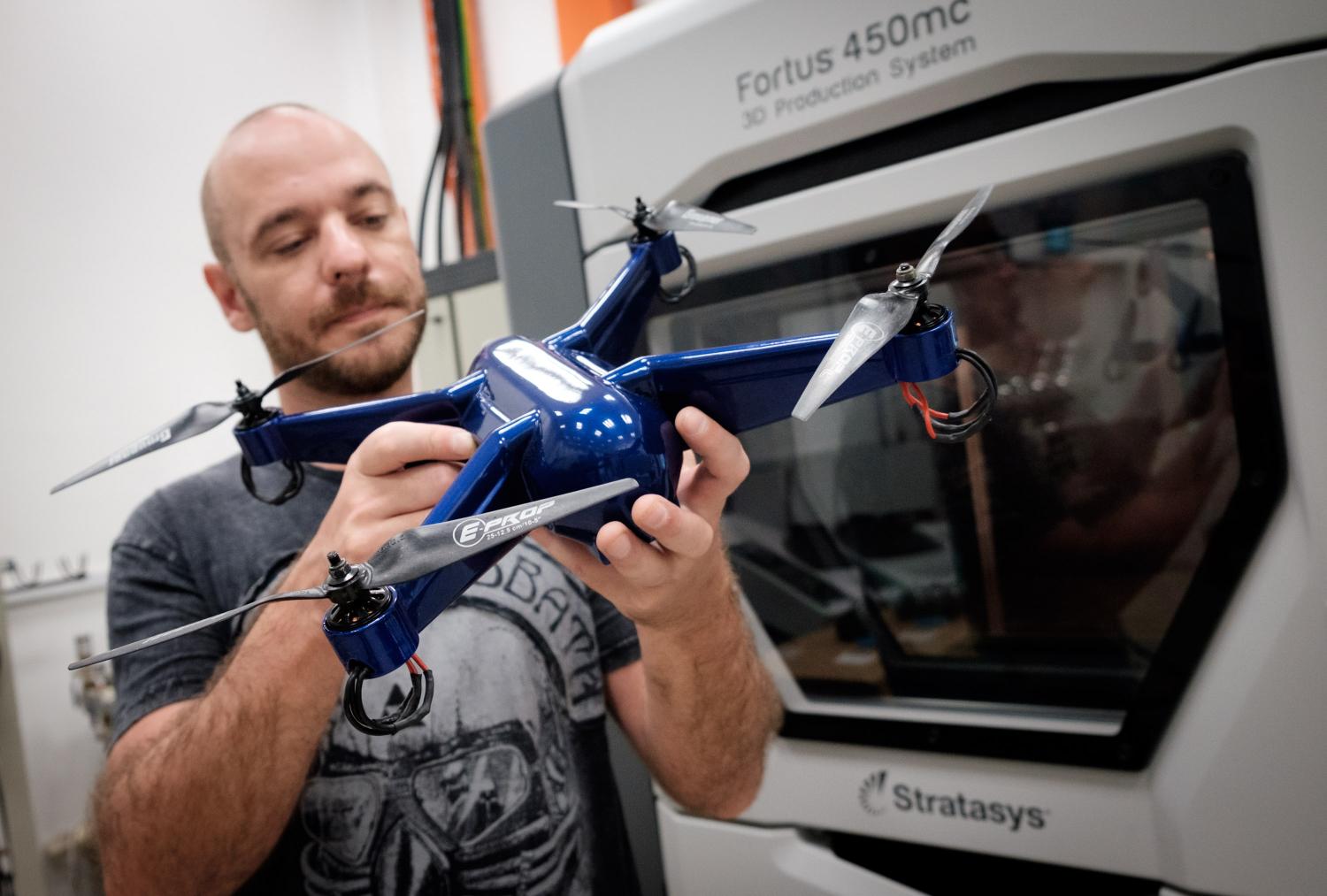



Nanyang Technological University (NTU) researchers in Singapore have embedded electronics into a 3D printed drone. Using Stratasys’ 3D printers and the advanced ULTEM 9085 material Phillip Keane produced the device as part of the Singapore Center for 3D Printing (SC3DP) at NTU. The quadcopter, it has four propellers, with its impressive construction and embedded electronics is impressive, but still has some way to go to catch up with TERN, DARPA’s military drone currently under development.
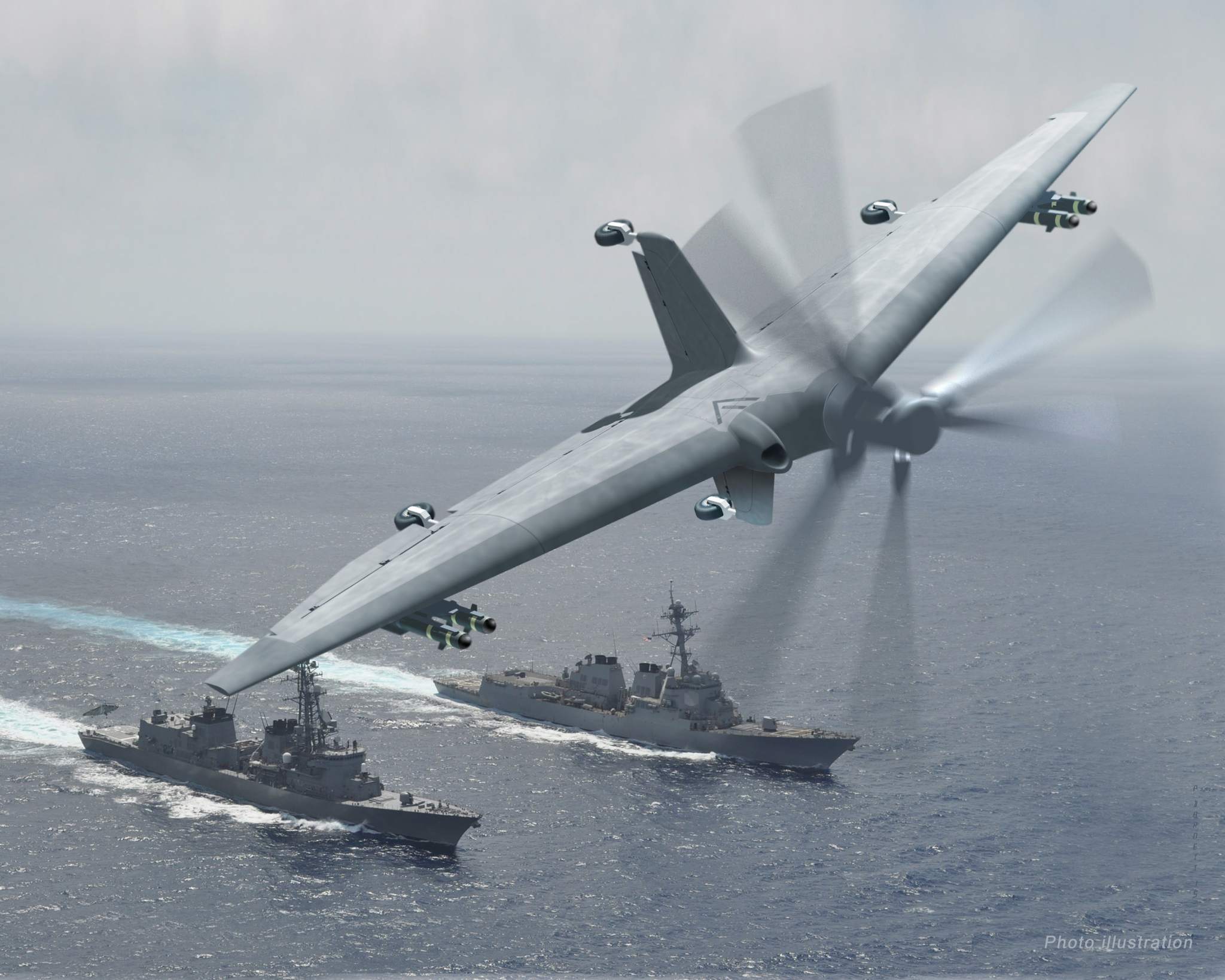

DARPA recently performed a critical design review (CDR) in mid-October of the design’s General Electric engine. The GE engine will enable the drone to fly both vertically and horizontally. GE are rarely far from 3D printing news, not just for developing their 3D printing portfolio but also for repairing 3D printed engines with 3D printing. Naturally, the details of TERN’s engine have not been made public by DARPA but it may be fair to speculate that GE would have looked to use their latest developments with 3D printing in the project, especially given the value of 3D printing for making low volume or one-off complex components.
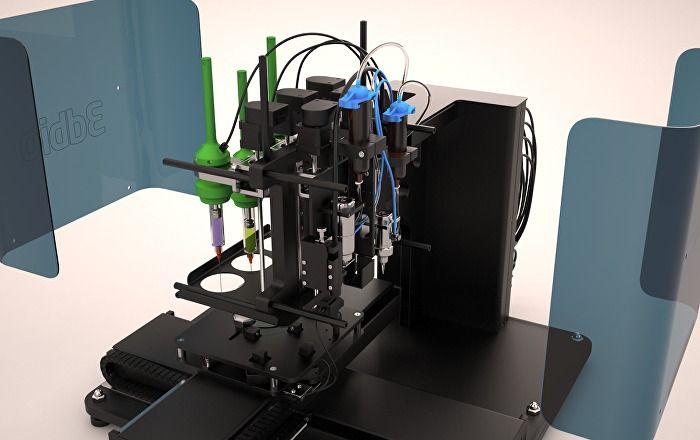
Bioprinting has been all over the news in the past several years with headline-worthy breakthroughs like printed human skin, synthetic bones, and even a fully functional mouse thyroid gland.
3D printing paved the way for bioprinting thanks to the printers’ unique ability to recreate human tissue structures; their software can be written to ‘stack’ cells in precise patterns as directed by a digital model, and they can produce tissue in just hours and make numerous identical samples.
Despite the progress in bioprinting, however, more complex human organs continue to elude scientists, and resting near the top of the ‘more complex’ list are the kidneys.
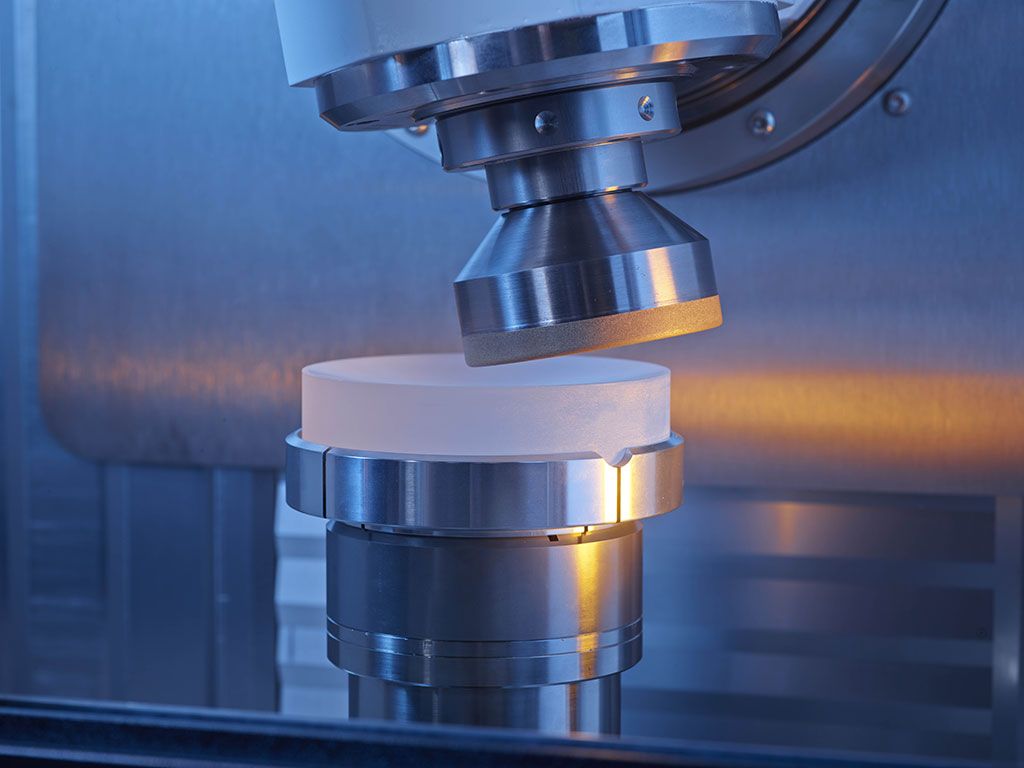

Lenses with a surface accuracy in the nanometer range are behind ever more accurate laser and optical systems. Manufacturers depend on ultra-precise optical and mechanical ablation processes, innovative coating processes and extremely accurate measuring technology to venture into these nano-worlds. The latest trends in optical manufacturing will be showcased by the world’s leading trade fair LASER World of PHOTONICS, from June 26–29, 2017 in Munich.
Nanoscribe GmbH’s 3D printing process creates three-dimensional micro and nano lenses from photosensitive coatings. The structures are built up a pulse at a time by highly focused femtosecond lasers employing two-photon polymerization. Source: Nanoscribe GmbH
The diversity of lenses, their shapes, sizes and materials is growing all the time. Applications in non-visible wavelengths from x-rays and ultraviolet to the far infrared also require special optics, such as material processing using short pulse and ultrashort pulse lasers or imaging techniques in the medical and research fields and industrial quality control.
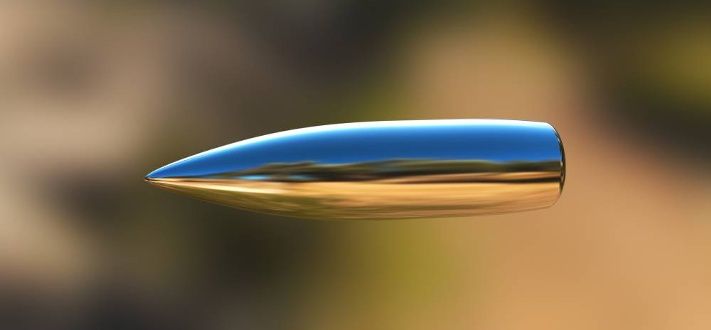
A collaboration between Russia’s Foundation for Advanced Research Projects and the Central Scientific – Research Institute for Precision Machine Engineering known as TSNIITOCHMASH has produced 3D printed bullets.
The Foundation formed in 2012 serves as an advanced research facility for military projects, an equivalent of the American DARPA. The project, conducted by the Foundation’s Laboratory of Additive Technologies and Design materials used selective laser melting technology to create an experimental batch of bullets. This same batch of bullets was then successfully fired.
According to the head of the laboratory, Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Professor Vladimir Chuvildeeva, the current development team was formed more than ten years ago at the University of Nizhni Novgorod. The team has become specialized in developing laser alloying technology to develop complex physical models. Their end goal is being to develop equipment much more sophisticated for military purposes.
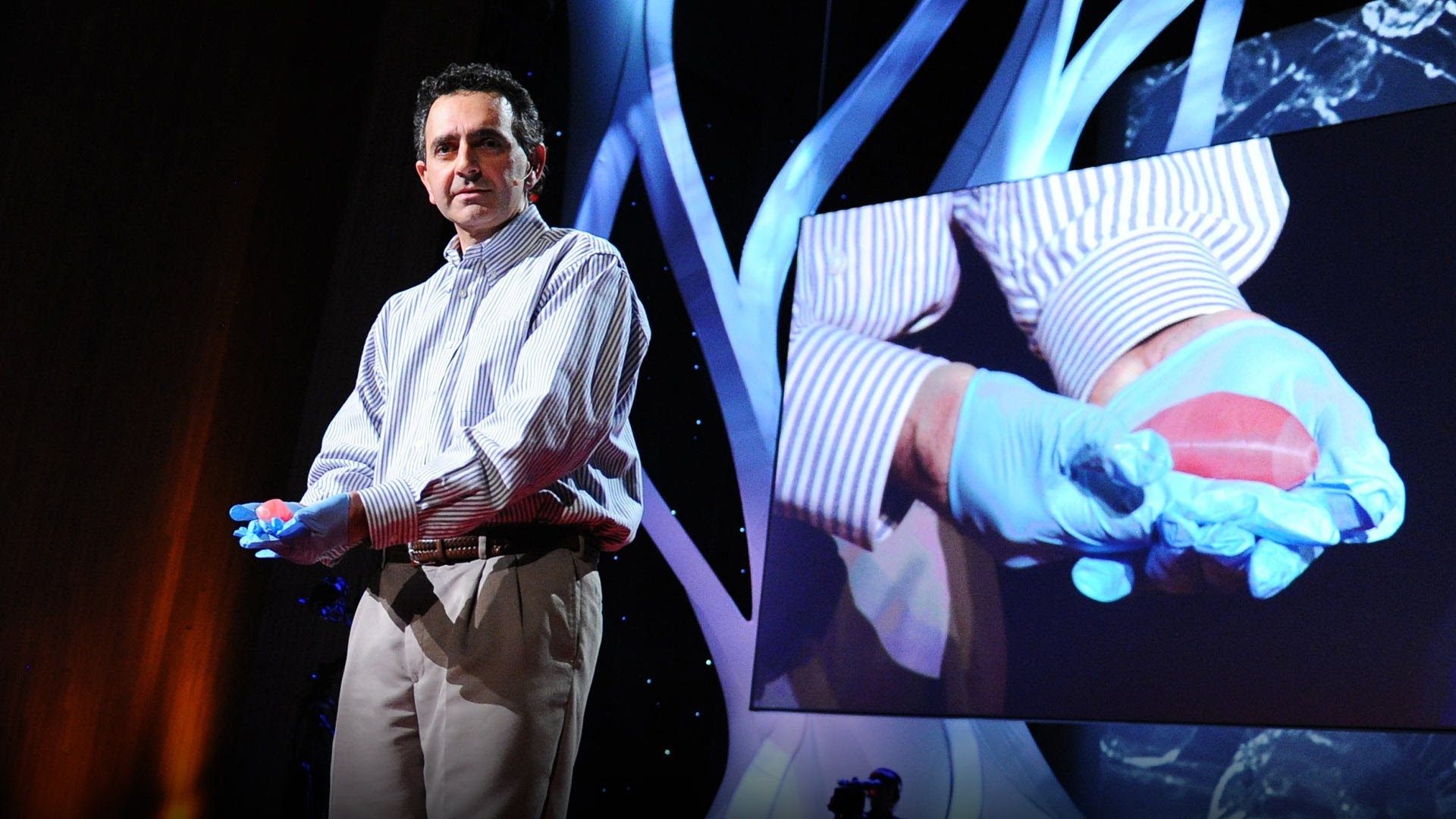


A woman living on a dialysis machine is grown a new kidney using her own cells. A father struggling with age-related vision loss has his eyesight restored. A soldier suffers extensive burns and has his skin regenerated.
This is a glimpse of the holy grail of regenerative medicine. The ultimate goal of the field is to develop therapies that restore normal function to diseased tissues and organs. Advances in 3D bioprinting, the process of fabricating functional human tissue outside the body in a layer-by-layer fashion, have pushed the envelope on what is considered possible in the field.