Luv this. True Girl Power!
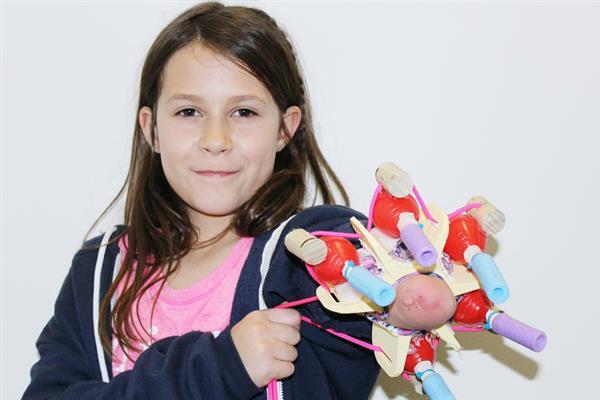
11-year-old Jordan Reeves, who last year made the world a bit jollier with her 3D printed, glitter-shooting prosthetic arm, has become a source of inspiration for many. The young and remarkably ambitious girl, who was born without most of her left arm (it stops just above the elbow), has been showing off her 3D printed glitter prosthetic all around the U.S. for the past several months, was presented with Disney’s Dream Big, Princess award, and was given a 3D printer courtesy of Autodesk and Dremel.
Not only is she receiving recognition, however, but Reeves has continued her steadfast work and is creating more 3D printed prosthetic accessories and assistive tools. Her latest project, for instance, is working on developing a device that combines a medical-grade prosthetic arm with 3D printed, changeable attachments. Though decidedly less sparkly than her first make, the hybrid prosthetic could allow for a variety of 3D printed attachments (like a hand or a pirate hook). Jordan is developing the 3D printed prosthesis with the help of her prosthetist and her Autodesk mentor Sam Hobish.
While many 3D printable prosthetic hand models do already exist, Reeves is one of many people who cannot use them, mainly because they mostly rely on wrist or elbow mobility, which she does not have. As Jordan’s mother Jen Reeves told Fast Company, “She came with the challenge because she and Sam were trying to figure out a way to use those standard 3D printed hands, and it got pretty aggravating. She realized that it was not possible with any of the current 3D-printed design concepts, since she doesn’t have an elbow.”
Read more