Every time there’s a new technology, criminals immediately take advantage of it, explains Steven Kotler. It’s only a matter of time before they find new, nefarious uses for 3D printing and synthetic biology.



California-based commercial aerospace company Moon Express, are on track to send their Electron rocket to the Moon in 2017. The Electron is propelled by 3D printed engines made by Rocket Lab, headquartered in Los Angeles. The project is designed for Google’s modern-day space race: the Lunar X Prize.
3D printed engines
Nine liquid-propellant Rutherford engines are behind the Electron. The rocket engines, the first to use 3D printing for the all core parts, use kerosene and liquid oxygen (LOX) for fuel.
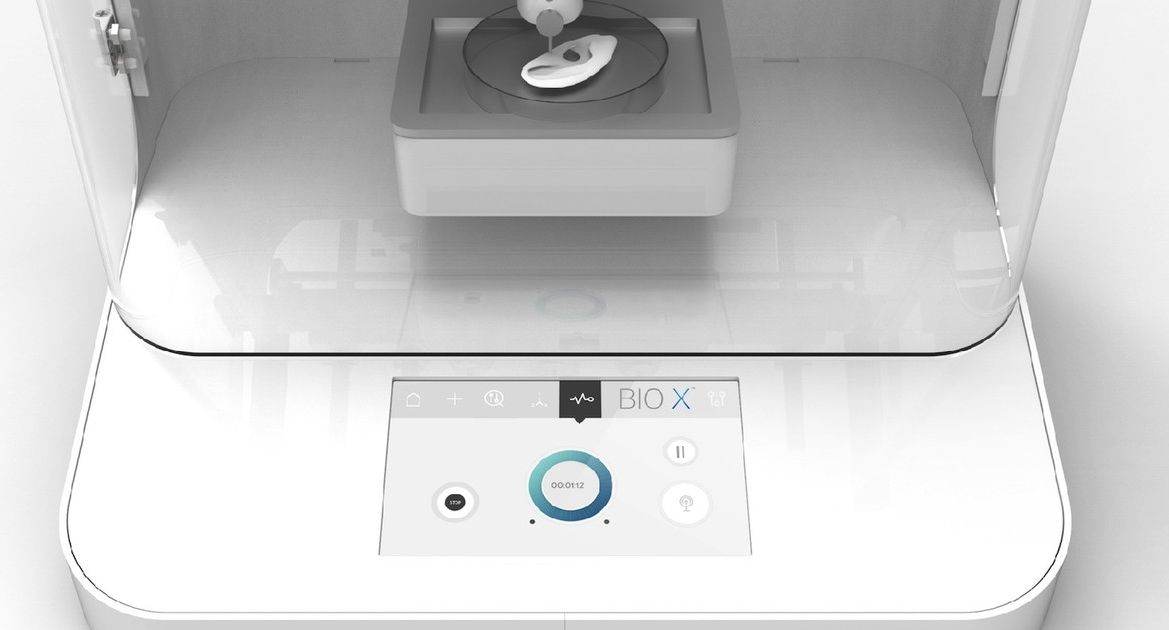

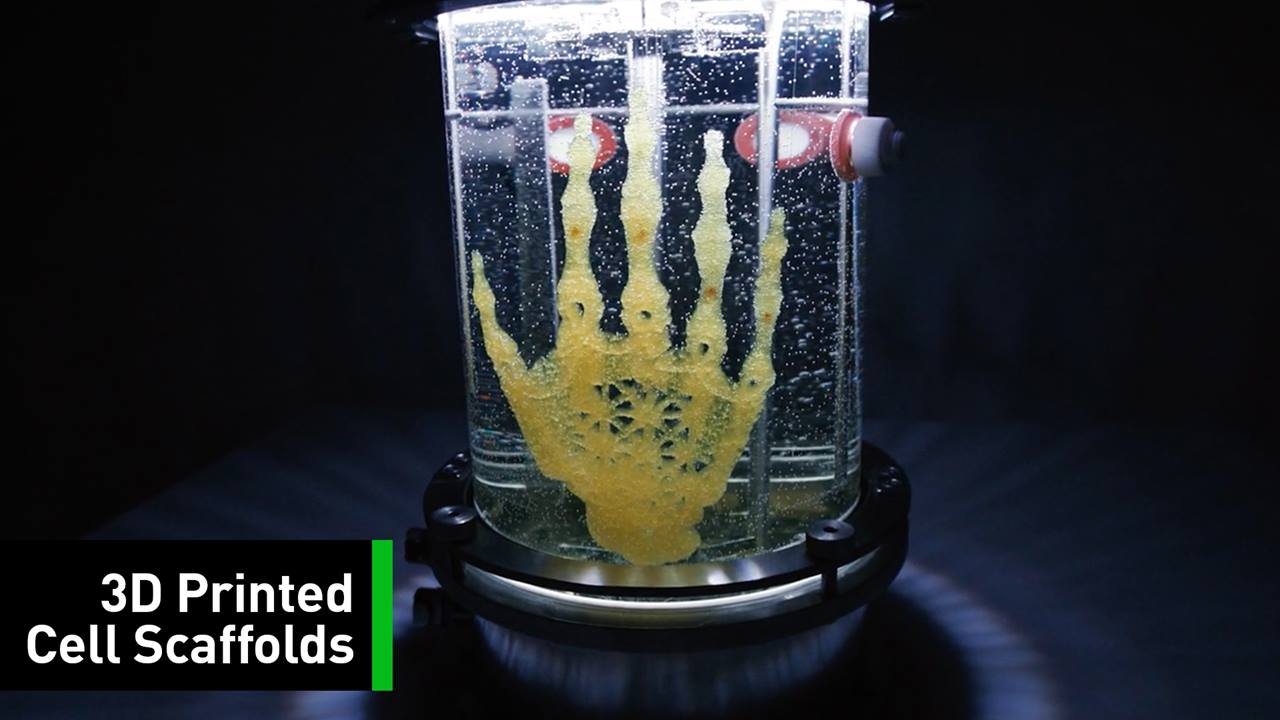
If you were to pick one emerging technology with the potential to have a massive positive impact on humanity in the coming years, there’s a good chance you’d go with 3D bioprinting.
The ability to use “bio-ink” to print out biomaterials ranging from heart tissues to bone and cartilage is incredibly exciting — although at present it’s not exactly the most user-friendly of tech.
One company hoping to change that is Cellink, which this week has announced the launch of its new Bio X printer, which it hopes will bring 3D bioprinting to a whole new audience.
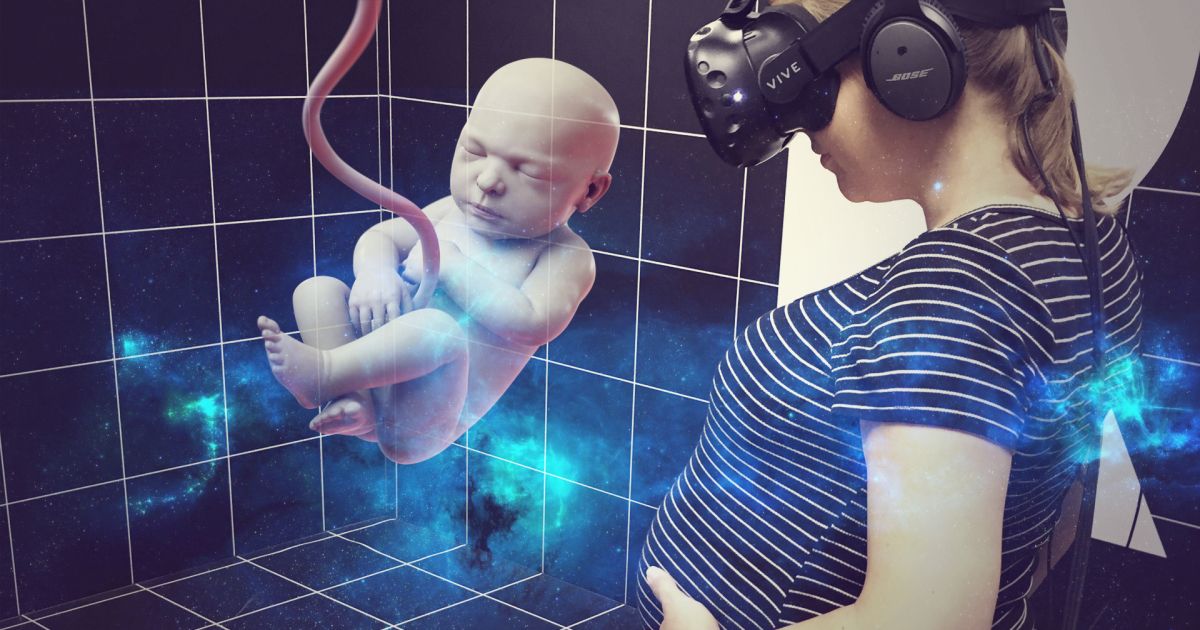


A while ago I got an idea: how awesome would it be to use 4D ultrasound to scan my unborn baby and make a VR experience of that. So I talked my girlfriend over even though the idea felt a bit weird and almost scary.
Show Full Text
How to make it happen? I searched for similar cases online, but couldn’t find any. All I could find was some examples of using ultrasound images for a 3D print of your unborn baby. So this was the first time in the world someone was doing this. Luckily I got people at the Aava Medical Centre excited about the idea, and they helped me forward. I also contacted GE, a manufacturer of 4D ultrasound systems, and they advised me how to extract the right kind of files from the ultrasound machine.

Syn Diamonds is a field that I have been educating many on the importance of in areas of QC, healthcare/ medical, and now we’re looking at transportation such as driverless cars. I told folks if we could have a joint venture with Intel and HP in this space; we could see these to companies re-emerge as leaders again just for this one area of technology. Who ever comes up with the 3D or 4D printer that can mass produce the quality we need in syn diamond materials in various scales/ sizes will dominate and make billions as this technology is a core piece to QC.
Lab-grown red diamonds with an atomic defect could one day replace GPS systems thanks to their remarkable sensitivity to magnetic waves, scientists have suggested.
A team at Element Six, a tech company based in Oxfordshire, are exploring the remarkable properties of crystals with a so-called ‘nitrogen vacancy defect’ — a gap in the atomic lattice at the heart of the diamond.
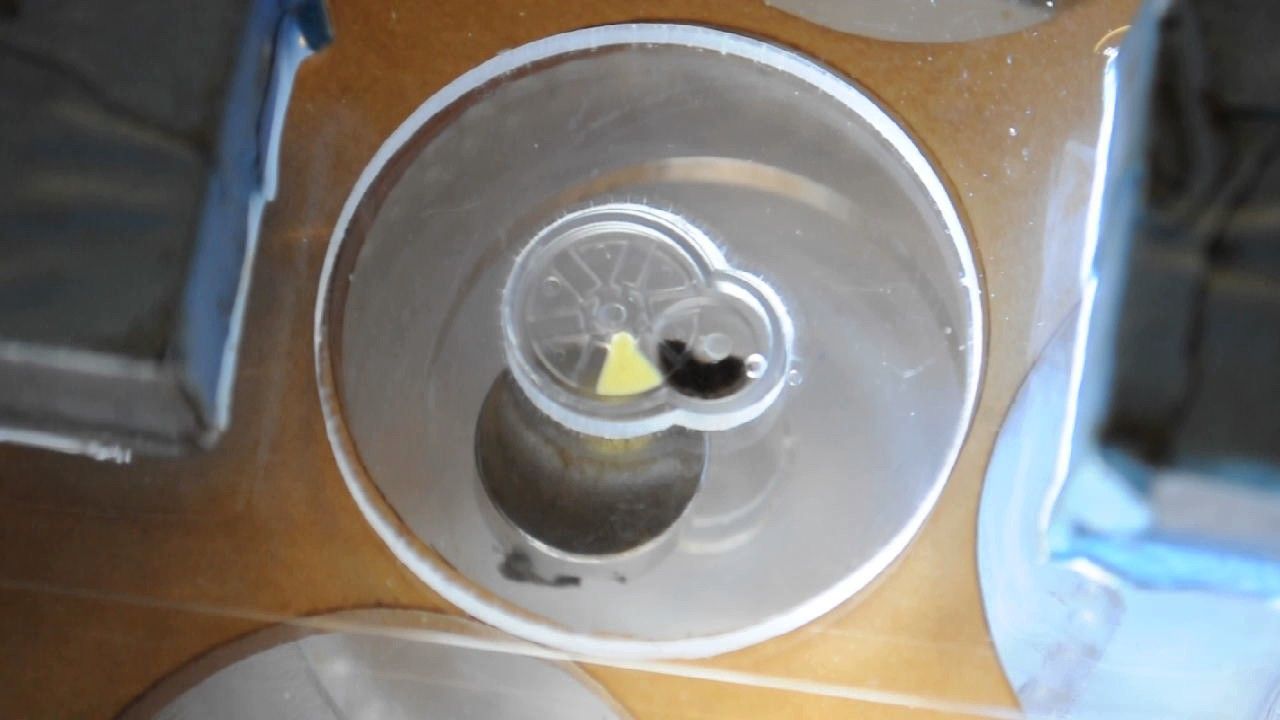


Samuel Sia, a professor of biomedical engineering at New York City’s Columbia University, has developed a 3D printed biobot that can be implanted in the body to release controlled doses of drugs. The amazing device can be controlled from outside the body using only magnets.
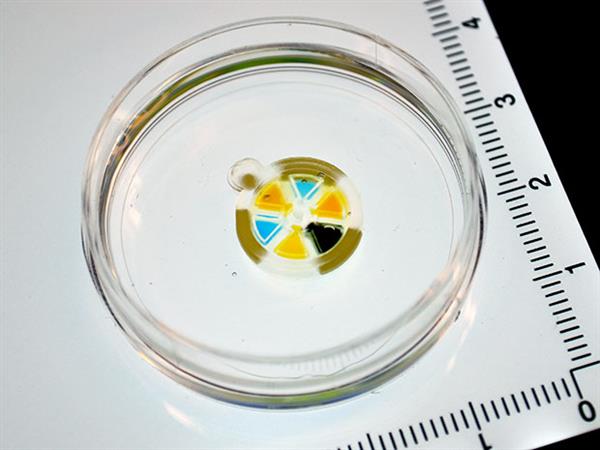

For patients who have been diagnosed with cancer, treatment options are often few and far between, and in many serious cases, starting an intense course of chemotherapy becomes a necessity rather than a choice. But despite being a powerful weapon against cancer, chemotherapy takes its toll on the body in a number of ways: chronic pain, nausea, fatigue, hair loss, and the chance of infertility are just some of the adverse effects that chemotherapy can present. Fortunately, scientists are working hard to develop more effective ways of delivering chemotherapy drugs, including a new 3D printing method that involves fabricating squishy, “clockwork” micromachines that deliver precise drug doses from within the body.
Speculation on 3D printed tissue coming to humans sooner than we think is backed by new pre-clinical findings from 3D bioprinting company Organovo (NASDAQ: ONVO). Though it will still be 3 – 5 years before the U.S. based Organovo apply for clearance of their liver tissue, that is still sooner than perhaps even the FDA had in mind.
Pre-clinical trial data shows that 3D bioprinted liver tissue has been successfully planted into lab-bred mice. The human liver-cell tissue shows regular functionality and, at this stage, is being explored as a suitable patch for the organ.
