Here is another economics/policy question that I was asked to address at Quora. It provides great fodder for a quick Lifeboat economics review.
The US used quantitative easing to deal with one monetary crisis, and a bailout of the automotive and banking industry to deal with another. If nations, economies or individuals begin to embrace a decentralized currency, they will inevitably shift away from government issued money. Won’t this hinder a nation’s ability to intervene in a crisis?
Answering this question goes to the very heart of the ethics and politics of cryptocurrency.
Yes. Without centralized control over monetary policy, government options for intervention in a money crisis would be severely limited. But this fact may lead to a false impression…
First, most money crises begin with government, and so there are likely to be far fewer monetary emergencies.
Here’s how the options would be limited:
- Governments would have fewer ways to manipulate a public resource. They will still have the ability to budget, tax, borrow, build infrastructure and even wage war. But…
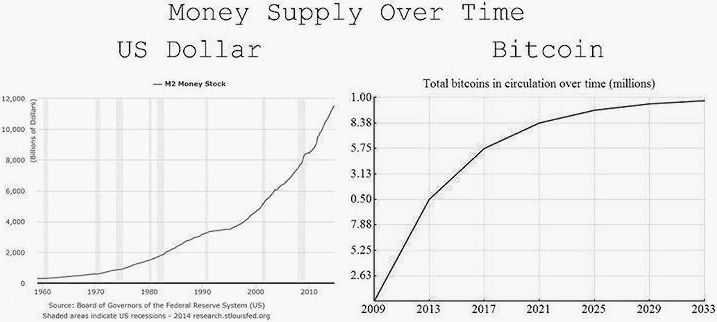
- Governments could no longer amass debts that outstrip their ability to be accountable. That’s because they can no longer covertly tax via rampant printing of money.
- They could not “raise the debt ceiling” without demonstrating fiscal responsibility, because they no longer control what everyone uses as money.
- Government spending (and intervention, such as quantitative easing) would have to be balanced by revenue. Borrowing would be limited to creditors who truly believe in their will and ability to repay debt.
All of these “limitations” are good things—even for the governments and banks involved. It only seems limiting, because our understanding of what is money is tainted by millennia of authoritarian systems.
A capped, open source, transparent, traceable, immutable, decentralized, distributed and permissionless money supply is both fair and more robust than Fiat paper, promises or credit.
Let’s explore that last bullet, above. The point is subtle—yet, it is the key to answering your question…
Every individual, household, business, state and NGO must balance its books. If one cannot cover bills, they must find a creditor who believes in their ability to get back to fiscal health. Even nations are eventually forced to balance their books or seek a bail-out from neighbors.
But, this is not the case for the United States. We have had an ability whitewash our largess and declining industrial productivity by printing more money. How has this been possible while retaining a strong dollar?
The US dollar has been the world’s reserve currency for 47 years. This development was one of the most clever, yet potentially damaging developments of the post war order. It led other nations and consumers to treat it like gold (even though the link to any underlying asset or promise was severed by Richard Nixon in 1972).
Now that other nations are shifting this special status away from the US, we are gradually becoming just as susceptible to a house-of-cards collapse as Venezuela, Argentina, Zimbabwe, or Germany between the wars. Our massive consumer market cannot protect us. Eventually, we must ship the fruit of our sweat and intellectual bounty to serve others. After all, for more than a half century, we have been giving them pieces of paper (dollars or treasury bonds) for their TVs, underwear, sneakers, toys and sheet rock.
This unbalanced trade must be reversed. Building walls at the boarder and stiff tariffs are desperate acts that fail to recognize cause or containment. They are certainly not the way to restore a robust economy. There must be a better way for nations to get their houses in order. Fortunately, there is.
A distributed currency built on math, trust and transparency—rather than the integrity of transient elected officials from one nation is far less susceptible to manipulation, inflation or any form of shock. It won’t solve all problems immediately, be it will prevent us from getting further mired in a debt that blows up like a balloon.
The decoupling of a money supply from government will yield benefits that are difficult to imagine today. Money doesn’t need authoritarian oversight like airline safety. The situation is more analogous to the deregulation of telephone and package delivery services. Without those blockbuster decisions of the 1980s, we would not have Smartphones or the internet today.
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, hosts the Bitcoin Event and is keynote speaker at Cryptocurrency Conferences. He is a top writer at Quora.