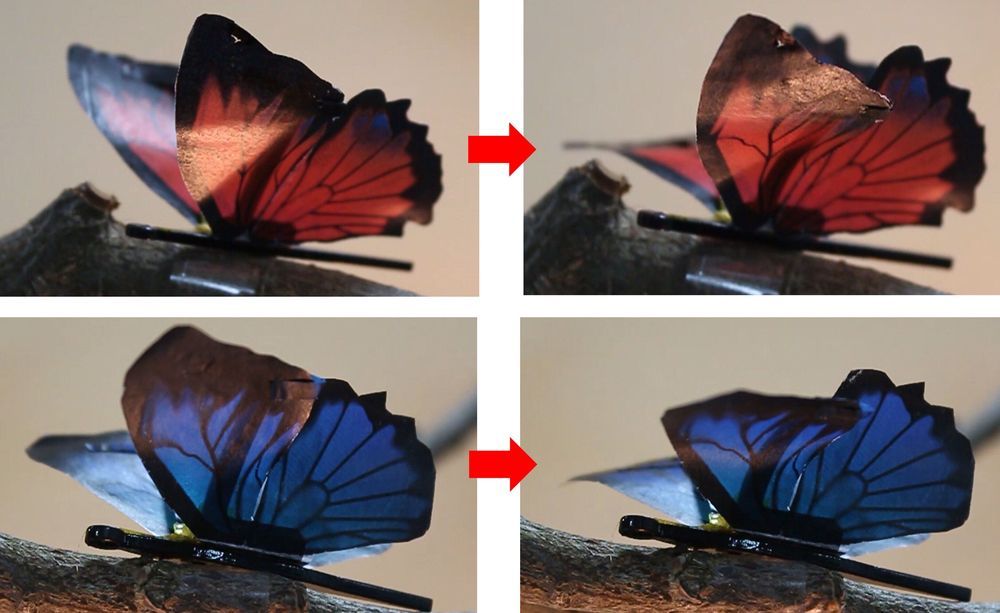
Wearing a flower brooch that blooms before your eyes sounds like magic. KAIST researchers have made it real with robotic muscles.
Researchers have developed an ultrathin, artificial muscle for soft robotics. The advancement, recently reported in the journal Science Robotics, was demonstrated with a robotic blooming flower brooch, dancing robotic butterflies and fluttering tree leaves on a kinetic art piece.
The robotic equivalent of a muscle that can move is called an actuator. The actuator expands, contracts or rotates like muscle fibers using a stimulus such as electricity. Engineers around the world are striving to develop more dynamic actuators that respond quickly, can bend without breaking, and are very durable. Soft, robotic muscles could have a wide variety of applications, from wearable electronics to advanced prosthetics.