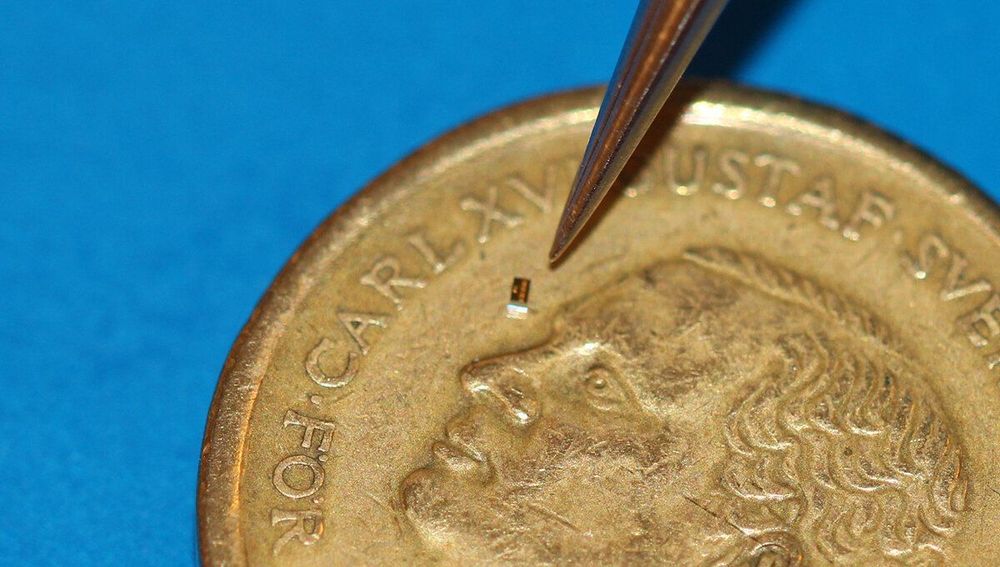
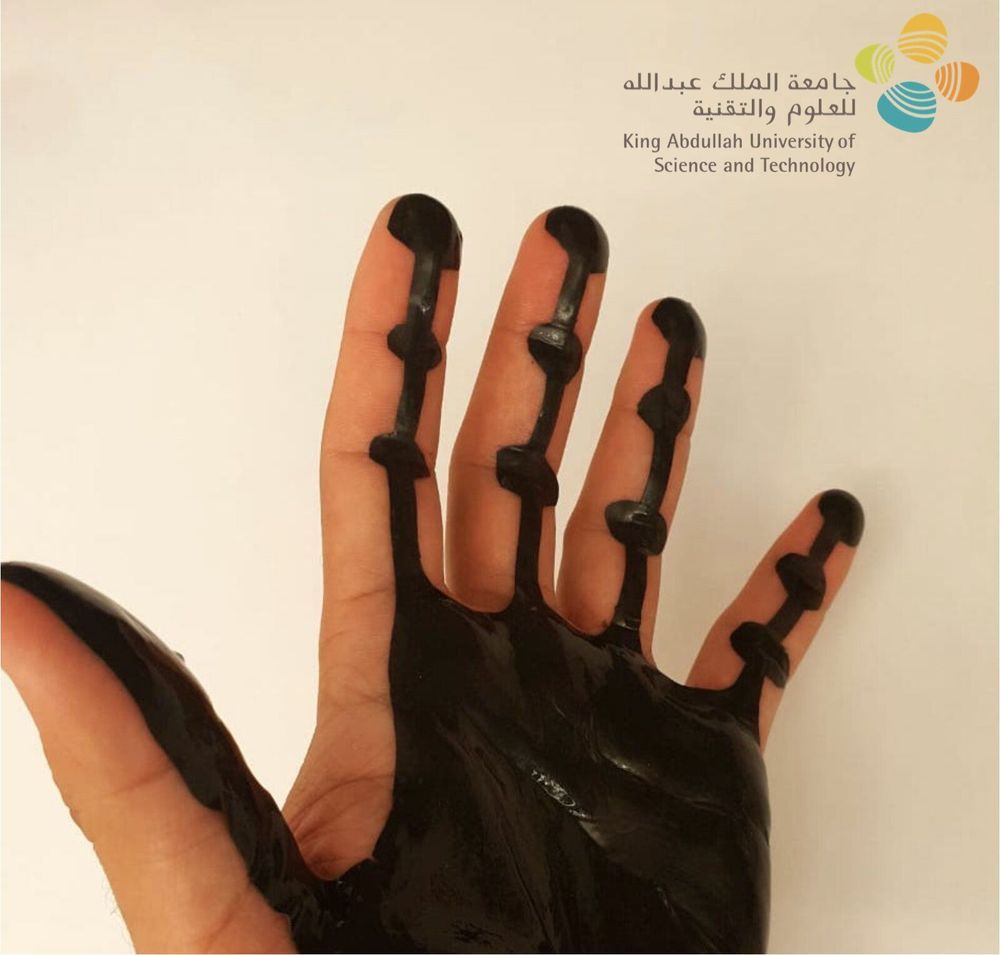
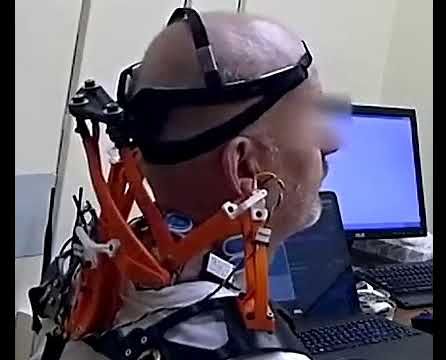
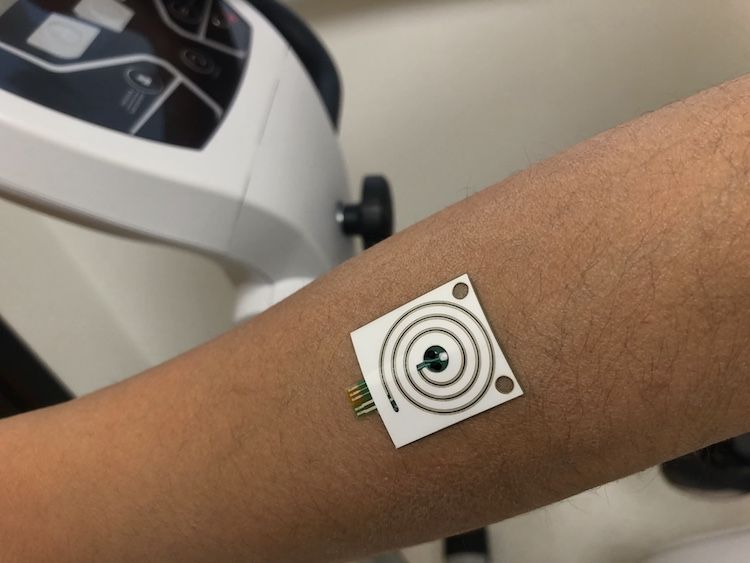
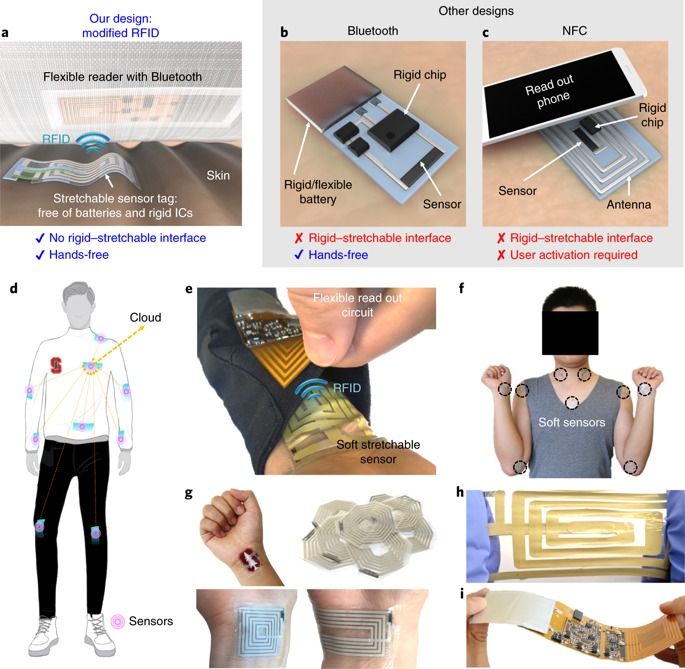
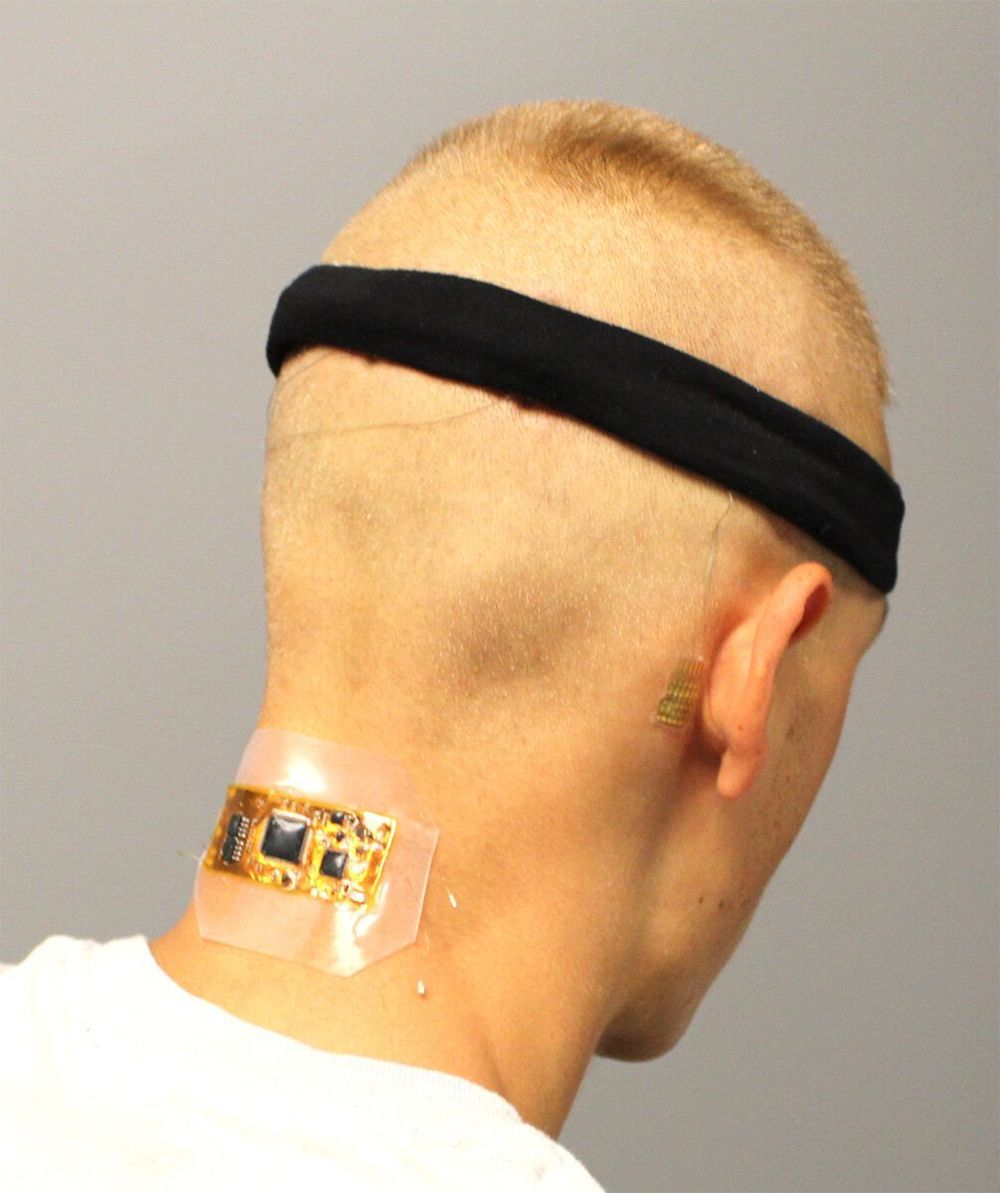
Combining new classes of nanomembrane electrodes with flexible electronics and a deep learning algorithm could help disabled people wirelessly control an electric wheelchair, interact with a computer or operate a small robotic vehicle without donning a bulky hair-electrode cap or contending with wires.
By providing a fully portable, wireless brain-machine interface (BMI), the wearable system could offer an improvement over conventional electroencephalography (EEG) for measuring signals from visually evoked potentials in the human brain. The system’s ability to measure EEG signals for BMI has been evaluated with six human subjects, but has not been studied with disabled individuals.
The project, conducted by researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology, University of Kent and Wichita State University, was reported on September 11 in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence.


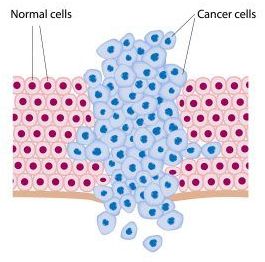 Malignant tumors release cells into a patient’s blood, meaning that researchers could detect the presence of cancer through a blood sample. The problem is that the cancerous cells enter the bloodstream and circulate so quickly that they may not appear in one single blood sample. This issue is what sparked Dr. Hayes and his team to develop a device that actually searches for the cancerous cells.
Malignant tumors release cells into a patient’s blood, meaning that researchers could detect the presence of cancer through a blood sample. The problem is that the cancerous cells enter the bloodstream and circulate so quickly that they may not appear in one single blood sample. This issue is what sparked Dr. Hayes and his team to develop a device that actually searches for the cancerous cells.